查看 MySQL 数据库中每个表占用的空间大小
迁入RDS后为什么数据库变慢的分析
MySQL隐式转化整理
show global status like ‘Connections’;
show status like ‘Uptime’;
show global status like ‘Slow_queries’;
show status like ‘Com_select’;
show status like ‘Com_insert’;
show status like ‘Com_select’;
show status like ‘Com_update’;
show status like ‘Com_delete’;
show status like ‘Handler_read%’; 查看索引使用情况
analyze table finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy;
check table finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy;
optimize table finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy;
analyze check optimize 这三个操作执行期间将对表进行锁定
优化查询语句
使用索引查询
优化子查询:使用连接查询代替子查询
show processlist; 查看当前数据库连接状态
优化插入语句
禁用索引
禁用唯一性检查
一次插入多值而不是执行多个INSERT单个语句
LOAD DATA INFILE 从文本装载一个表 速度一般比insert 快20倍
explain 执行计划
MySQL - Show Processlist 整理
[置顶] MySQL执行计划解读 转他人文章!!!
MySQL查询优化之explain的深入解析 http://www.jb51.net/article/38357.htm!!
MySQL explain执行计划解读
Extra
Using index 该值表示相应的select操作中使用了覆盖索引(Covering Index)
TIPS:覆盖索引(Covering Index)
MySQL可以利用索引返回select列表中的字段,而不必根据索引再次读取数据文件
包含 称为 覆盖索引(Covering Index)
注意:
如果要使用覆盖索引,一定要注意select列表中只取出需要的列,不可select *,因为如果将所有字段一起做索引会导致索引文件过大,查询性能下降
Using where
是使用上了where限制,表示MySQL服务器在存储引擎收到记录后进行“后过滤”(Post-filter),如果查询未能使用索引,Using where的作用只是提醒我们MySQL将用where子句来过滤结果集
Using temporary
表示MySQL需要使用临时表来存储结果集,常见于排序和分组查询
(表示MySQL需要使用临时表来存储结果集,常见于排序和分组查询),使用filesort和temporary的话会很吃力,WHERE和ORDER BY的索引经常无法兼顾,如果按照WHERE来确定索引,那么在ORDER BY时,就必然会引起Using filesort,这就要看是先过滤再排序划算,还是先排序再过滤划算。
Using filesort
MySQL中无法利用索引完成的排序操作称为“文件排序”
当我们试图对一个没有索引的字段进行排序时,就是filesoft。它跟文件没有任何关系,实际上是内部的一个快速排序。
impossible where 表示用不着where,一般就是没查出来啥。
extra 中出现以下 2 项意味着 MYSQL 根本不能使用索引,效率会受到重大影响。应尽可能对此进行优化:
Using filesort
Using temporary
- 主键默认都是有索引的!
- 执行SELECT语句时,只会从 possible_keys里面找一个key索引运用,
- 只能用一个索引,从两个里面选一个最优的!
如果为某个外键字段定义了一个外键约束条件,MySQL就会自行定义一个内部索引来帮助自己以最有效率的方式去管理和使用外键约束条件。
如果没有该索引的话,MySQL每次在你插入,修改数据的时候都需要全表扫描主表中所有的记录以确定是否遵守外键约束,效率上显示不合适。
mysql后面的条件顺序可以无关,可能是mysql自己做了一些优化。条件中如果是区间会影响索引的选择
where t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 and t.Time =1471968060 使用主键索引
where t.Time >= 1473609600 and t.Time <=1476201550 and t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 使用外键索引R_267
Time、TerminalID、ProbeID的摆放顺序与索引的选择无关
where Time=
where Time= TerminalID= ProbeID=
where Time= TerminalID=
where ProbeID=
同时有主键和外键索引的情况下,只有这四种情况下,才会调用主键索引
即有 TerminalID条件的都用外键索引,有Time条件的都用主键索引
ALTER TABLE finaldata_lowfreq_magn ADD INDEX R_267 (TerminalID, ProbeID) USING BTREE
ALTER TABLE finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy ADD CONSTRAINT finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy_ibfk_1 FOREIGN KEY (TerminalID, ProbeID) REFERENCES r_deploy (TerminalID, ProbeID) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT;
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM rawdata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = 60005 ORDER BY TimeSave DESC LIMIT 0, 5
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM rawdata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = ‘60005’ ORDER BY TimeSave DESC LIMIT 0, 5
字段TerminalID是smallint型的,而条件传入了一个字符串,所以会很慢
传入数值60005,速度就会有明显提升!
WHERE TerminalID = ‘60005’慢的原因在于,数据库会把字段TerminalID的值转换成字符串后再与 ‘60005’匹配(隐式转换),原本存在的TerminalID的索引反而用不到了
??对吗?
后面研究发现,好像速度不受影响?
隐式转换导致全表扫描?
也议MySQL中隐式转换
- 针对数据类型字段,即使类型不一致,并不影响是否使用索引,执行计划是一样的,不会产生隐式转换。但仍然建议在生产库中尽量避免出现这样的SQL
- 如果是字符类型,当出现类型不一致时,是会影响索引的使用的,会产生隐式转换的,如String—》Int
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM rawdata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = ‘60005’ ORDER BY TimeSave DESC LIMIT 0, 5
经试验’60005’并不会是速度的限制因素,按TimeSave排列反而是速度的主要影响因素。
使用order by 一定场景下会带来creating sort index。这里creating sort index占了查询时间的绝大部分时间。
所以这里的优化建议是:TimeSave改为Time,该字段有索引,速度快
and Time >=1474387200
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = ‘60005’ and Time >1475769600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = ‘60005’ and Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC
explain SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = ‘222’ and Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC;
登登
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 AND TerminalID = 60005 and ProbeID=60005 ORDER BY Time ASC;
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = 60005 and ProbeID=60005 AND Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC;
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = 60005 AND Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC;
SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE TerminalID = 60005 and ProbeID=60005 AND Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY TimeSave ASC;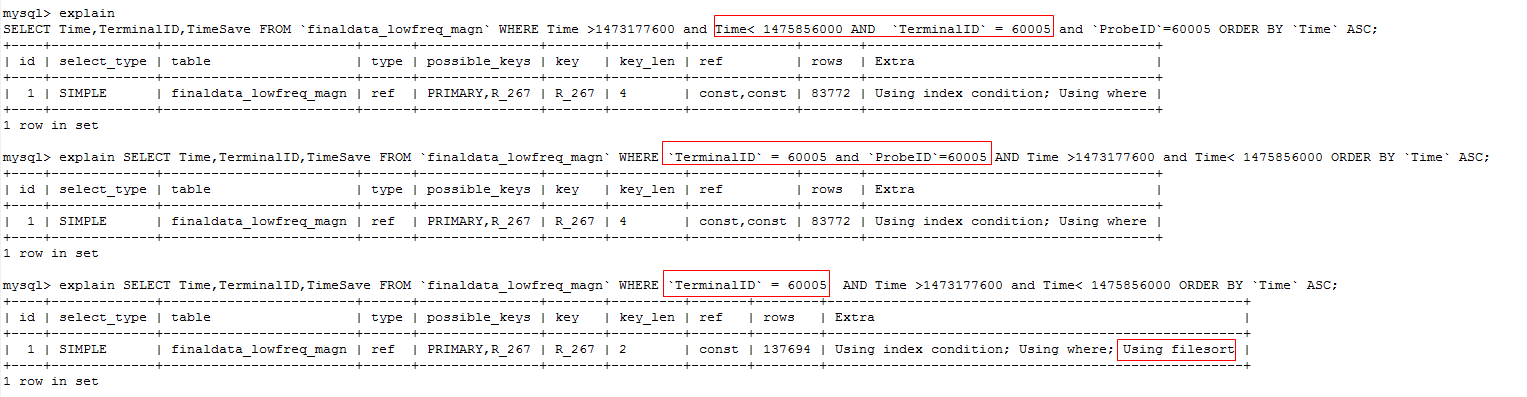

从这里可以看出,SQL1没有加上ProbeID=60005,没有充分用到那个R_247的索引,所以查询时出现Using filesort的选项,会更加耗时。
SQL4采用无索引的TimeSave来排序,也产生了Using filesort的信息
explain SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 ORDER BY Time ASC;
explain SELECT Time,TerminalID,TimeSave FROM finaldata_lowfreq_magn WHERE Time >1473177600 and Time< 1475856000 AND TerminalID = 60005 and ProbeID=60005 ORDER BY Time ASC;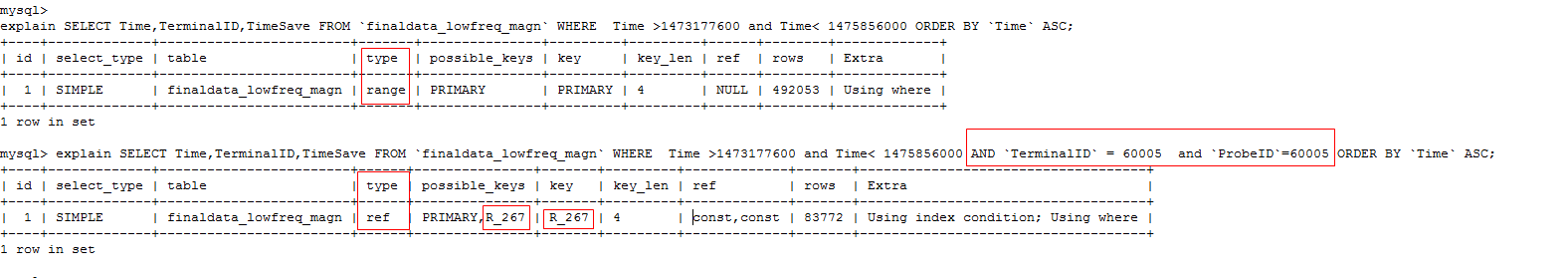
Type这里有不同,ref比range更优
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn_copy t
where t.Time >= 1473609600 and t.Time <=1476201550 and t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 order by t.Time asc;
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t
where t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 and t.Time >= 1473609600 and t.Time <=1476201550 order by t.Time asc;
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t
where t.Time = 1471968060 and t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 order by t.Time asc;
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t
where t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 and t.Time =1471968060 order by t.Time asc;
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t where t.Time >= 1469980800 and t.Time <=1475251200 and t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 order by t.Time asc;
explain select
t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t where t.Time >= 1467302400 and t.Time <=1475251200 and t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 order by t.Time asc;
explain select t.Time,t.average,t.zero_crossing_rate,t.Ring_down_count,t.average_crossing_rate,t.energy_distribution1,t.energy_distribution2,t.energy_distribution3,t.energy_distribution4,t.peak_frequency,t.peak_amplitude from finaldata_lowfreq_magn t where t.TerminalID = 60010 and t.ProbeID = 60010 and t.Time >= 1469980800 and t.Time <=1475251200 order by t.Time asc;
分析得这两个语句是一样的,没有明显区别
7.1 1467302400
8.1 1469980800
9.1 1472659200
10.1 1475251200
Sending data
Creating sort index

