原理
分析: 他们改变的this指向的原理:
- 其实就是通过在 某个对象上添加这样一个方法,
- 然后拿到参数,
- 再去调用这个对象的这个方法(符合this指向调用者。) 。
- 得到结果后,再在这个对象上删去这个属性方法。
- 最后返回结果。(想一想,其实很简单是不是)
1.call
概念
概念:方法使用一个指定的 this 值和单独给出的一个或多个参数来调用一个函数。 语法:function.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, …) 参数: thisArg:可选的。在 function 函数运行时使用的 this 值。请注意,this可能不是该方法看到的实际值:如果这个函数处于非严格模式下,则指定为 null 或 undefined 时会自动替换为指向全局对象,原始值会被包装。 arg1, arg2, …:指定的参数列表。 返回值:使用调用者提供的 this 值和参数调用该函数的返回值。若该方法没有返回值,则返回 undefined。
实现
- 首先 context 为可选参数,如果不传的话默认上下文为 window ;
- 接下来给 context 创建一个 fn 属性,并将值设置为需要调用的函数;
- 因为 call 可以传入多个参数作为调用函数的参数,所以需要将参数剥离出来;
- 然后调用函数并将对象上的函数删除。
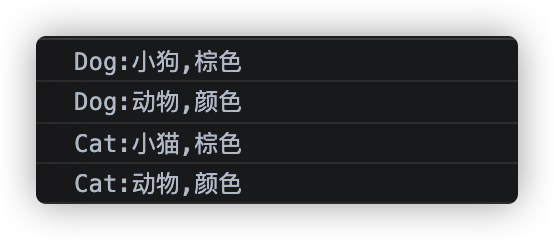
function Animal(name,color){this.name = name||'动物';this.color = color||'颜色';this.say=function(){console.log(`Animal:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}function Dog(name,color){Animal.call(this,name,color);this.say=function(){console.log(`Dog:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}let newDog = new Dog('小狗','棕色');let newDog2 = new Dog();newDog.say()newDog2.say();Function.prototype.myCall=function(context){// 判断调用者是否为函数// if (typeof this !== 'function') {// throw new TypeError('Error')// }//如果不传默认windowcontext = context || window;// 新增 fn 属性,将值设置为需要调用的函数context.fn = this;// 将 arguments 转化为数组将 call 的传参提取出来 [...arguments]let args= [...arguments].slice(1);// 传参调用函数let result = context.fn(...args);// 删除函数delete context.fn;// 返回执行结果return result}function Cat(name,color){Animal.myCall(this,name,color);this.say=function(){console.log(`Cat:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}let newCat = new Cat('小猫','棕色');let newCat2 = new Cat();newCat.say()newCat2.say();
示例
- 使用call方法调用父构造函数
- 使用 call 方法调用匿名函数
- 使用 call 方法调用函数并且指定上下文的 ‘this’
- 使用 call 方法调用函数并且不指定第一个参数(argument)
2.apply
概念
概念:方法调用一个具有给定this值的函数,以及以一个数组(或类数组对象)的形式提供的参数。 语法:function.apply(thisArg, [argsArray]) 参数: thisArg:必选的。在 func 函数运行时使用的 this 值。请注意,this可能不是该方法看到的实际值:如果这个函数处于非严格模式下,则指定为 null 或 undefined 时会自动替换为指向全局对象,原始值会被包装。 argsArray:可选的。一个数组或者类数组对象,其中的数组元素将作为单独的参数传给 func 函数。如果该参数的值为 null 或 undefined,则表示不需要传入任何参数。从ECMAScript 5 开始可以使用类数组对象。 返回值:调用有指定this值和参数的函数的结果。
实现
- 首先 context 为可选参数,
- 如果不传的话默认上下文为 window 接下来给 context 创建一个 fn 属性,并将值设置为需要调用的函数
- 因为 apply 传参是数组传参,所以取得数组,将其剥离为顺序参数进行函数调用
- 然后调用函数并将对象上的函数删除
function Animal(name,color){this.name = name||'动物';this.color = color||'颜色';this.say=function(){console.log(`Animal:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}function Dog(name,color){Animal.apply(this,[name,color]);this.say=function(){console.log(`Dog:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}let newDog = new Dog('小狗','棕色');let newDog2 = new Dog();newDog.say()newDog2.say();Function.prototype.myApply=function(context){// 判断调用者是否为函数if (typeof this !== 'function') {throw new TypeError('Error')}//如果不传默认windowcontext = context || window;// 新增 fn 属性,将值设置为需要调用的函数context.fn = this;// 返回执行结果let result;//判断是否有参数传入if(arguments[1]){result = context.fn(...arguments[1])}else{result = context.fn();}// 删除函数delete context.fn;return result}function Cat(name,color){Animal.myApply(this,[name,color]);this.say=function(){console.log(`Cat:${this.name},${this.color}`)}}let newCat = new Cat('小猫','棕色');let newCat2 = new Cat();newCat.say()newCat2.say();
示例
- 用 apply 将数组各项添加到另一个数组
- 使用apply和内置函数
- 使用apply来链接构造器
3.bind
概念
概念:方法创建一个新的函数,在 bind() 被调用时,这个新函数的 this 被指定为 bind() 的第一个参数,而其余参数将作为新函数的参数,供调用时使用。 语法:function.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, …]]]) 参数: thisArg:调用绑定函数时作为 this 参数传递给目标函数的值。 如果使用new运算符构造绑定函数,则忽略该值。当使用 bind 在 setTimeout 中创建一个函数(作为回调提供)时,作为 thisArg 传递的任何原始值都将转换为 object。如果 bind 函数的参数列表为空,或者thisArg是null或undefined,执行作用域的 this 将被视为新函数的 thisArg。 arg1, arg2, …:当目标函数被调用时,被预置入绑定函数的参数列表中的参数。 返回值:返回一个原函数的拷贝,并拥有指定的 this 值和初始参数。
实现
- 判断调用者是否为函数。
- 截取参数,注意:这里有两种形式传参。
- 返回一个函数,判断外部哪种方式调用了该函数(new | 直接调用)
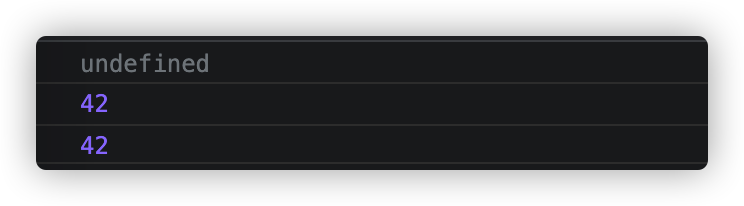
const module = {x:42,getX:function(){return this.x;}}const unboundGetX = module.getX;console.log(unboundGetX());console.log(unboundGetX.bind(module)())Function.prototype.myBind= function(context){// 判断调用者是否为函数if (typeof this !== 'function') {throw new TypeError('Error')}let args = [...arguments].slice(1)//_this指向调用函数const _this = this;return function F(){// 因为返回了一个函数,我们可以 new F(),所以需要判断// 对于 new 的情况来说,不会被任何方式改变 thisif(this instanceof F){return new _this(...args,...arguments)}else{return _this.apply(context,args.concat(...arguments))}}}console.log(unboundGetX.myBind(module)())
示例
- 创建绑定函数
- 偏函数
- 配合 setTimeout