前言
前一篇文章 图书管理系统实战(上)中,我们已经编写了 pojo、dao 层以及配置 dao 层对应的 mapper,从现在开始,我们开始编写 service 层和 controller 层。
service 层
预约业务操作码
在正式编写 service 层之前,我们先定义一个预约图书操作返回码的数据字段,用于反馈给客户信息;
| 返回码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 预约成功 |
| 0 | 预约失败 |
| -1 | 预约重复 |
| -2 | 系统异常 |
package com.cunyu.utils;import com.cunyu.dto.AppointDto;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Getter;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : AppointStateEnum* @date : 2020/7/24 10:50* @description : 定义预约业务的数据字典*/@Getter@AllArgsConstructorpublic enum AppointStateEnum {SUCCESS(1, "预约成功"), FAILURE(0, "预约失败"), REPEAT(-1, "预约重复"), SYSTEMERROR(-2, "系统异常");private int state;private String stateInfo;/*** @param stat 状态码* @return* @description 获取状态码对应 enum* @date 2020/7/24 10:57* @author cunyu1943* @version 1.0*/public static AppointStateEnum stateOf(int stat) {for (AppointStateEnum state : values()) {if (stat == state.getState()) {return state;}}return null;}}
数据传输层
定义好预约业务的数据字典之后,新建一个数据传输类用来传输我们的预约结果;
package com.cunyu.dto;import com.cunyu.pojo.Appointment;import com.cunyu.utils.AppointStateEnum;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : AppointDto* @date : 2020/7/24 10:46* @description : 用于数据传输,封装*/@Data@NoArgsConstructorpublic class AppointDto {private int bookId;// 状态码private int state;// 状态信息private String stateInfo;// 预约成功的对象private Appointment appointment;// 预约失败的构造器public AppointDto(int bookId, AppointStateEnum appointStateEnum) {this.bookId = bookId;this.state = appointStateEnum.getState();this.stateInfo = appointStateEnum.getStateInfo();}// 预约成功的构造器public AppointDto(int bookId, AppointStateEnum appointStateEnum, Appointment appointment) {this.bookId = bookId;this.state = appointStateEnum.getState();this.stateInfo = appointStateEnum.getStateInfo();this.appointment = appointment;}}
service 业务代码编写
BookService.java
package com.cunyu.service;import com.cunyu.dto.AppointDto;import com.cunyu.pojo.Book;import java.util.List;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : BookService* @date : 2020/7/24 10:44* @description : Book 业务接口*/public interface BookService {/*** @param bookId 图书 ID* @return 对应 ID 的图书* @description 根据图书 id 查询图书* @date 2020/7/24 11:41* @author cunyu1943* @version 1.0*/Book getById(int bookId);/*** @param* @return 所有图书的列表* @description 获取图书列表* @date 2020/7/24 11:41* @author cunyu1943* @version 1.0*/List<Book> getList();/*** @param bookId 图书 id* @param studentId 学生 Id* @return* @description 返回预约结果* @date 2020/7/24 11:39* @author cunyu1943* @version 1.0*/AppointDto appoint(int bookId, int studentId);}
BookServiceImpl.java
package com.cunyu.service.impl;import com.cunyu.dao.AppointmentDao;import com.cunyu.dao.BookDao;import com.cunyu.dto.AppointDto;import com.cunyu.pojo.Appointment;import com.cunyu.pojo.Book;import com.cunyu.service.BookService;import com.cunyu.utils.AppointStateEnum;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.List;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : BookServiceImpl* @date : 2020/7/24 11:43* @description : Book 业务接口实现类*/@Servicepublic class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {// 依赖注入@Autowiredprivate BookDao bookDao;@Autowiredprivate AppointmentDao appointmentDao;public Book getById(int bookId) {return bookDao.queryById(bookId);}public List<Book> getList() {return bookDao.queryAll(0, 3);}public AppointDto appoint(int bookId, int studentId) {AppointDto appointDto = null;try {// 减库存int update = bookDao.reduceNumber(bookId);if (update <= 0) {System.out.println(AppointStateEnum.FAILURE);} else {// 执行预约操作int insert = appointmentDao.insertAppointment(bookId, studentId);if (insert <= 0) {System.out.println(AppointStateEnum.REPEAT);} else {Appointment appointment = appointmentDao.queryByKeyWithBook(bookId, studentId);appointDto = new AppointDto(bookId, AppointStateEnum.SUCCESS, appointment);}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return appointDto;}}
测试
package com.cunyu.service.impl;import com.cunyu.service.BookService;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : BookServiceImplTest* @date : 2020/7/24 11:53* @description : BookServiceImpl 测试类*/@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring/spring-*.xml")public class BookServiceImplTest {@Autowiredprivate BookService bookService;@Testpublic void testAppoint() {int bookId = 1;int studentId = 18301343;System.out.println(bookService.appoint(bookId, studentId));}}
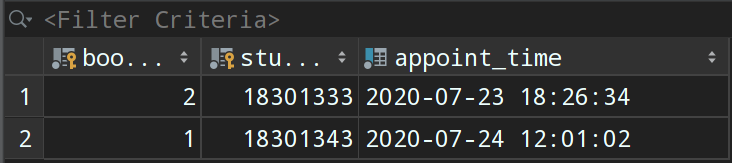
下图是我们测试后数据库中的数据,说明此时我们的 service 层接口测试成功。
封装结果
既然我们的 service 层接口和实现类都编写好了,我们就需要将结果进行封装成 json 格式,方便我们传到 controller 交互使用。
package com.cunyu.dto;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : ResultDto* @date : 2020/7/24 12:11* @description : 封装结果为 json*/@Data@NoArgsConstructorpublic class ResultDto<T> {// 是否预约成功private boolean success;// 预约成功返回的数据private T data;// 错误信息private String error;// 预约成功的构造器public ResultDto(boolean success, T data) {this.success = success;this.data = data;}// 预约失败的构造器public ResultDto(boolean success, String error) {this.success = success;this.error = error;}}
controller 层
编写好 service 层之后,我们就剩下最后的 controller 层了;
package com.cunyu.controller;import com.cunyu.dto.AppointDto;import com.cunyu.dto.ResultDto;import com.cunyu.pojo.Book;import com.cunyu.service.BookService;import com.cunyu.utils.AppointStateEnum;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import java.util.List;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : BookController* @date : 2020/7/24 12:20* @description : Book controller 层*/@Controller@RequestMapping("/book")public class BookController {@Autowiredprivate BookService bookService;// url:ip:port:/book/list@GetMapping("/list")private String list(Model model) {List<Book> bookList = bookService.getList();model.addAttribute("bookList", bookList);return "list";}@GetMapping(value = "/{bookId}/detail")private String detail(@PathVariable("bookId") Integer bookId, Model model) {if (bookId == null) {return "redirect:/book/list";}Book book = bookService.getById(bookId);if (book == null) {return "forward:/book/list";}model.addAttribute("book", book);return "detail";}//ajax 传递 json 数据到前端@RequestMapping(value = "/{bookId}/appoint", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = {"application/json; charset=utf-8"})@ResponseBodyprivate ResultDto<AppointDto> appoint(@PathVariable("bookId") Integer bookId, @RequestParam("studentId") Integer studentId) {if (studentId == null || studentId.equals("")) {return new ResultDto<>(false, "学号不能为空");}AppointDto appointDto = null;try {appointDto = bookService.appoint(bookId, studentId);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return new ResultDto<AppointDto>(true, appointDto);}}
前端
好了,我们的后台就开发完毕了,接下来就可以去编写前端页面了。然后启动 Tomcat,访问对应 url 即可。
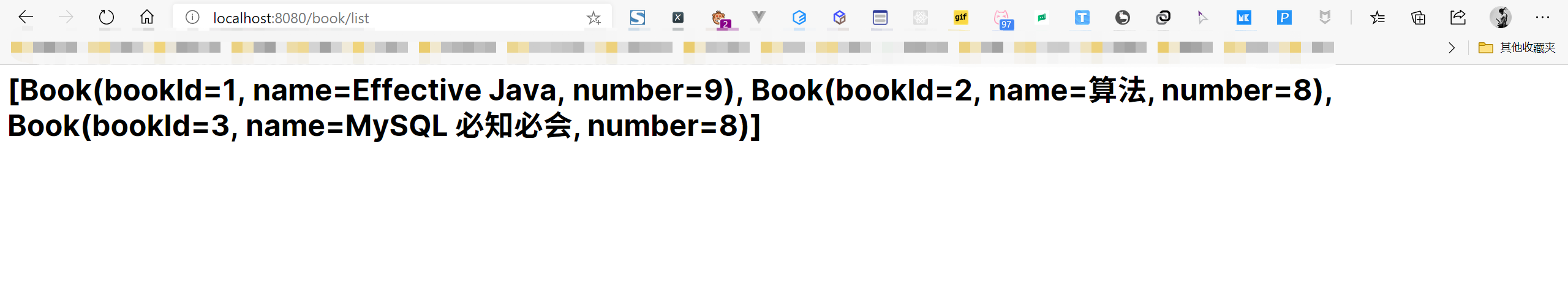
list.jsp
<%--Created by IntelliJ IDEA.User: cunyuDate: 2020/7/23Time: 9:47To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.--%><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>图书列表页</title></head><body><h1>${bookList}</h1></body></html>
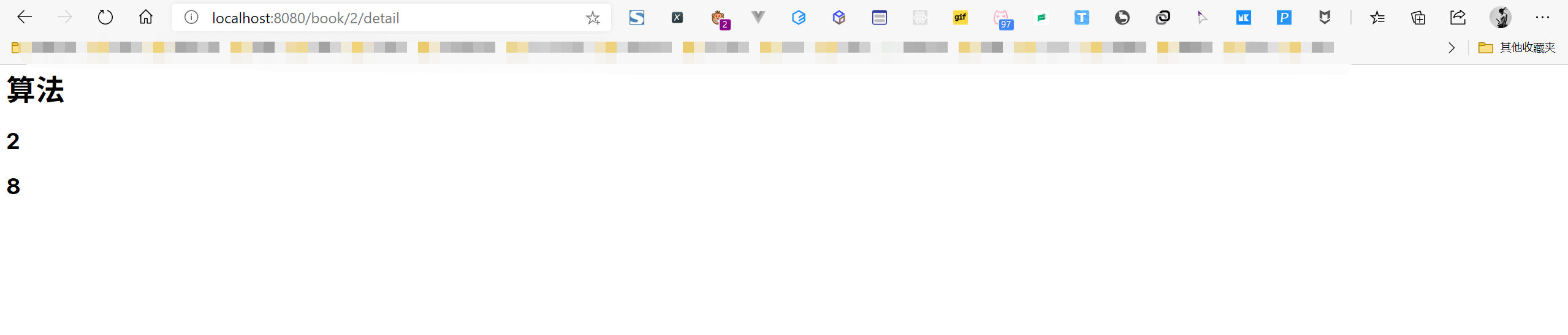
detail.jsp
<%--Created by IntelliJ IDEA.User: cunyuDate: 2020/7/23Time: 10:02To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.--%><%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head><title>图书详情页</title></head><body><h1>${book.name}</h1><h2>${book.bookId}</h2><h2>${book.number}</h2></body></html>
总结
到此,我们的后台所有服务都写好了,SSM 框架整合配置,与应用实例部分已经结束,前端部分就简单写了个数据展示页面。
感兴趣的小伙伴可以接着去实现前哦 ~

