实例 51
题目
定义一个圆柱体类 Cylinder,创建相应的对象,然后计算圆柱体的底面积和体积。
分析
考察如何定义一个类,以及如何在类中定义成员变量与方法,最后则是如何创建一个对象并调用方法。
实现
import java.util.Random;import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : 村雨* @version : 1.0* @Project : Java 编程实例* @Package : PACKAGE_NAME* @ClassName : Example51.java* @createTime : 2021/6/25 23:19* @Email : 747731461@qq.com* @公众号 : 村雨遥* @Website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @Description :*/public class Example51 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入圆柱体半径");float radius = scanner.nextFloat();System.out.println("输入圆柱体高");float height = scanner.nextFloat();Cylinder cylinder = new Cylinder();System.out.println("底面积:" + cylinder.area(radius));System.out.println("体积:" + cylinder.volume(radius, height));}}class Cylinder {final double PI = 3.14;// 半径float radius;// 高float height;/*** 求圆柱体的底面积** @param radius 半径* @return 圆柱体底面积*/public double area(float radius) {return PI * radius * radius;}/*** 求圆柱体体积** @param radius 半径* @param height 高度* @return 圆柱体体积*/public double volume(float radius, float height) {return height * area(radius);}}
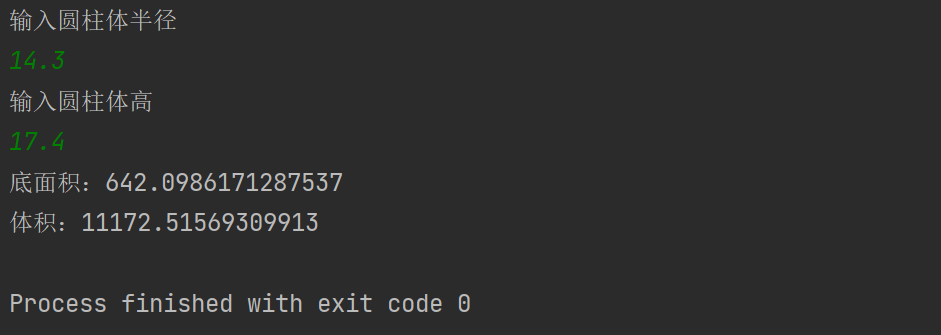
结果
实例 52
题目
创建一个图书类,类中包含的属性有:书名、作者、出版社、书籍状态;包含的方法有:构造方法,设置书籍状态,查看书籍状态(书籍状态指 在馆 和 外借)。
分析
考察如何设计一个类,此外还包括如何定义类中成员变量、方法、构造方法等知识点。最后则是如何定义一个对象并调用方法。
实现
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : 村雨* @version : 1.0* @Project : Java 编程实例* @Package : PACKAGE_NAME* @ClassName : Example52* @createTime : 2021/6/25 23:42* @Email : 747731461@qq.com* @公众号 : 村雨遥* @Website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @Description :*/public class Example52 {public static void main(String[] args) {Book book = new Book("《Java 从入门到放弃》", "村雨遥", "胡编乱造出版社");book.setBorrow(true);System.out.println(book.getName() + " 的状态是:" + book.isBorrow());}}class Book {private String name;private String author;private String press;private boolean borrow;public Book() {}public Book(String name, String author, String press) {this.name = name;this.author = author;this.press = press;}public String isBorrow() {return borrow ? "外借" : "在馆";}public void setBorrow(boolean borrow) {this.borrow = borrow;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}}
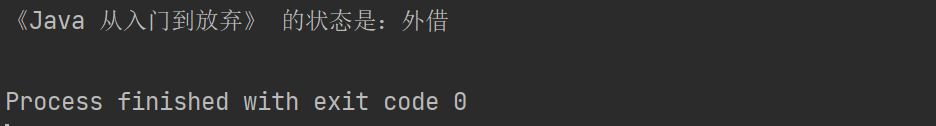
结果
实例 53
题目
设计一个 Birthday 类,其成员变量有:year、month、day。提供构造方法、输出 Birthday 对象值的方法和计算年龄的方法。
分析
除开类的设计之外,还涉及如何重写方法,以及如何调用 Java 中内置的 Calendar,用于求当前时间的年份。
实现
import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : 村雨* @version : 1.0* @Project : Java 编程实例* @Package : PACKAGE_NAME* @ClassName : Example53* @createTime : 2021/6/26 0:00* @Email : 747731461@qq.com* @公众号 : 村雨遥* @Website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @Description :*/public class Example53 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入生日年份");int year = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("输入生日月份");int month = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("输入生日日期");int day = scanner.nextInt();Birthday birthday = new Birthday(year, month, day);System.out.println("生日是:" + birthday.toString());System.out.println("年龄是:" + birthday.getAge(year));}}class Birthday {int year;int month;int day;public Birthday() {}public Birthday(int year, int month, int day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return year +" 年 " + month +" 月 " + day +" 日";}/*** 求年龄** @param year 生日的年份* @return 年龄*/public int getAge(int year) {// 获取当前时间Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();return calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR) - year;}}
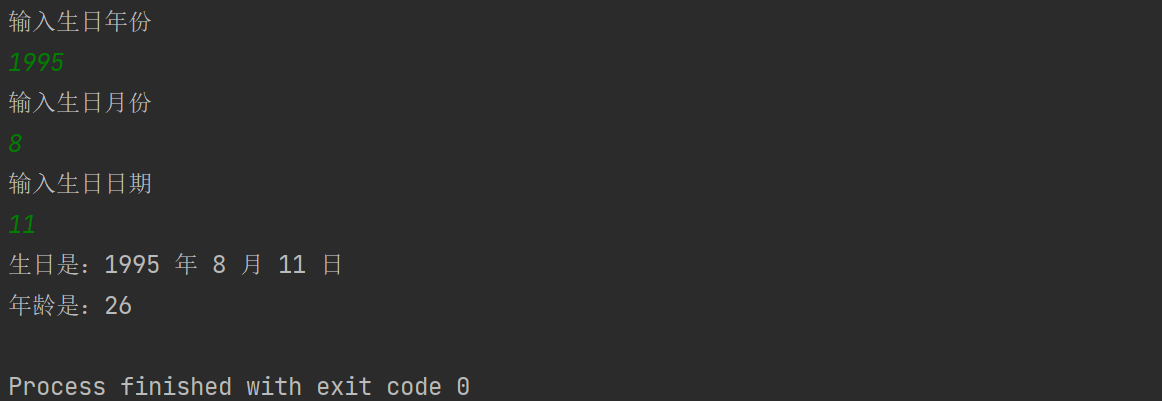
结果
实例 54
题目
定义一个类 Student,属性为学号、姓名和成绩;方法为增加记录 setRecord 和得到记录 GetRecord,增加记录给出学号、姓名和方法的赋值,得到记录方法则是通过学号得到考生的成绩。
分析
主要考察类定义以及方法的设置。
实现
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : 村雨* @version : 1.0* @Project : Java 编程实例* @Package : PACKAGE_NAME* @ClassName : Example54* @createTime : 2021/6/26 9:15* @Email : 747731461@qq.com* @公众号 : 村雨遥* @Website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @Description :*/public class Example54 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student = new Student();Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入 id");int id = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("输入姓名");String name = scanner.next();System.out.println("输入成绩");float score = scanner.nextFloat();student.setRecord(id, name, score);System.out.println("输入要查询考生的学号");id = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("该考生的成绩:" + student.getRecord(id));}}class Student {private int id;private String name;private float score;public void setRecord(int id, String name, float score) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.score = score;}public float getRecord(int id) {return (this.id == id) ? this.score : -1;}}
结果
实例 55
题目
定义猴子类,它有名字,性别等属性,并定义猴子说话的方法。然后定义一个人类,人类也有名字和性别等属性,且定义人说话的方式,使用继承,让代码具有复用性。
分析
主要考察类的定义以及继承的相关知识点。
实现
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : 村雨* @version : 1.0* @Project : Java 编程实例* @Package : PACKAGE_NAME* @ClassName : Example55* @createTime : 2021/6/26 21:28* @Email : 747731461@qq.com* @公众号 : 村雨遥* @Website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @Description :*/public class Example55 {public static void main(String[] args) {Person person = new Person("村雨遥", 1);person.speak();}}class Monkey {private String name;private int sex;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getSex() {return sex;}public void setSex(int sex) {this.sex = sex;}public Monkey(String name, int sex) {this.name = name;this.sex = sex;}public Monkey() {}public void speak() {System.out.println(this.name + " 咿咿呀呀!");}}class Person extends Monkey {public Person(String name, int sex) {super(name, sex);}@Overridepublic void speak() {System.out.println(this.getName() + ", 你好呀!");}}
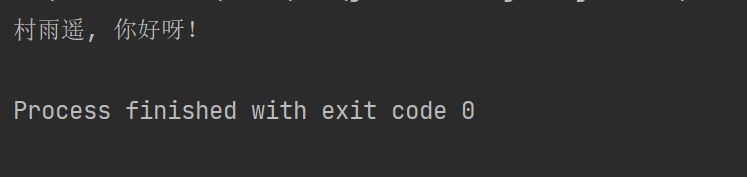
结果