前言
为了 Spring Boot 能够更好地生成配置元数据文件,我们可以在创建项目时添加 Spring Configuartion Processor 依赖,或者在创建好项目后的 pom.xml 文件中手动添加。添加该依赖后,我们在编写配置时就会有属性提示,大大降低编写错误。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency>
application.properties
自定义属性
application.properties 配置文件是创建项目后就自带的,如果我们要自定义属性,可以在其中直接配置,配置过程如下:
- 在
application.properties中添加我们要自定义的配置;
cunyu.id=1024cunyu.name=村雨遥cunyu.website=https://cunyu1943.github.io
- 创建实体类来映射我们配置的属性;
package com.cunyu.pojo;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : CunyuProperties* @date : 2020/7/29 13:34* @description : TODO*/@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cunyu")@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructorpublic class CunyuProperties {private int id;private String name;private String website;}
- 定义 Controller 来注入测试;
package com.cunyu.controller;import com.cunyu.pojo.CunyuProperties;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : CunyuPropertiesController* @date : 2020/7/29 13:37* @description : TODO*/@RestController@RequestMapping("/cunyu")public class CunyuPropertiesController {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CunyuPropertiesController.class);@AutowiredCunyuProperties cunyuProperties;@GetMapping("/profile")public String cunyuProfile(){logger.info("---------------");logger.info(cunyuProperties.toString());logger.info("---------------");return cunyuProperties.toString();}}
- 打开网页测试,打开 1,同时观察控制台,显示如下内容则说明属性注入成功;
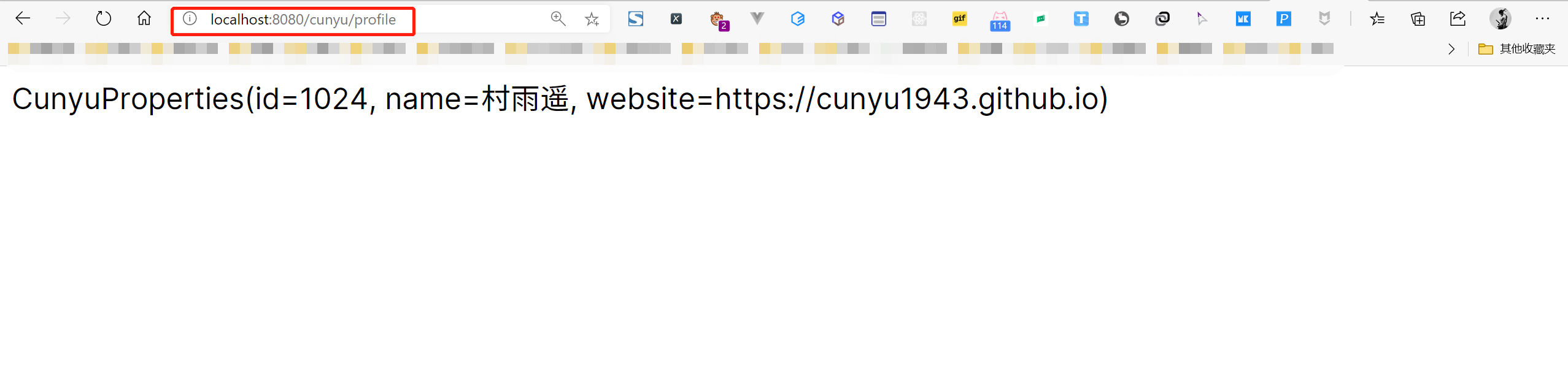
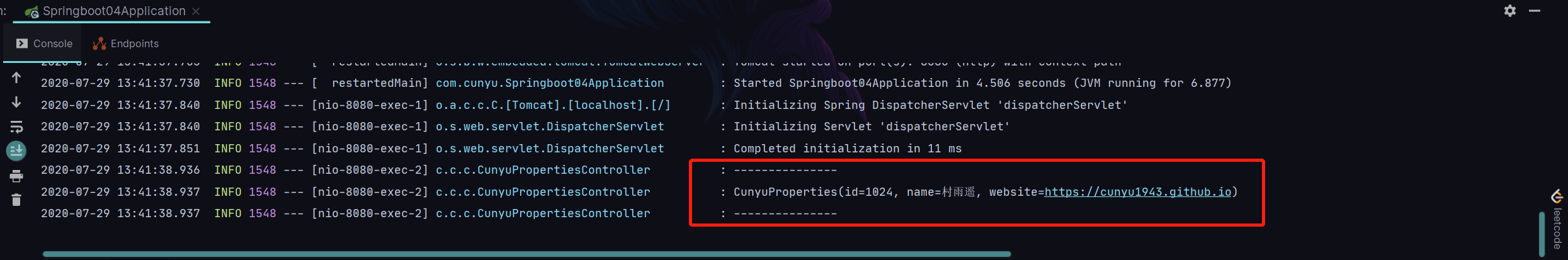
多环境配置
实际开发过程中,常常需要多个环境(如 开发、测试、生产等),而不同环境的配置都不一样,此时配置方法如下;
- 创建不同环境对应的配置文件,配置文件名为
application-{profile}.properties,{profile}为我们自定义环境,如下:
开发环境:application-dev.properties
server.servlet.context-path=/dev
测试环境:application-test.properties
server.servlet.context-path=/test
生产环境:application-prod.properties
server.servlet.context-path=/prod
- 然后在
application.properties中加入激活的环境,此时就会激活对应环境的配置;
# {profile} 对应上述的 dev、test、prodspring.profiles.active={profile}
之所以要分为多个环境的配置,主要是方便在不同环境中开发的需求,比如我们要开发新功能,那此时就可以激活开发配置文件的相关设置,等待我们开发完成之后,然后再切换到测试环境进行测试。而经过严格的测试之后,我们就可以将新推出的功能上线到生产环境中。纵观整个开发流程,我们既完成了新功能的开发,也没有影响到用户对现有系统的使用,所以现在大家基本都是基于这种模式来进行业务开发。
自定义配置文件
假如我们不想用项目自带的 application.properties 配置环境,那我们也可以自定义我们需要的配置。但该如何配置呢?接下来我们就来看看 ~
- 首先创建一个自定义配置文件
my.properties,文件名可以自定义,但是后缀要保持一致,然后在其中加入我们自定义配置的属性;
my.id=1024my.name=村雨遥my.website=https://cunyu1943.github.io
- 定义实体类,用于映射自定义配置文件中的内容;
package com.cunyu.pojo;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : MyProperties* @date : 2020/7/29 14:05* @description : TODO*/@Component@PropertySource("classpath:my.properties")@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "my")@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructorpublic class MyProperties {private int id;private String name;private String website;}
- 定义 Controller 来注入测试
package com.cunyu.controller;import com.cunyu.pojo.MyProperties;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/*** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @className : MyPropertiesController* @date : 2020/7/29 14:07* @description : TODO*/@RestController@RequestMapping("/my")public class MyPropertiesController {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyPropertiesController.class);@AutowiredMyProperties myProperties;@GetMapping("/profile")public String myProfile() {logger.info("=============");logger.info(myProperties.toString());logger.info("=============");return myProperties.toString();}}
- 打开网页测试,打开
http://localhost:8080/my/profile,同时观察控制台,显示如下内容则说明属性注入成功;


注意
application.properties 和 my.properties 会优先加载 application.properties。
.yml 和 .properties
一般来说,使用 IDEA 创建一个 Spring Boot 项目时,默认都会生成一个 application.properties 的配置文件。该配置文件是用来 修改 Spring Boot 自动配置的默认值。 但有的朋友会更倾向于使用 application.yml,那么问题来了,这两种格式到底有啥区别呢?
开始比较之前,我们先来看看各自的实例:
- .properties 格式
server.port=8081spring.datasource.type=org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourcespring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://aliyuncs.com:3306/database?useUnicode=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&autoReconnect=truespring.datasource.username=rootspring.datasource.password=******spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- .yml 格式
server:port: 8082spring:datasource:name: testurl: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/databaseusername: rootpassword: ******type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourcedriver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
从上面的实例我们可以发现,两者的区别主要有以下几点:
- 语法结构
.properties格式使用的是 键值对形式(key=value),而.yml格式则使用的是 树状结构(key: value);.properties格式通过.来连接,=来赋值,结构上比较直接,而.yml格式则使用:来分层,结构上呈现树状结构,层次感明显,而且赋值时:的后边必须 接着一个空格再赋值
- 执行先后顺序
如果一个工程中同时存在两种格式的文件,那么会 优先加载 **.yml** 文件,然后再加载 **.properties**,而且后加载的 **.properties** 会覆盖之前加载的 **.yml** 文件。
此外,.yml 配置时需要注意以下几点:
- 缩进必须用空格,不能用 Tab
@PropertySource注解不能加载yml文件
总结
以上就是关于 Spring Boot 中的配置相关内容了。本文主要介绍了 Spring Boot 项目自带的配置文件的相关信息,同时也介绍了如果我们想要满足自己需求如何进行自定义配置。最后,则是对 .yml 和 .properties 不同格式的配置文件的区别进行解释。

