实例 46
题目
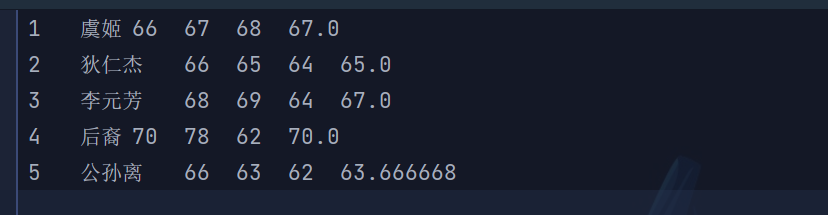
两个字符串连接程序。
分析
要实现两个字符串的连接有多种方法,其中最简单的就是利用 + 来实现。
实现
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/7 15:29* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example46* @description :*/public class Example46 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入一个字符串");String str1 = scanner.nextLine();System.out.println("再输入一个字符串");String str2 = scanner.nextLine();System.out.println("连接后的字符串为:" + str1 + str2);}}
结果
实例 47
题目
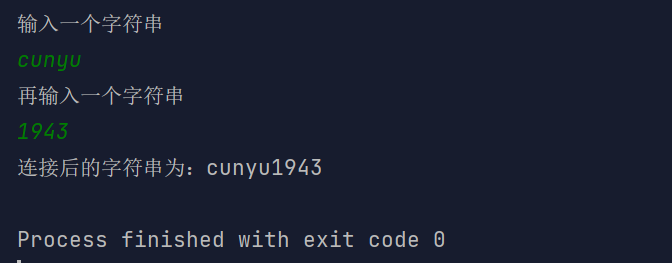
读取 7 个数(1 - 50)的整数值,每读取一个值,就打印该值个数的 *;
分析
主要就是考验循环和打印的用法,难度不大。
实现
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/7 15:29* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example47* @description :*/public class Example47 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int num = 0;int count = 1;while (count <= 7) {do {System.out.println("输入一个 1 - 50 之间的整数");num = scanner.nextInt();} while (num < 1 || num > 50);// 打印 * 号for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {System.out.print("*");}System.out.println();count++;}}}
结果
实例 48
题目
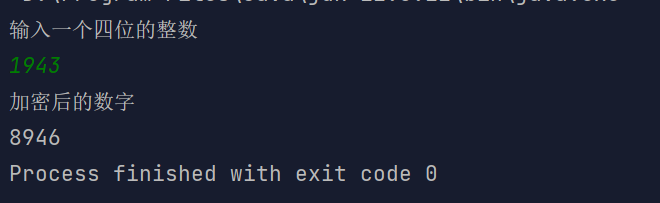
某公司采用公用电话传递数据,数据是四位整数,在传递过程中是加密的,加密规则如下:每位数字都加上 5 然后用和除以 10 的余数来代替该数字,再将第一位和第四位交换,第二位和第三位交换。
分析
实现起来很简单,只不过要把步骤分开:
- 首先输入四位数之后,将其个位、十位、百位、千位都分解出来;
- 然后将各位都加上 5,然后求和后除以 10 的余数代替各位上的数;
- 最后则是将第一位和第四位交换,第二位和第三位交换;
实现
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/7 15:29* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example48* @description :*/public class Example48 {public static int SIZE = 4;public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入一个四位的整数");int num = scanner.nextInt();int[] arr = new int[SIZE];// 千位arr[0] = num / 1000;// 百位arr[1] = num % 1000 / 100;// 十位arr[2] = num / 10 % 10;// 个位arr[3] = num % 10;// 每个数字都加上 5,然后除以 10 的余数代替for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {arr[i] += 5;arr[i] %= 10;}// 交换 1,3 位,2,4 位for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {int tmp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[SIZE - 1 - i];arr[SIZE - 1 - i] = tmp;}System.out.println("加密后的数字");for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i]);}}}
结果
实例 49
题目
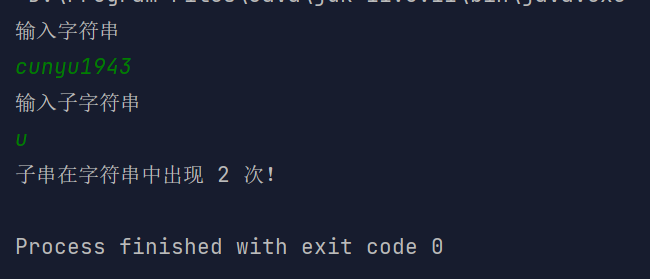
计算字符串中子串出现的次数。
分析
分别输入两个字符串,然后利用 equals() 对比字符串中等同于子字符串的情况,出现则次数加一,不过要注意的是当两个字符串均为空的时候,此时无法比较。
实现
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/7 15:29* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example49* @description :*/public class Example49 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入字符串");String str = scan.nextLine();System.out.println("输入子字符串");String subStr = scan.nextLine();// 计数int count = 0;if (str.equals("") || subStr.equals("")) {System.out.println("无输入字符串或子串,无法比较");System.exit(0);} else {// 对比字符串中出现子字符串,统计次数for (int i = 0; i < str.length() - subStr.length(); i++) {if (subStr.equals(str.substring(i, subStr.length() + i))) {count++;}}}System.out.println("子串在字符串中出现 " + count + " 次!");}}
结果
实例 50
题目
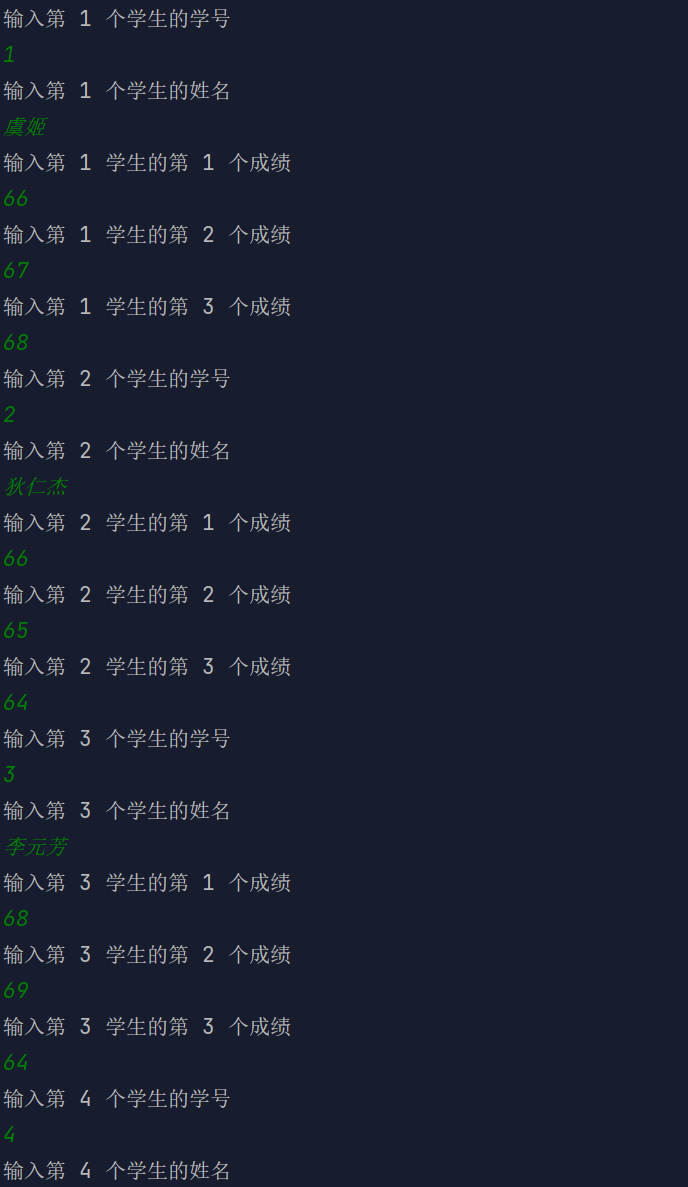
有五个学生,每个学生有 3 门课程成绩,从键盘上输入数据(学号、姓名、三门课程成绩),计算出平均成绩,并把原有数据和计算出的平均分数存放于磁盘中。
分析
分析题目,将功能逐一拆分,先是要定义一个二维数组来存放五个学生的 6 个信息,然后分别输入五个学生的前 5 个信息,接着计算平均成绩,最后则是写入磁盘,值得注意的是,在读写文件时要注意流的关闭。
实现
import java.io.BufferedWriter;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/7 15:29* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example50* @description :*/public class Example50 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);// 存放 5 个学生的信息String[][] info = new String[5][6];for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {System.out.println("输入第 " + (i + 1) + " 个学生的学号");info[i][0] = scanner.next();System.out.println("输入第 " + (i + 1) + " 个学生的姓名");info[i][1] = scanner.next();for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {System.out.println("输入第 " + (i + 1) + " 学生的第 " + (j + 1) + " 个成绩");info[i][j + 2] = scanner.next();}}// 求平均分,并存入数组float avg = 0.0f;int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {{sum = 0;for (int j = 2; j < 5; j++) {sum += Integer.parseInt(info[i][j]);}avg = (float) sum / 3;info[i][5] = String.valueOf(avg);}}// 写入磁盘String line = null;File file = new File("./student.txt");if (file.exists()) {System.out.println("文件已存在");} else {try {file.createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}try (BufferedWriter output = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file))) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {line = info[i][j] + "\t";output.write(line);}output.write("\n");}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("数据已写入~");}}
结果