实例 36
题目
有 N 个整数,使其前面各数顺序向后移 M 个位置,最后 M 个数变成最前面的 M个数。
分析
首先是设置输入,输入数组及相关参数值之后,将原数组复制到新数组中,然后通过计算新位置和原来位置的关系 index = (i + m) % n,将原数组中的元素进行位置交换。
实现
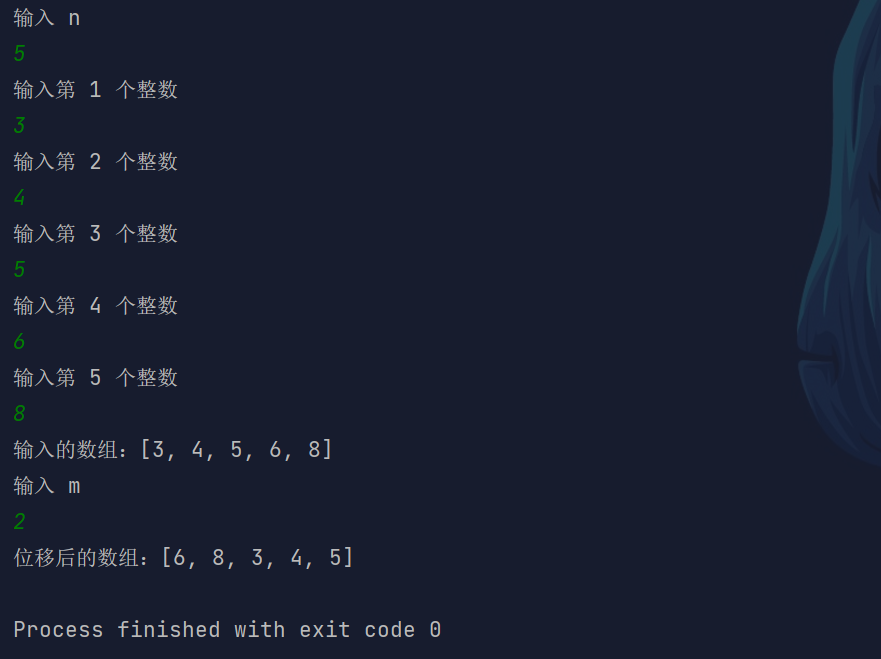
import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/4 14:34* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example36* @description :*/public class Example36 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入 n");int n = scanner.nextInt();int[] arr = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {System.out.println("输入第 " + (i + 1) + " 个整数");arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();}System.out.println("输入的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));System.out.println("输入 m");int m = scanner.nextInt();int[] newArray = new int[n];// 定义一个新的数组,与原来的数组长度相同for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {newArray[i] = arr[i];}// 计算新的位置for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int tmp = (i + m) % n;arr[tmp] = newArray[i];}System.out.println("位移后的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));}}
结果
实例 37
题目
有 N 个人围成一圈,顺序排号。从第一个人开始报数(从 1 报到 3),凡是报到 3 的人则退出圈子,问最后留下的是原来第几号的人?
分析
著名的约瑟夫环问题,用数组求解的基本思想就是用一个一维数组去标识这 n 个人的状态,默认全为 true ,也就是都在圈子内,当数到 m 的人出圈之后,标识置为 false(就是出圈了),同时报数器清 0,下一个人要从 1 开始。在每次报数之前要判断他是否在圈子内(也就是他的标识是否为 true ),如果在圈子里面才会继续报数。定义一个变量记录出圈的人数, 出圈的人数等于 n-1 时,则游戏结束。
实现
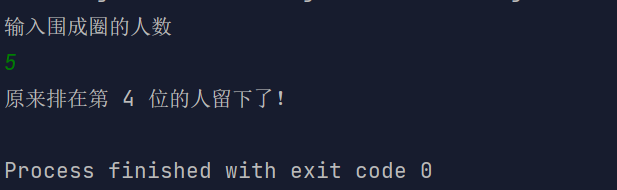
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/4 15:00* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example37* @description :*/public class Example37 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入围成圈的人数Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入围成圈的人数");int num = scanner.nextInt();// 设置对应人的标志boolean[] arr = new boolean[num];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = true;}// 计数int left = num;// 报号int counter = 0;// 对应围成圈的人在标志数组中的索引int index = 0;while (left > 1) {// 一旦数到 3 的人,标志位置为 false,表示出局if (arr[index] == true) {counter++;if (counter == 3) {counter = 0;arr[index] = false;left--;}}index++;if (index == num) {index = 0;}}// 最后标志数组中为 true 的人,则代表最后留下来的人for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {if (arr[i] == true) {System.out.println("原来排在第 " + (i + 1) + " 位的人留下了!");}}}}
结果
实例 38
题目
写一个函数,求一个字符串的长度,在 main 函数中输入字符串,并输出其长度。
分析
求一个字符串的长度,只需要调用 length() 方法即可,但是这里应该是不允许使用该方式,所以我们换用一种方式。
实现
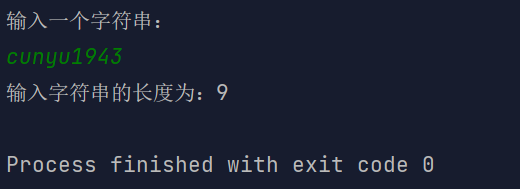
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/4 15:16* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example38* @description :*/public class Example38 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入一个字符串:");String str = scanner.nextLine();System.out.println("输入字符串的长度为:" + getLength(str));}public static int getLength(String str) {char[] chArr = str.toCharArray();return chArr.length;}}
结果
实例 39
题目
编写一个函数,输入 N 为偶数时,调用函数求 ,当输入 N 为奇数时,调用函数求
。
分析
先判断输入的数的奇偶,然后调用对应求和即可。
实现
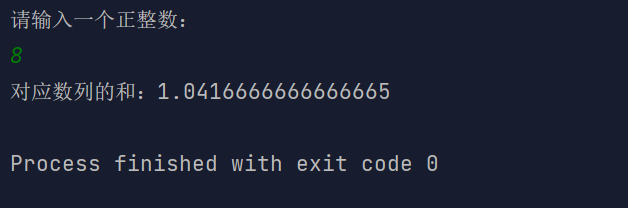
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/4 16:03* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example39* @description :*/public class Example39 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入一个正整数:");int num = scanner.nextInt();System.out.println("对应数列的和:" + sum(num));}public static double sum(int num) {double result = 0;if (num % 2 == 0) {for (int i = 2; i <= num; i += 2) {result += 1.0 / i;}} else {for (int i = 1; i <= num; i += 2) {result += 1.0 / i;}}return result;}}
结果
实例 40
题目
字符串排序。
分析
分别输入字符串存入字符串,然后调用 Arrays.sort() 对数组进行排序即可。
实现
import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Scanner;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.** @author : cunyu* @version : 1.0* @email : 747731461@qq.com* @website : https://cunyu1943.github.io* @date : 2021/6/4 18:52* @project : Java 编程实例* @package : PACKAGE_NAME* @className : Example40* @description :*/public class Example40 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入字符串个数");int size = scanner.nextInt();String[] arr = new String[size];for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {System.out.println("输入第 " + (i + 1) + " 个字符串");arr[i] = scanner.next();}System.out.println("输入的字符为:" + Arrays.toString(arr));Arrays.sort(arr);System.out.println("排序后的字符串数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));}}
结果


