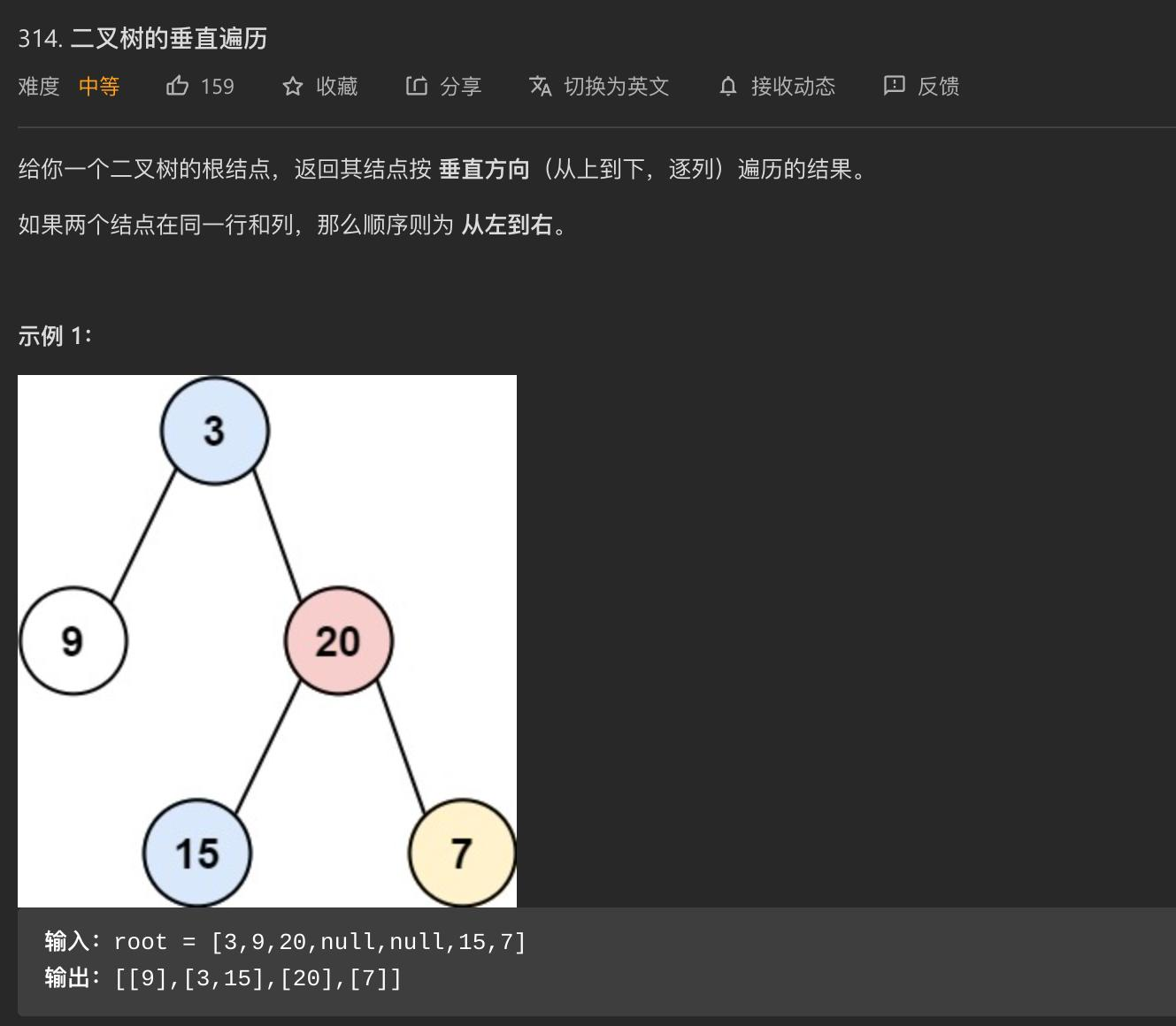
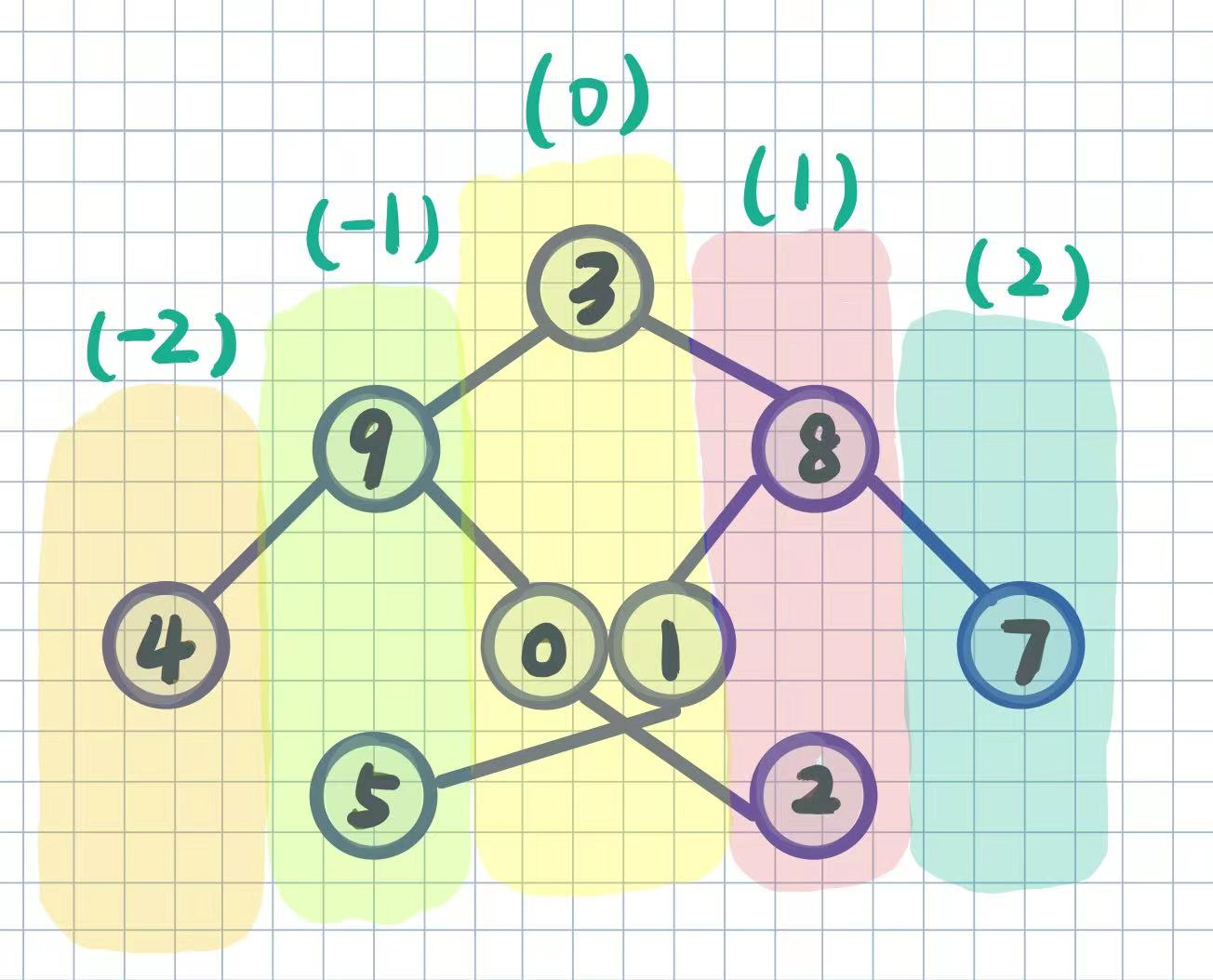
思路:BFS + map
- 首先,每个节点都有一个自己的位置参数
cur_pos,就是通过这个参数分类节点,初始的root节点的位置参数是0,后面的节点,左边则 ,右边则
,右边则
- 常规的做法是使用队列来进行BFS,这里采用
for循环去遍历数组,也是可以的,因为nodes.size()是动态更新的,空间消耗大一点,其他倒是差不多 - 利用map自动排序,边BFS边往数组里面插入,最后得到结果
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */class Solution {public: vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> vert_seq; if (!root) { return vert_seq; } // 第二个参数表示偏移的坐标 vector<pair<TreeNode*, int>> nodes; nodes.push_back({root, 0}); map<int, vector<int>> map_pos; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) { pair<TreeNode*, int> cur_node = nodes[i]; int cur_pos = cur_node.second; // 插入map当中, 利用map实现自动排序 map_pos[cur_pos].push_back(cur_node.first->val); if (cur_node.first->left) { nodes.push_back({cur_node.first->left, cur_pos - 1}); } if (cur_node.first->right) { nodes.push_back({cur_node.first->right, cur_pos + 1}); } } // map to vector for (map<int, vector<int>>::iterator it = map_pos.begin(); it != map_pos.end(); ++it) { vert_seq.push_back(it->second); } return vert_seq; }};
,右边则



