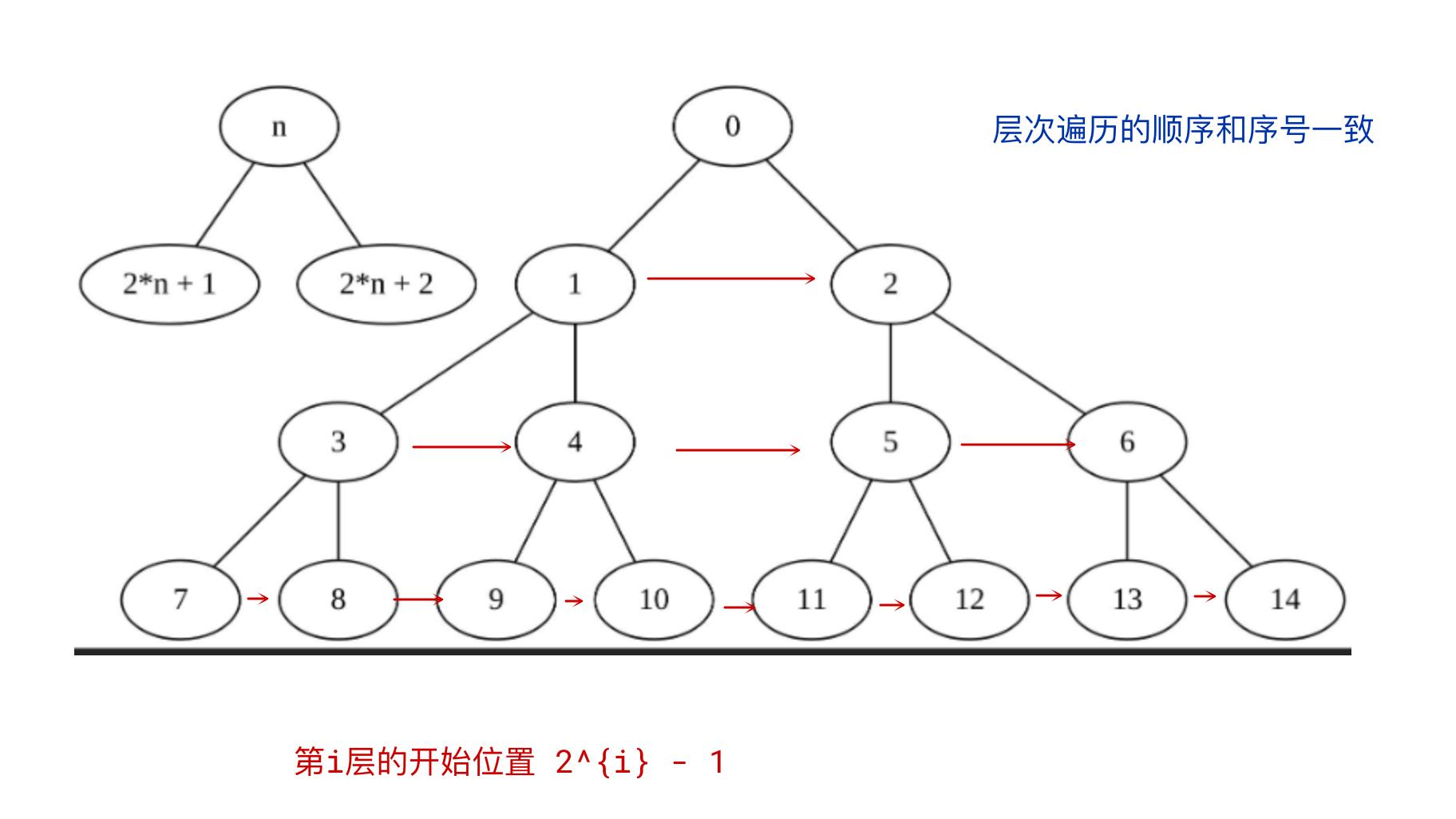
思路1:BFS:利用下标进行计数
- 用BFS数组来存储完全二叉树,如果数组大小和数组中最后一个元素的下标相同,那么就是完全二叉树,反之必然不是。
- 每个元素都有一个自己的编号,代表它是层序遍历中第
index个访问到的元素 - 编号
的节点,其左孩子的编号为
,右孩子编号
(编号从0开始)
- 通过
node_seq.size() - 1 == 最后一个元素的下标判断是不是完全二叉树 - 无论什么情况下,假设层数为
,最后一个元素的下标必然是
(因为下标从0开始,实际上就是如果此树是完全二叉树,
)
- 此题提供了利用数组方式BFS的一种思路,常见的队列方式也可以做,大部分BFS问题两种方法都可以换着来。
代码1:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode* root) {// 利用标记进行BFSvector<pair<TreeNode* ,int>> node_seq;node_seq.push_back({root, 0});// queue的大小不断变化for (int i = 0; i < node_seq.size(); ++i) {pair<TreeNode*, int> cur_pos;cur_pos.first = node_seq[i].first;cur_pos.second = i;if (cur_pos.first->left) {node_seq.push_back({cur_pos.first->left, 2 * i + 1});}if (cur_pos.first->right) {node_seq.push_back({cur_pos.first->right, 2 * i + 2});}}// 因为是从0开始的return node_seq.size() - 1 == node_seq[node_seq.size() - 1].second;}};
思路2:BFS主流做法,判断之前是否出现过空节点
- 设置一个
have_nullptr判断是不是出现过空节点 - 如果出现过空节点之后,仍然会出现非空节点,立即返回
false - 可以通过常规的队列去做,这里采用了按照下标构建数组的方式,大部分BFS问题,两种2方式都可以换着使用
代码2:
class Solution {public:bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode* root) {vector<pair<TreeNode*, int>> nodes;nodes.push_back({root, 0});bool have_nullptr = false;for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) {pair<TreeNode*, int> cur_node = nodes[i];if (cur_node.first->left) {if (have_nullptr) return false;nodes.push_back({cur_node.first->left, 2 * i + 1});} else {have_nullptr = true;}if (cur_node.first->right) {if (have_nullptr) return false;nodes.push_back({cur_node.first->right, 2 * i + 2});} else {have_nullptr = true;}}return true;}};
思路3:DFS + 标号
- 所有节点的数量可以通过
dfsCount(root)求出 - 所有节点可以按照一定顺序来标号(逐层标号,从左到右,没有节点也要占用标号),也就是
root.left.val = 2 * root.val + 1,root.right.val = 2 * root.val + 2,记最大标号为maxIndex。 如果
maxIndex + 1 == dfsCount(root),就说明是完全二叉树,否则不是。代码3:
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):# self.val = val# self.left = left# self.right = rightclass Solution:def __init__(self):self.maxIndex = 0def dfsCount(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:if not root:return 0if not root.left and not root.right:return 1return self.dfsCount(root.left) + self.dfsCount(root.right) + 1def recMaxIndex(self, root: TreeNode, curIndex: int) -> None:if not root:returnself.maxIndex = max(self.maxIndex, curIndex)self.recMaxIndex(root.left, 2 * curIndex + 1)self.recMaxIndex(root.right, 2 * curIndex + 2)def isCompleteTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:self.recMaxIndex(root, 0)return self.maxIndex + 1 == self.dfsCount(root)