Problem statement
Benefits

Pain points & problem statements
| Pain points | Problem statements | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | UX issue or friction that frustrates the user and blocks them from getting what they need. | A clear description of the user’s need that should be addressed. |
| Goal | - keeps users happy - encourages them to keep interacting with the product. |
- Provide clarity about your users’ goals - help UX designers identify constraints that prevent users from meeting those goals. |
| Framework | Financial, Product, Process, Support | 5Ws and H: who, what, when, where, why, and how |
The 5 Ws and H: who, what, when, where, why, and how
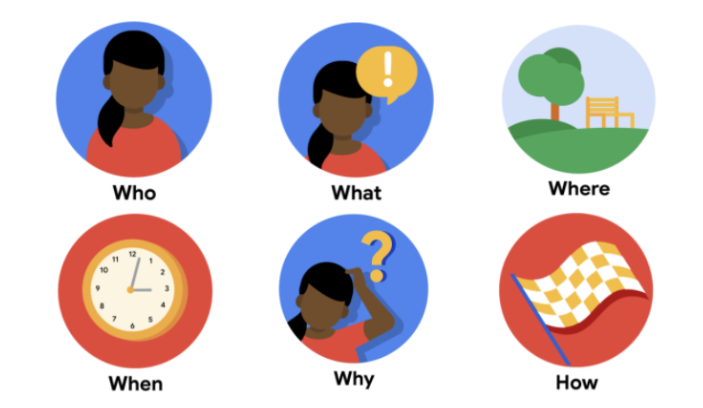

Who is experiencing the problem? Knowing your users and their background is key to creating successful solutions for them.
What are the pain points you’re trying to solve? Determining a user’s pain points early allows you to answer the rest of these questions and clarify the context of the pain points.
Where is the user when they’re using the product? A user’s physical context matters to your design.
When does the problem occur? Maybe it’s right after the end of a long and tedious process, or maybe it’s something that happens daily. Knowing when the problem occurs can help you better empathize with the user’s feelings.
Why is the problem important? Knowing how this problem affects your user’s experience and life will help to clarify the potential consequences.
How are users reaching their goals by using the product? Understanding how users reach their goals allows you to map the user journey that they take through your product.
The problem statement formula

With these parts clearly defined, the problem statement is:
- Human-centered and focused on the needs of a specific type of user.
- Broad enough for creative freedom.
- Narrow enough to be solved by a practical design solution.
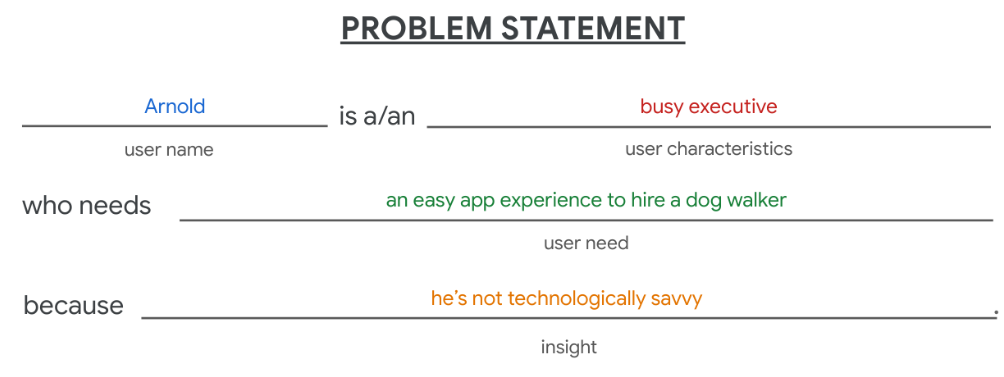
Example:Dog walker app
- Who: A busy executive
- What: Arnold wants to hire a daily dog walker for his three dogs.
- Where: Arnold is likely using the app at work, on the go.
- When: Arnold gets frustrated when he opens the app, starting from the very beginning of the user journey.
- Why: Arnold doesn’t have a lot of experience with phone apps or similar technology.
- How: Arnold wants to go easily from the home screen of the app to the list of dog walkers to the confirmation screen.
Learn more about defining user problems
- Design Problem Statements: What They Are and How to Frame Them from Toptal
- User Need Statements: The ‘Define’ Stage in Design Thinking from Nielsen Norman Group
- Are you solving the right problem? from Harvard Business Review
If there is no problem, there is no solution, and no reason for a company to exist. – Vinod Khosla, Khosla Ventures (a Silicon Valley venture capital firm)
Define hypothesis statements
Hypothesis statements an educated guess about what you think the solution to a design problem might be.
如何撰写Hypothesis statements?
Formula
- States a specific action and tells us what your solution should enable the user to do?
- States the desired outcome that determines whether your solution was successful in meeting the user’s need?
- if / then format

特点:focus directly on the needs of users
举例:CoffeeShop app
- we believe format

特点:take the perspective of your team into account, while remaining empathetic to the needs of users.
Value proposistion
Value propositions summarize why a consumer should use a product or service.
To answer these two questions:
- What does your product do? Clearly explain the offering that your product provides users.
- Why should the user care? Describe how your product addresses users’ pain points.
Steps
Step 1. Describe your product’s features and benefits.
Create a list of all the great features and benefits of your product, big and small. Don’t hold back; list everything that comes to mind and then narrow it down later.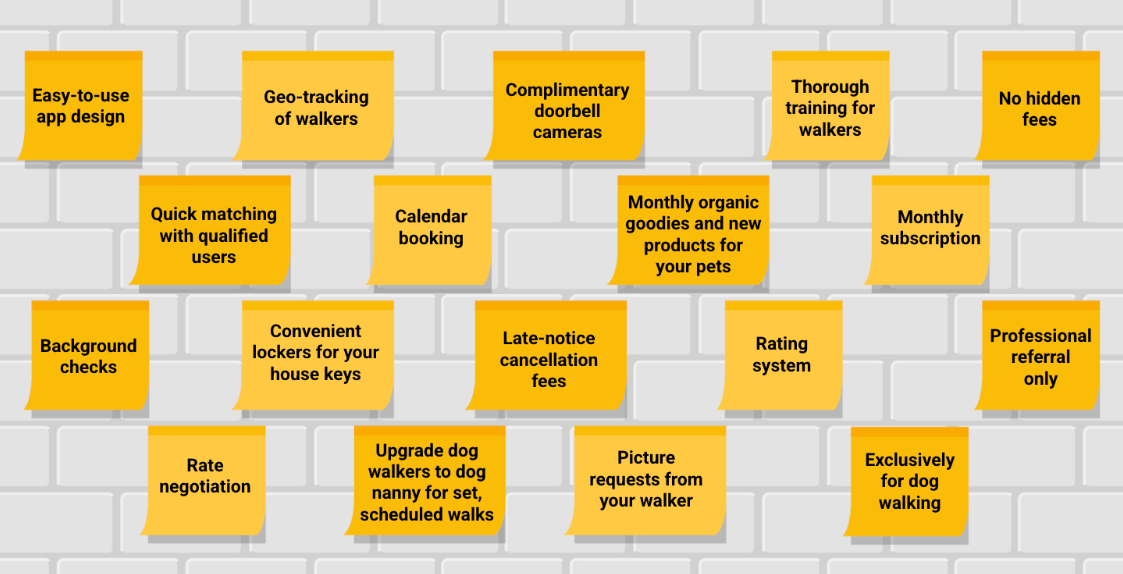
Step 2. Explain the value of the product.
Anything that you identify as a value proposition needs to be beneficial to your users. In this example, for the dog walker app, there were four categories of product values that were identified during user interviews: accessible, professional experience of the dog walkers, cost, and reliability. The giant list of features and benefits from step one is sorted into those four categories.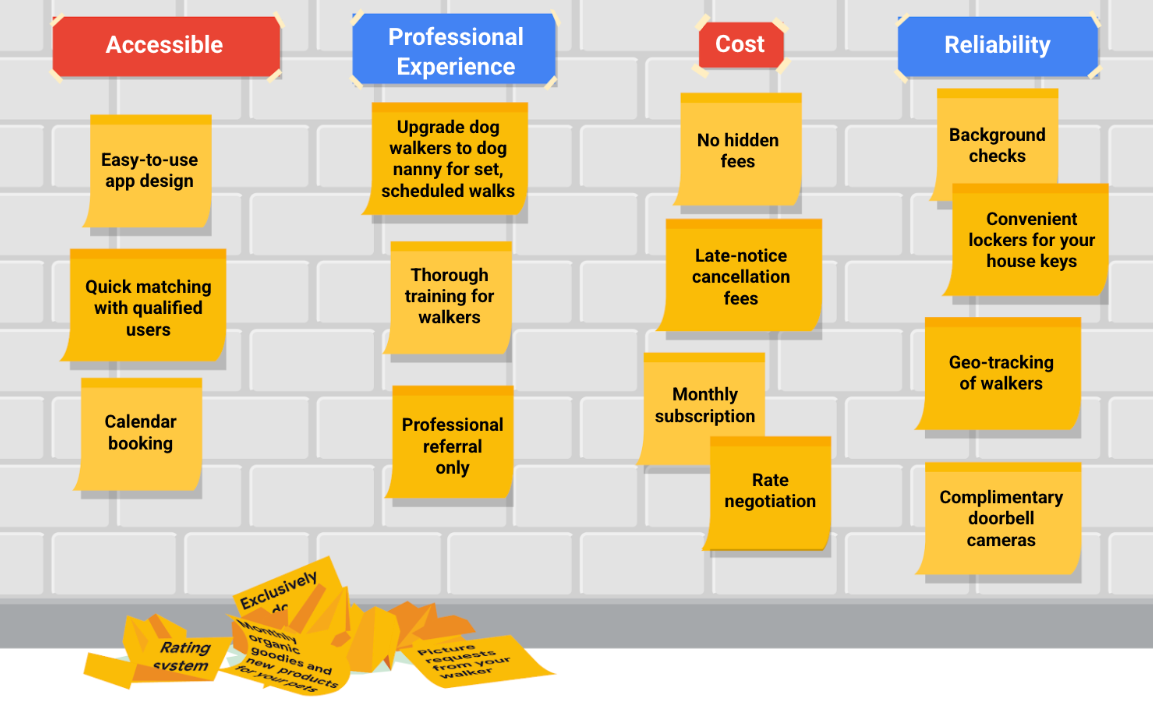
Step 3. Connect these features and benefits with the needs of your users.
You’ve narrowed your list down of lots of benefits and features by matching them with actual user needs. Now it’s time to review the list of value propositions your product offers. For the dog walker app, here are the value propositions that matched with the personas that were developed earlier:
- Thorough training for walkers
- Upgrade dog walkers to dog nanny for set, scheduled walks
- Geo-tracking of walkers
- Calendar booking
- Late-notice cancellation fees
- Convenient lockers that hold your house keys
- Easy-to-use app design
And there you have it, your list of value propositions! However, some of these features and benefits are also offered by your competitors. So how do you know what makes your product stand out from the competition? Identify your app’s unique value proposition. This means reviewing the list of value propositions that match to your personas and removing those that your competition also offers.
Key takeaways
One of the most important things to know about value propositions is that they need to be short, clear, and to the point. Users want to be able to easily identify exactly how your product will meet their unique needs and what sets your product apart in the market. Sometimes users won’t know what they need until you explain it to them. That’s the real heart of product design innovation.
Influence of psychology
Human factors

历史:
- 一战战斗机:飞行员适应机器
- 二战产生大量训练需求:机器适应人
Common human factors that inform design

How to design with human factors
2 Psychological concepts that can help you design with the human factor in mind.
Mental model 心智模型

Feedback loops 反馈回路

Psychology principles that influence design
Von Restorff effect or isolation effect


对群体中差异化的东西会产生更强的注意力。
这个效应应用到了CTA(call-to-action)的设计
Serieal position effect

Hick’s law

(当选项过多,用户会产生选择困难症)


