- User experience
- Product
- Good Product
- Why is UX important to business?
- Different kinds of UX designers
- The most common colleagues a UX designer might work with:
- The product development life cycle
- Job responsibilities of entry-level UX designers
- UX specialist,T-shaped, generalist
- Cross-functional teams
- UX design jobs at different types of companies
- The influence of company size and industres
- Common Career Path
- UX research methods
User experience
How a person, the user, feels about interacting with, or experiencing, a product
Product
A good, service, or feature
Good Product
- Usable
- Equitable
- Enjoyable
- Useful
Usability
the design, structure, and purpose of the product are clear to everyone
Equitable
Being equitable means your designs are useful and marketable to people with diverse abilities and backgrounds.
Enjoyable
User experience is also about making things enjoyable to use, which creates a positive connection between the user and the product.
Useful
As humans, we want products that are useful, meaning they solve our problems.
Why is UX important to business?
McKinsey & Company found that, regardless of industry, businesses that focused on good usability and design performed better than their competitors.
Different kinds of UX designers
interaction designers.
They figure out how to connect the users’ needs and the business’s goals with what’s actually feasible to build.
visual designers
focus on how a product or technology looks.
motion designers
They think about what it feels like for a user to move through a product and how to create smooth transitions between pages on an app or a website.
The most common colleagues a UX designer might work with:
UX researchers, conduct studies or interviews that help us learn how people use a product.
UX writers, who think about how to make the language within a product clearer to make the user experience more intuitive.
Production designers, who often act as a bridge between interaction designers and engineers.
UX engineers(work with most frequently), translate the design’s intent into a functioning experience, like a website or an app.
UX program managers, ensure clear and timely communication so that the process of building a useful product moves smoothly from start to finish.
The product development life cycle
from the first spark of an idea to the release of the final product.
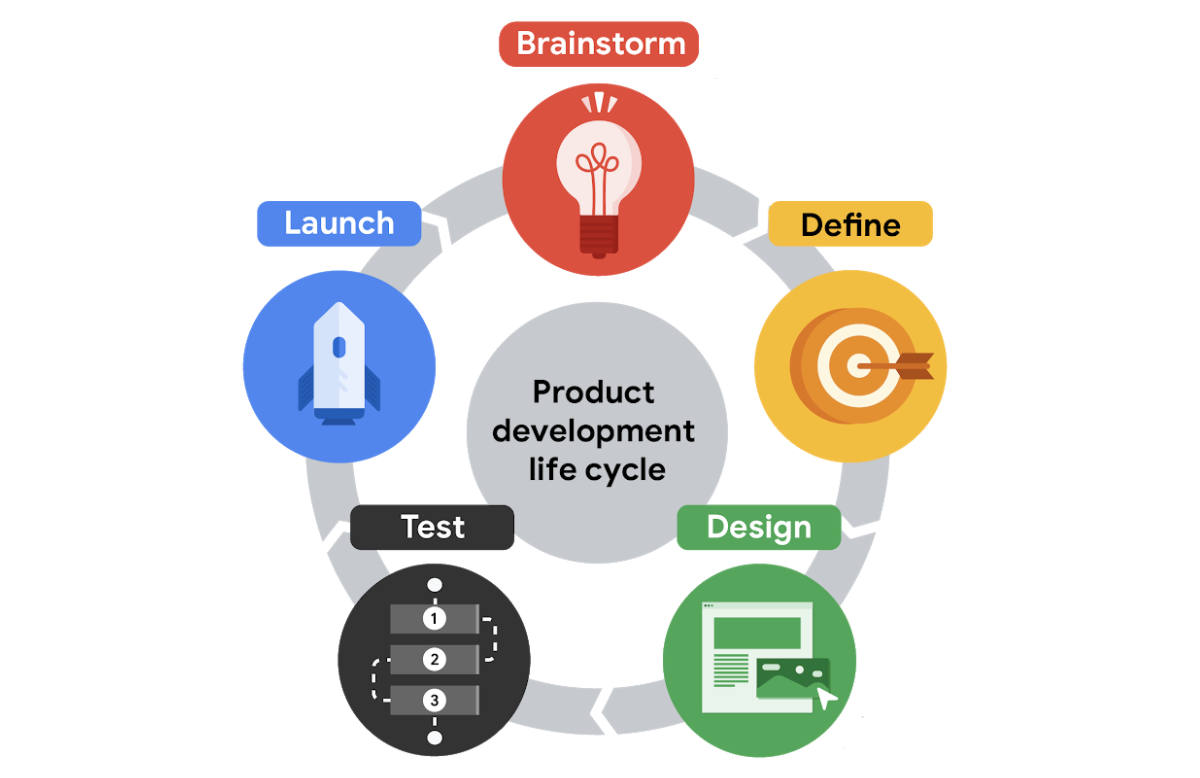
Brainstorm
重点:diversity
Teams that have meaningful diversity across identifiers like race, gender, abilities, family structure, and ethnicity are generally more effective at brainstorming because they bring together a lot of different lived experiences.
Also, check out your product’s competitors
Define
重点:Research
answering questions like: Who is the product for? What will the product do? And, what features need to be included for the product to be successful?
Design
wireframes—>prototypes
Test
With engineers
internally—>shareholders—>external with potential users
Launch
App store上架
Job responsibilities of entry-level UX designers
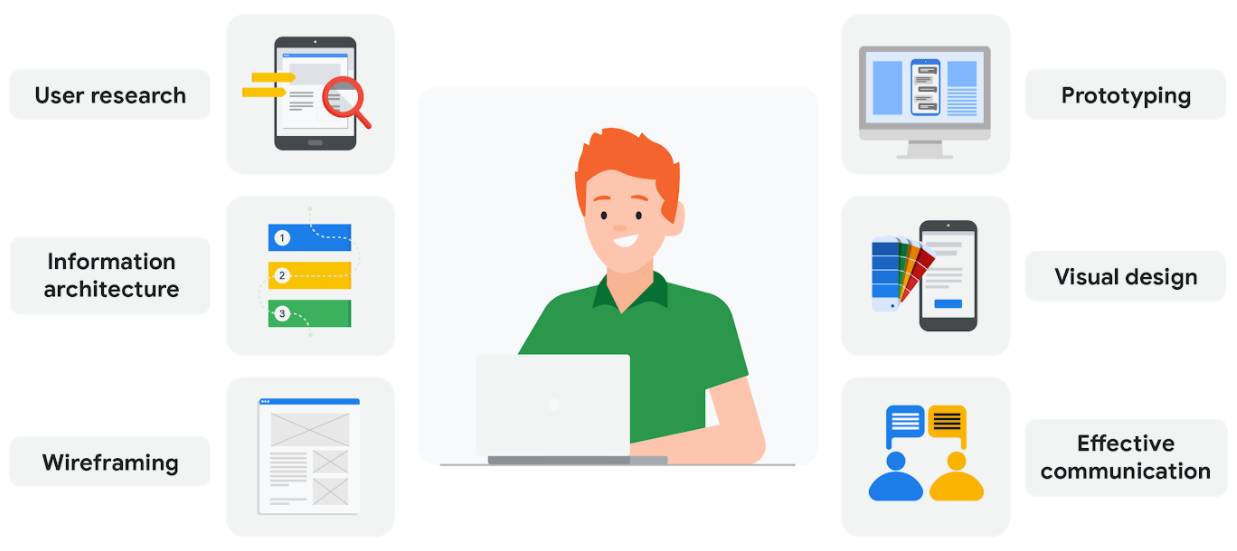

User research: User research is about understanding the people who use your product. Through research, you’ll learn about users’ backgrounds, demographics, motivations, pain points, emotions, and goals. Your research methods might include surveys, observations, and interviews. We’ll explore user research in much more detail in an upcoming course.
Information architecture:Information architecture, or IA for short, involves deciding how your product is organized and structured. Think of IA as a skeleton that outlines how users interact with your product. Everything in your product should be organized in ways that make sense to the user and meets their expectations.
Wireframing: A wireframe is a basic outline or sketch of a product or a screen, like an app or website. As the name suggests, wireframes look like they were created with wires. They’re mostly lines and shapes, with some text. Wireframes can be drawn by hand or created digitally using software. Wireframing helps you bring your design ideas to life, so other people on your team can provide input and feedback.
Prototyping: A prototype is an early model of a product that demonstrates its functionality. Prototypes can be in physical or digital formats and can vary in complexity. Sometimes a prototype is made to demonstrate one specific feature of a product, like the transition between screens or the way the product physically looks and feels. You’ll make multiple prototypes for any given product throughout the design process.
Visual design: Visual design focuses on how the product or technology looks. As a UX designer, you need to understand the foundations of visual design in order to communicate the connection between a product’s functionality and its appearance to users. You’ll learn some of the most important principles of visual design throughout this certificate program.
Effective communication: Effective communication as a UX designer means connecting with your colleagues through emails, meetings, presentations, and design software. UX design is a very collaborative field, so being able to communicate both digitally and face-to-face with teammates is important. You need to be a good listener, be receptive to feedback, and share your ideas in a clear way.
A day in the life of an entry-level UX designer
- Identify problems
- Interact with teammates
Get feedback and push forward
All about solution
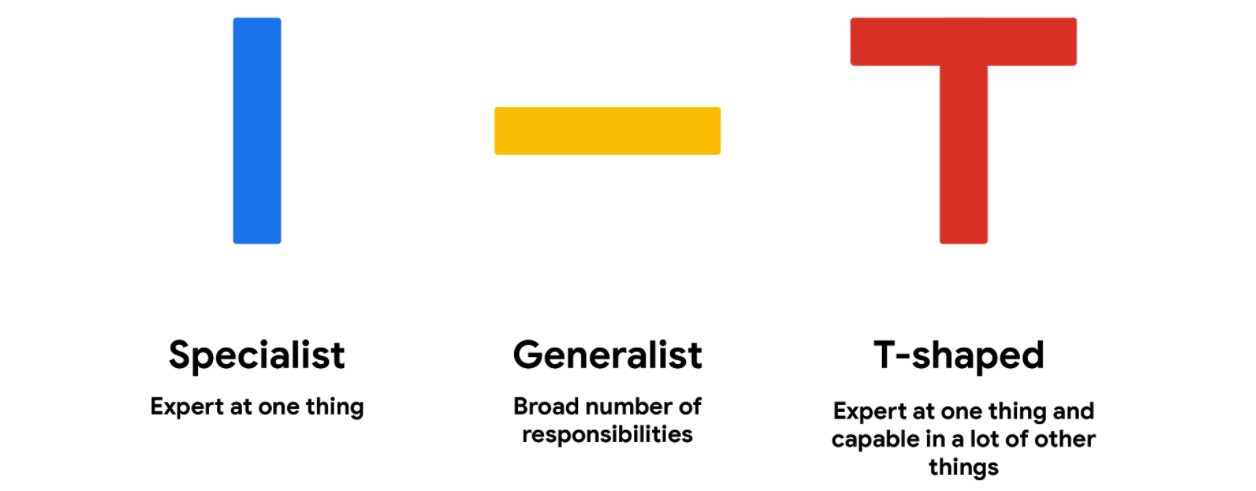
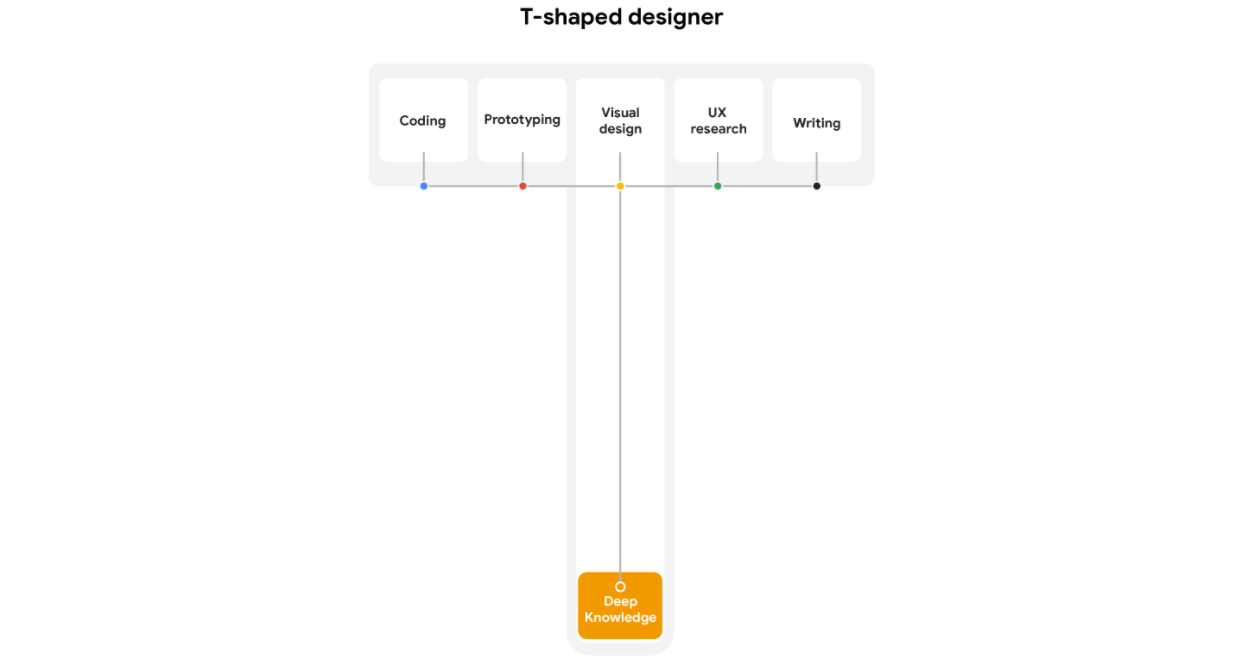
UX specialist,T-shaped, generalist
Cross-functional teams

UX design jobs at different types of companies
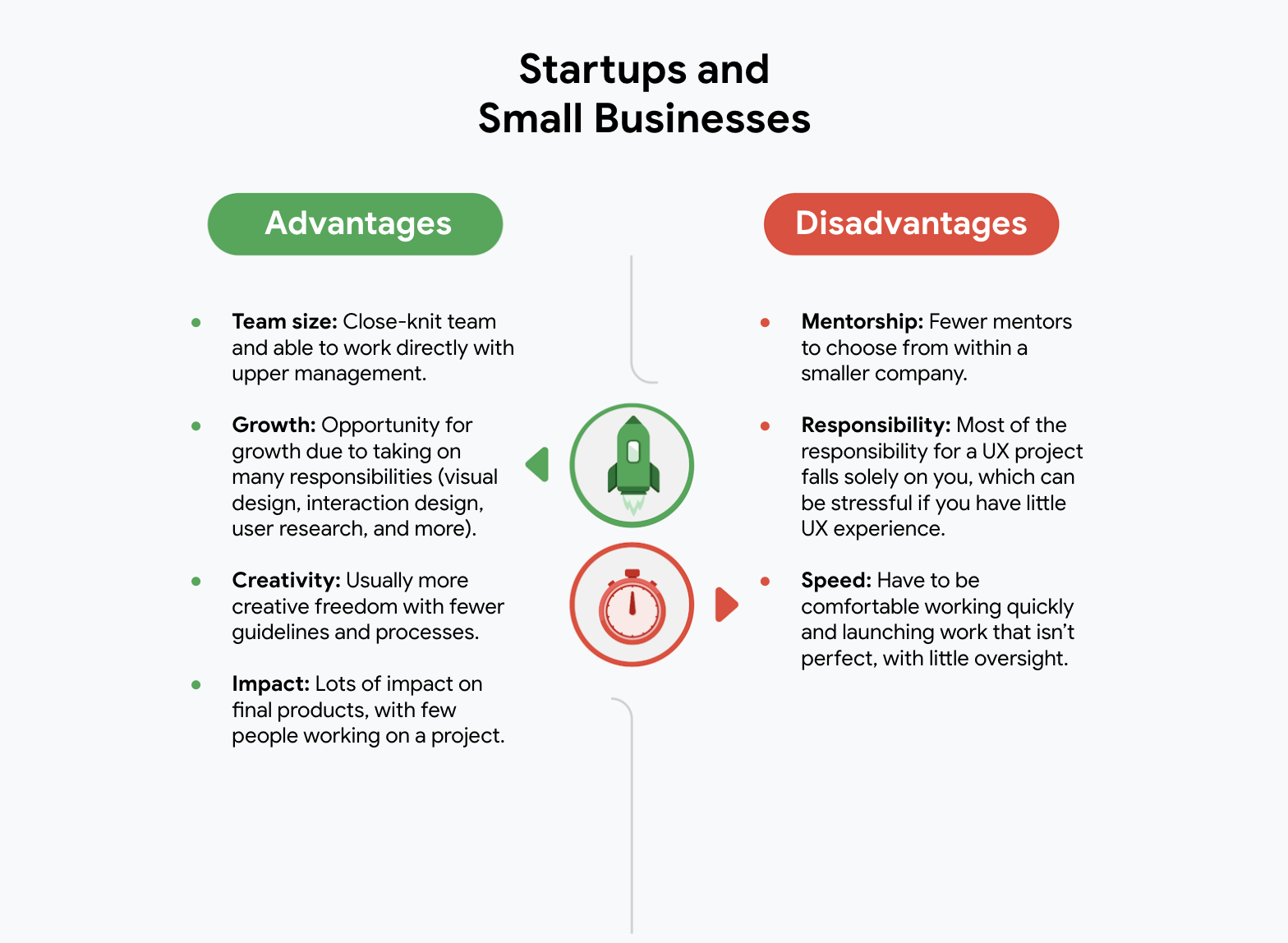
- Start-up
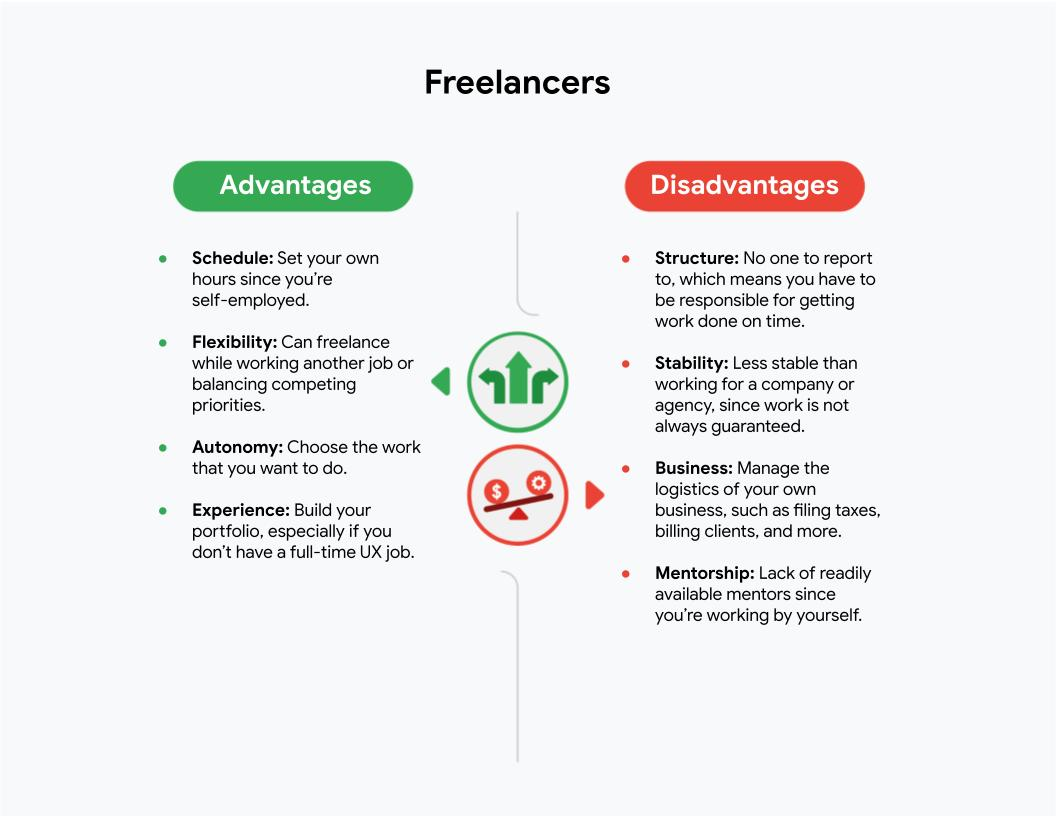
- Freelance
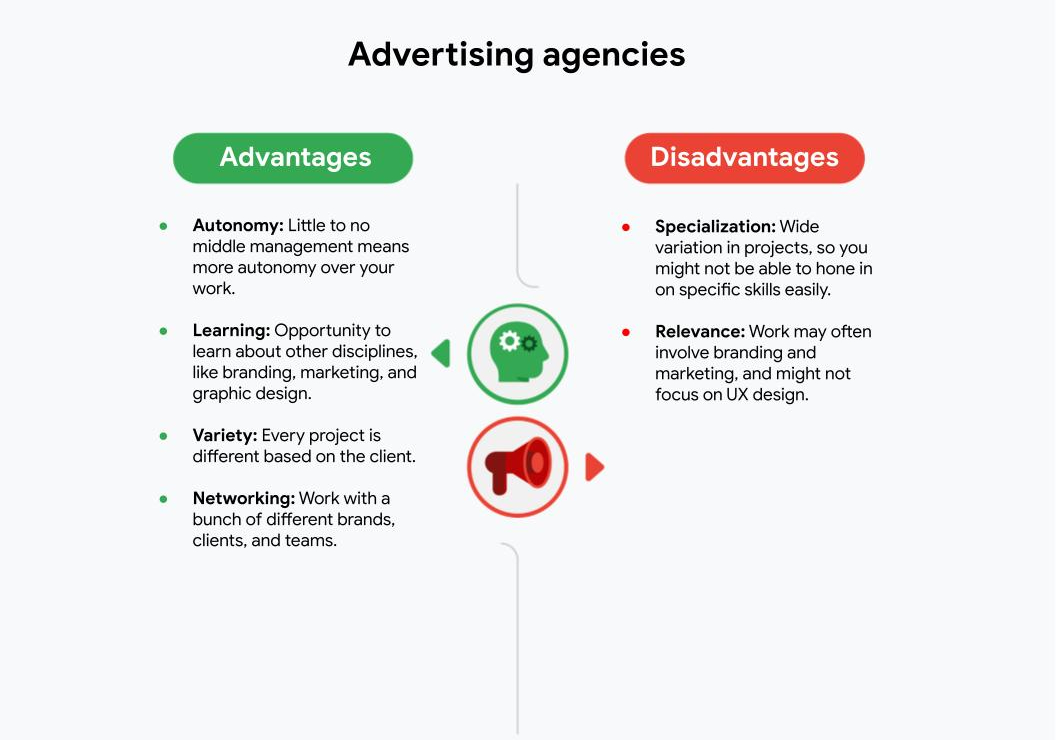
- Advertising agencies
- Design Agencies
- Big corporation
The influence of company size and industres
Common Career Path
Where to start
- Internship: short-term, limited responsibilities
- Apprenticeships: longer 1-2 years, paid
- Freelancing: work for yourself
- Entry-level job: most common, do not require prior experience
UX research methods
2 ways to categorize
- Who conduct the research
Primary research is research you conduct yourself.
- For example, you might interview users, survey users, or conduct a usability study to hear from users directly.
Secondary research is research that uses information someone else has put together.
- Secondary research can be information from books, articles, or journals.
- Often before ideation, at the very beginning of product development lifecycle
- The type of data collected
Qualitative research focuses on observations.
- often based on interviews, where we focus on a smaller number of users and understand their needs in greater detail.——> why
Quantitive research focuses on data that can be gathered by counting or measuring.
- often answers questions like: How many? How much? ——> what
Methods
Interviews
Interviews are research method used to collect in-depth information on people’s opinions, thoughts, experiences, and feelings.
- Interviews are usually conducted in person and include a series of open-ended questions where the researcher asks the user about their experience.
- Use interviews when your questions require a detailed response.
- eg. How was your experience using this app?
Surveys
An activity where many people are asked the same questions in order to understand what most people think about a product
- most useful after you have some initial understanding of the users’ pain points and want to solidify that by surveying a larger number of people
Usability studies
Usability studies are a technique that help us evaluate a product by testing it on users. The goal of a usability study is to identify pain points that the user experiences with different prototypes, so the issues can be fixed before the final product launches.
- If the product has already launched, a post-launch usability study might include data like success metrics and key performance indicators(KPIs)
- KPIs are critical measures of progress toward an end goal.
- The KPIs for an app or new product launch might include things like how much time the user spent on a task or the number of clicks they used to make a purchase.

