前言
典型的SpringMVC在Web.xml中的配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaeehttp://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"version="3.0"><display-name>springmvc-demo</display-name><context-param><param-name>appName</param-name><param-value>SpringMVCDemo</param-value></context-param><!-- 请求参数编码过滤器 --><filter><filter-name>SetCharacterEncoding</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>UTF-8</param-value></init-param><init-param><param-name>forceEncoding</param-name><param-value>true</param-value></init-param></filter><filter-mapping><filter-name>SetCharacterEncoding</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping><!-- 加载spring根环境 --><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><!-- servlet映射到springmvc --><servlet><servlet-name>frontend</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:web/webmvc-frontend.xml</param-value></init-param></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>frontend</servlet-name><url-pattern>/frontend/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><servlet><servlet-name>backend</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:web/webmvc-backend.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>backend</servlet-name><url-pattern>/backend/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
这里通过ContextLoadListender指定了一个Spring上下文文件,一般称为Root AC,在配置Servlet也指可指定属于此Servlet的Spring上下文,一般称为Web AC,依赖关系为:容器启动后,WebAC会设置其parent为RootAC,因此整个WebAC环境里用到的所有Bean都可通过RootAC获得。如图为: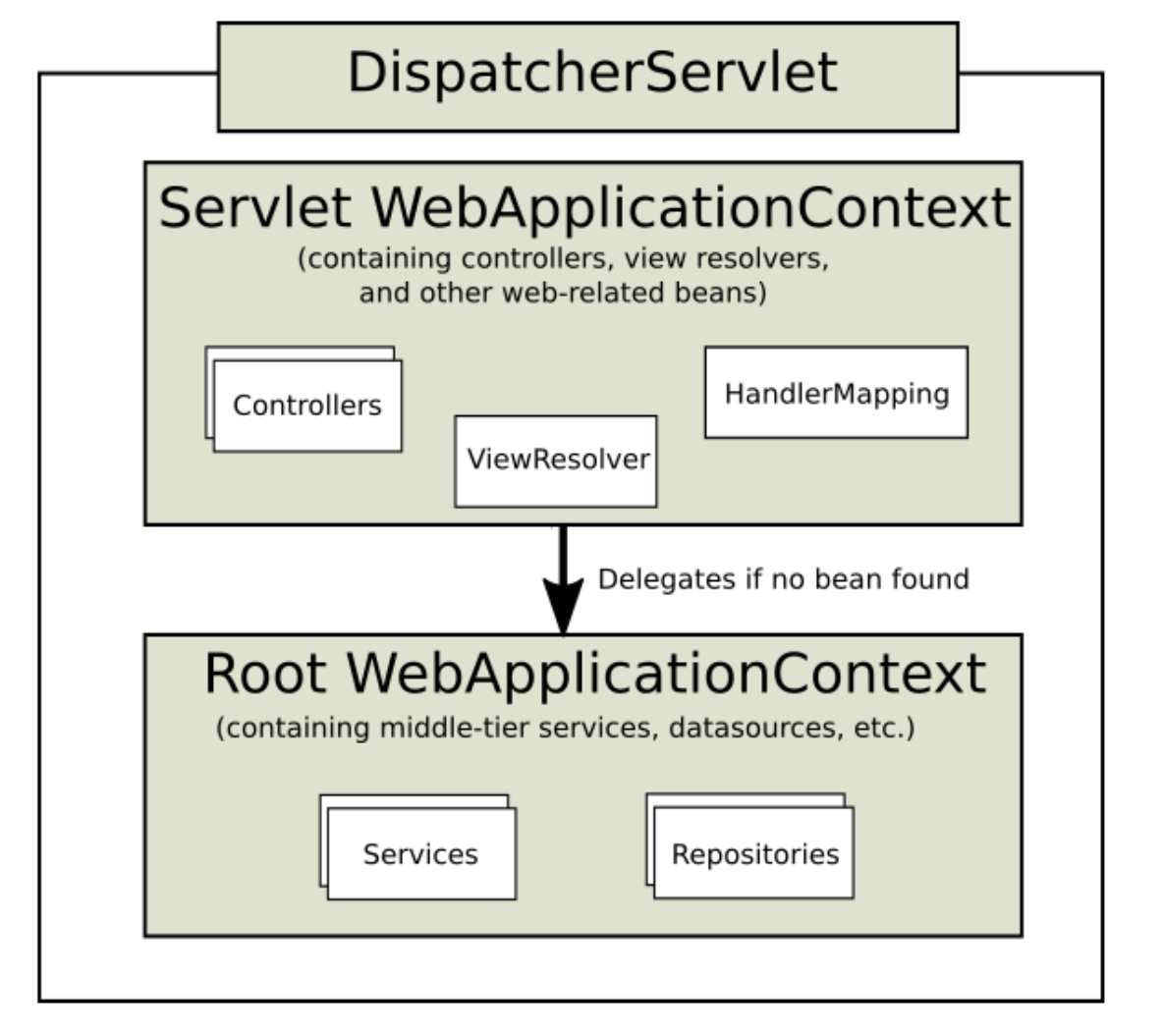
实例化ROOT Application
Servlet容器加载web.xml时,首先执行org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener,其内部实现逻辑为:获取contextParam中的配置,如:
<context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param>
然后初始化一个WebXmlApplicationContext,然后设置到ServletContext中,放到容器环境里。
ServletContext的属性为:
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + “.ROOT”;
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT
代码示例:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");}Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");}long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.if (this.context == null) {this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);}if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;if (!cwac.isActive()) {// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etcif (cwac.getParent() == null) {// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->// determine parent for root web application context, if any.ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);cwac.setParent(parent);}configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);}}servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
createWebApplicationContext 方法主要是通过反射创建一个ApplicationContext,实现逻辑为:
首先查看Web.xml中是否有配置:contextClass,如果存在则直接反射创建。
如果不存在,则加载Jar包中的ContextLoader.properties文件里的配置,默认配置如下:
# Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader.# Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context-param.# Not meant to be customized by application developers.org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
表示使用:XmlWebApplicationContext
然后通过反射创建一个XmlWebApplicationContext实例:
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);return ctor.newInstance(args);
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 方法为XmlWebApplicationContext配置属性,从ServletConfig中读取在Web.xml里配置的contextConfigLocation,表示设置一个上下文的配置文件,用来初始化容器Bean工厂,最好执行容器的refresh方法,表示:在Web容器启动过程中,直接实例化ROOT Application,并提前初始化Bean。
代码如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {// The application context id is still set to its original default value// -> assign a more useful id based on available informationString idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);if (idParam != null) {wac.setId(idParam);}else {// Generate default id...wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));}}wac.setServletContext(sc);String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);if (configLocationParam != null) {wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);}// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refreshConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);}customizeContext(sc, wac);wac.refresh();}
实例化Servlet Application
一般建议配置Servlet时,指定
0
不指定默认情况下为负数,表示当前首次请求时才初始化Servlet, 而配置大于等于0,表示Web容器启动时则执行初始化,这样可以提前初始化。
初始化DispatchServlet,执行顺序为:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init
读取Web.xml中的所有配置:如并把当前DispatcherServlet包装为一个Bean,通过setPropertyValue可调用属性对应的setter方法,典型的配置如下:
<servlet><servlet-name>backend</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:web/webmvc-backend.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup></servlet>
DispatchServlet对应的参数setter方法如下:
/*** Set the context config location explicitly, instead of relying on the default* location built from the namespace. This location string can consist of* multiple locations separated by any number of commas and spaces.*/public void setContextConfigLocation(String contextConfigLocation) {this.contextConfigLocation = contextConfigLocation;}
执行org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init完成后,contextConfigLocation的值为:classpath:web/webmvc-backend.xml
代码如下:
public final void init() throws ServletException {// Set bean properties from init parameters.PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {try {BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));initBeanWrapper(bw);bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);}throw ex;}}// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.initServletBean();}
然后执行DispatcherServlet的initServletBean,此方法的关键逻辑为:查找ServletConfig中的ROOT WebApplicationRoot并重新创建一个与当前Servlet相关的WebApplicationContext,设置WAC的parent为ROOT AC,然后放到ServletContext中。
当前DispacherServlet在ServletContext中的属性Key为:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.#{ServletName}
这样可以做到隔离。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {WebApplicationContext rootContext =WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());WebApplicationContext wac = null;if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use itwac = this.webApplicationContext;if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;if (!cwac.isActive()) {// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etcif (cwac.getParent() == null) {// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parentcwac.setParent(rootContext);}configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);}}}if (wac == null) {// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context idwac = findWebApplicationContext();}if (wac == null) {// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local onewac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);}if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh// support or the context injected at construction time had already been// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.onRefresh(wac);}if (this.publishContext) {// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");}}return wac;}
创建Servlet WebApplicationContext的相关代码在FrameworkServlet#createWebApplicationContext(org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext)
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();...ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());wac.setParent(parent);wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);return wac;}
其中:getContextClass默认为:XmlWebApplicationContext
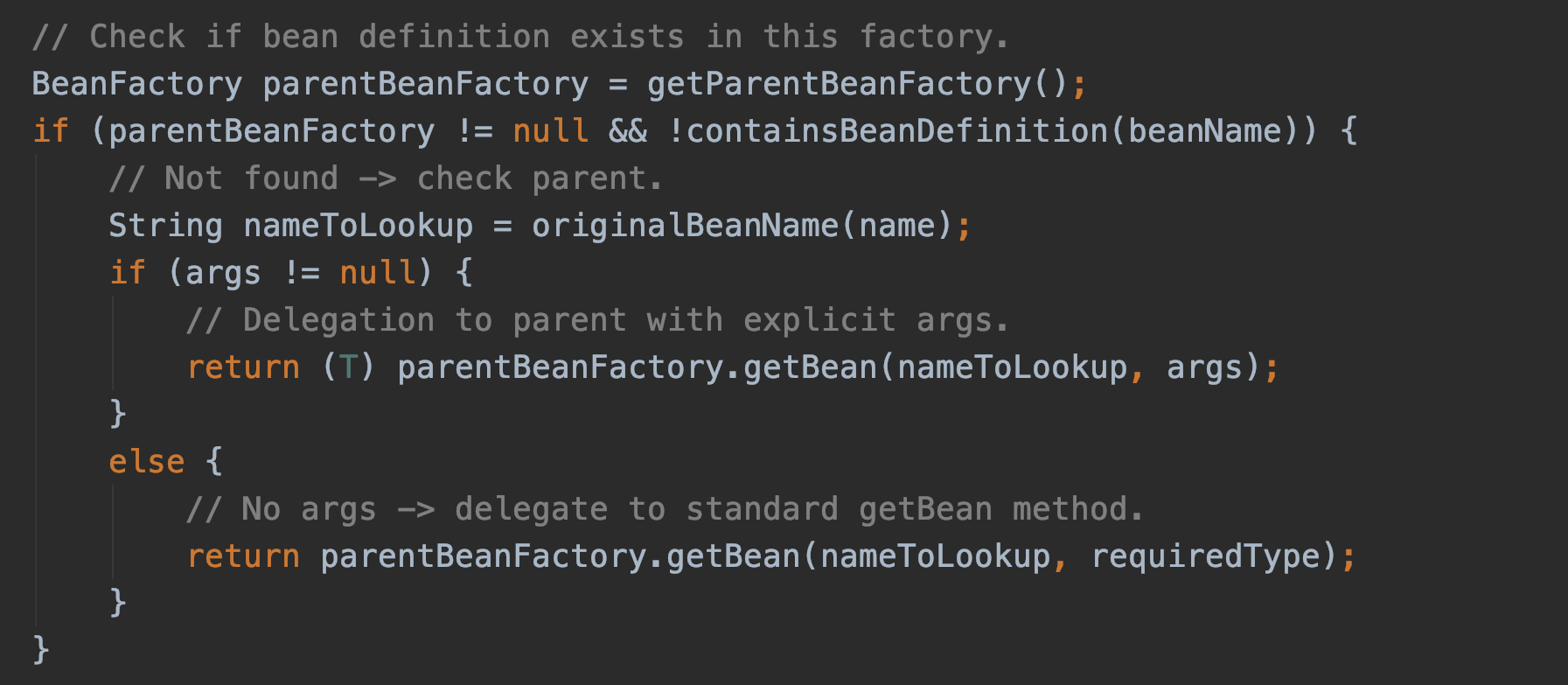
所以在执行请求时,SpringMVC管辖的Controller可以任意调用Service或DAO层的Bean,原因在于通过SpringApplicationContext的parent来进行二次查找,首先查找Parent上下文里的Bean,找不到则查找当前上下文里的Bean。有点类似Java的类加载机制,采用的双亲委派模型。
实现简要代码: