前言
分布式ID在多种场景下都有广泛的应用,如分库分表后生成全局用户Id,订单Id,分布式事物中的全局Id,消息队列中的全局消息Id.因此本文分析一下常用的分布式Id的常见实现方案。
SnowFlake-雪花算法
SnowFlake是Twitter最早提出的一种全局ID生成算法,可以产生一个Time-Based的全局ID, 由于生成简单、ID趋势递增,业界采用的比较广泛。比如在snowflake中的64-bit分别表示如下图(图片来自网络)所示:
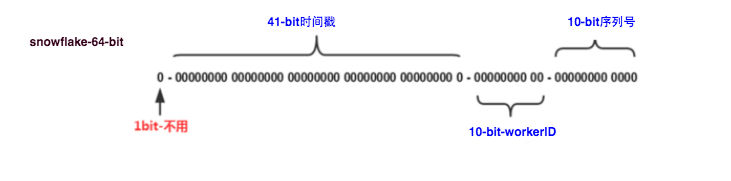
41-bit的时间可以表示(1L<<41)/(1000L_3600_24*365)=69年的时间,10-bit机器可以分别表示1024台机器。如果我们对IDC划分有需求,还可以将10-bit分5-bit给IDC,分5-bit给工作机器。这样就可以表示32个IDC,每个IDC下可以有32台机器,可以根据自身需求定义。12个自增序列号可以表示2^12个ID,理论上snowflake方案的QPS约为409.6w/s,这种分配方式可以保证在任何一个IDC的任何一台机器在任意毫秒内生成的ID都是不同的。
SnowFlakeID是一个64 bit,8 bytes的整数类型,结构如下:
bit[0]:最高位填0,保证ID是正整数。
bit[1-41]:时间戳,41 bit。表示自某个起始时间(可自行设定)以来的毫秒数,支持69年跨度。
bit[42-51]:Worker ID,10 bits。表示节点的唯一标识,能同时支持1024个不同的Worker。Worker ID可依赖外部配置中心生成,推荐前5位数据中心ID,后5位PID。
bit[52-63]:并发ID序列号,12 bits。用于同一毫秒内并发产生的ID自增序号,采用原子递增计数器实现,每毫秒重新归0,一毫秒内可以并发产生4096个ID。如果在这个毫秒内生成的数量超过4096,可以阻塞等待到下个毫秒来生成。
这种方式的优缺点
1)本地化生成,算法简单,效率高
2)适合主键字段:时间戳位于ID的高位,毫秒内自增序列在低位,ID趋势递增;长度8个字节,适合数据库存储。
3)不足之处:
3.1)依赖机器时钟,如果时钟错误比如时钟不同步、时钟回拨,会产生重复ID
3.2)每个节点的Worker ID要借助外部服务比如Zookeeper、Redis、MySQL分配
ID容量局限性:时间偏移量支持2^41ms=69年,可以在算法中自定义起始时间,年限略短,一般够用。
Twitter SnowFlake实现
SnowFlake算法用来生成64位的ID,刚好可以用long整型存储,能够用于分布式系统中生产唯一的ID, 并且生成的ID有大致的顺序。 在这次实现中,生成的64位ID可以分成5个部分:
0 - 41位时间戳 - 5位数据中心标识 - 5位机器标识 - 12位序列号
5位数据中心标识跟5位机器标识这样的分配仅仅是当前实现中分配的,如果业务有其实的需要,可以按其它的分配比例分配,如10位机器标识,不需要数据中心标识。
/*** twitter的snowflake算法 -- java实现* @see @{https://github.com/beyondfengyu/SnowFlake?spm=ata.13261165.0.0.78d12ace8n92XX}* @author beyond* @date 2016/11/26*/public class SnowFlake {/*** 起始的时间戳*/private final static long START_STMP = 1480166465631L;/*** 每一部分占用的位数*/private final static long SEQUENCE_BIT = 12; //序列号占用的位数private final static long MACHINE_BIT = 5; //机器标识占用的位数private final static long DATACENTER_BIT = 5;//数据中心占用的位数/*** 每一部分的最大值*/private final static long MAX_DATACENTER_NUM = -1L ^ (-1L << DATACENTER_BIT);private final static long MAX_MACHINE_NUM = -1L ^ (-1L << MACHINE_BIT);private final static long MAX_SEQUENCE = -1L ^ (-1L << SEQUENCE_BIT);/*** 每一部分向左的位移*/private final static long MACHINE_LEFT = SEQUENCE_BIT;private final static long DATACENTER_LEFT = SEQUENCE_BIT + MACHINE_BIT;private final static long TIMESTMP_LEFT = DATACENTER_LEFT + DATACENTER_BIT;private long datacenterId; //数据中心private long machineId; //机器标识private long sequence = 0L; //序列号private long lastStmp = -1L;//上一次时间戳public SnowFlake(long datacenterId, long machineId) {if (datacenterId > MAX_DATACENTER_NUM || datacenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenterId can't be greater than MAX_DATACENTER_NUM or less than 0");}if (machineId > MAX_MACHINE_NUM || machineId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("machineId can't be greater than MAX_MACHINE_NUM or less than 0");}this.datacenterId = datacenterId;this.machineId = machineId;}/*** 产生下一个ID** @return*/public synchronized long nextId() {long currStmp = getNewstmp();if (currStmp < lastStmp) {throw new RuntimeException("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id");}if (currStmp == lastStmp) {//相同毫秒内,序列号自增sequence = (sequence + 1) & MAX_SEQUENCE;//同一毫秒的序列数已经达到最大if (sequence == 0L) {currStmp = getNextMill();}} else {//不同毫秒内,序列号置为0sequence = 0L;}lastStmp = currStmp;return (currStmp - START_STMP) << TIMESTMP_LEFT //时间戳部分| datacenterId << DATACENTER_LEFT //数据中心部分| machineId << MACHINE_LEFT //机器标识部分| sequence; //序列号部分}private long getNextMill() {long mill = getNewstmp();while (mill <= lastStmp) {mill = getNewstmp();}return mill;}private long getNewstmp() {return System.currentTimeMillis();}public static void main(String[] args) {SnowFlake snowFlake = new SnowFlake(1<<4, 1<<4);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(snowFlake.nextId());}}}
Java UUID
UUID(Universally Unique IDentifier)是一个全局Id的规范,标准型式包含32个16进制数字,以连字号分为五段,形式为8-4-4-4-12的36个字符.示例如:78f236de-a628-4ea7-9382-b6030fcd8454. 典型实现如下:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();System.out.println(uuid.toString());}
优点是:本地生成,性能较好。缺点:不易于存储:UUID太长,16字节128位,通常以36长度的字符串表示,很多场景不适用,无顺序,不利于作DB主键。
数据库批量获取
创建一个sequence表,用name表示序列名称,一般用于某业务,用value表示当前值,程序获取到当前值后在内存里缓存一个区间。区间最大值为配置的步长。关键逻辑为:
1)程序初始化,先根据name查询value,如果不存在则初始化0.
2)调用nextRange时,查询当前value,然后计算一个新value=oldValue+step.
3) 最后update sequence表的value字段为newValue。
单数据库批量获取实现
准备数据库表
CREATE TABLE `sequence` (`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(64) NOT NULL,`value` bigint(20) NOT NULL,`gmt_modified` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,PRIMARY KEY (`id`),UNIQUE KEY `unique_name` (`name`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
实现代码如下
SequenceRange定义:
/*** 定义一个从数据库获取的序列区间* 该区间表示从数据库里获取一个起始值,然后加上一个步长** @author xiele.xl* @date 2020-05-19 18:15*/public class SequenceRange {/*** 最小值*/private final long min;/*** 区间最大值*/private final long max;/*** 区间记录值*/private AtomicLong value;/*** 是否到达最大值*/private volatile boolean over = false;public SequenceRange(long min, long max) {this.min = min;this.max = max;this.value = new AtomicLong(min);}/*** 获取递增值* @return*/public long getAndIncrement() {if (over) {return -1;}long current = value.getAndIncrement();if (current > this.max) {over = true;return -1;}return current;}/*** Getter method for property <tt>min</tt>.** @return property value of min*/public long getMin() {return min;}/*** Getter method for property <tt>max</tt>.** @return property value of max*/public long getMax() {return max;}/*** Getter method for property <tt>over</tt>.** @return property value of over*/public boolean isOver() {return over;}/*** Setter method for property <tt>over</tt>.** @param over value to be assigned to property over*/public void setOver(boolean over) {this.over = over;}}
序列服务实现:
/*** @author xiele.xl* @date 2020-05-19 17:20*/public class SimpleBatchSequence implements SequenceService {private static final String jdbc_url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_demo";private static final String user = "root";private static final String password = "Xiele";// 定义可见变量private volatile SequenceRange range;private static final String DEFAULT_SEQ_NAME = "default";private static final String SELECT_SQL = "select value from sequence where name = ?";private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();private DataSource dataSource ;public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {return dataSource.getConnection();}public void init() throws SQLException {DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();ds.setUrl(jdbc_url);ds.setUsername(user);ds.setPassword(password);ds.init();setDataSource(ds);initValue(DEFAULT_SEQ_NAME);}public void initValue(String name) throws SQLException {Connection connection = null;PreparedStatement pst = null;ResultSet rs = null;try {connection = getConnection();pst = connection.prepareStatement(SELECT_SQL);pst.setString(1, name);rs = pst.executeQuery();int result = 0;while (rs.next()) {result++;}// 不存在插入初始化值if (result == 0) {pst = connection.prepareStatement("insert sequence (`name`,`value`,`gmt_modified`) value (?,?,?)");pst.setString(1, name);pst.setLong(2, 0L);pst.setTimestamp(3, new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));final int effectedRow = pst.executeUpdate();Assert.state(effectedRow == 1, "insert init value failed");}} finally {closeDbResource(pst, rs, connection);}}/*** 获取一个序列区间** @param name* @return* @throws SQLException*/public SequenceRange nextRange(String name) {Connection connection = null;PreparedStatement pst = null;ResultSet rs = null;long oldValue = 0L;long newValue = 0L;// 先取出当前值try {connection = getConnection();pst = connection.prepareStatement(SELECT_SQL);pst.setString(1, name);rs = pst.executeQuery();rs.next();oldValue = rs.getLong("value");// 校验value的范围if (oldValue < 0) {throw new RuntimeException("not expected sequence value " + oldValue);}if (oldValue > Long.MAX_VALUE) {throw new RuntimeException("sequence value is exceeded max long value");}newValue = oldValue + getStep();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {closeDbResource(pst, rs, connection);}// 在更新新值到db里try {connection = getConnection();pst = connection.prepareStatement("update sequence set value = ?, gmt_modified = ? where name = ? and value = ?");pst.setLong(1, newValue);pst.setTimestamp(2, new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));pst.setString(3, name);pst.setLong(4, oldValue);Assert.state(pst.executeUpdate() == 1, "update failed");} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {closeDbResource(pst, rs, connection);}return new SequenceRange(oldValue + 1, newValue);}@Overridepublic long nextValue() {if (range == null) {lock.lock();try {if (range == null) {range = nextRange(DEFAULT_SEQ_NAME);System.err.println(String.format("初次获取Range,线程编号=%s,获取成功", Thread.currentThread().getName()));}} finally {lock.unlock();}}long value = range.getAndIncrement();// 表示本区间已取完,需要重新从db里拿一个起始值// 由于存在多个线程同时来拿,因此只有一个线程可以拿成功// 如果多个线程同时拿完了,并发进入==-1,再次加锁,获取下一段。if (value == -1) {lock.lock();try {for (; ; ) {if (range.isOver()) {range = nextRange(DEFAULT_SEQ_NAME);System.err.println(String.format("用完Range,再次获取Range,线程编号=%s,获取成功", Thread.currentThread().getName()));}value = range.getAndIncrement();if (value == -1) {continue;}break;}} finally {lock.unlock();}}return value;}/*** 默认步长,可配置** @return*/public long getStep() {return 1000;}/*** Setter method for property <tt>dataSource</tt>.** @param dataSource value to be assigned to property dataSource*/public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {this.dataSource = dataSource;}private void closeDbResource(Statement st, ResultSet rs, Connection conn) {closeStatement(st);closeResultSet(rs);closeConnection(conn);}private void closeStatement(Statement st) {if (st != null) {try {st.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}private void closeResultSet(ResultSet rs) {if (rs != null) {try {rs.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}private void closeConnection(Connection connection) {if (connection != null) {try {connection.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, InterruptedException {// 测试case1:单线程测试正确性SimpleBatchSequence sequence = new SimpleBatchSequence();sequence.init();//int count = 1001;//while (count-- > 0) {// System.out.println("nextVal: " + sequence.nextValue());//}// 多线程并发获取:测试并发性final int nThreads = 100;final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nThreads);CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(nThreads);for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i++) {executor.execute(() -> {int cnt = 10;while (cnt-- > 0) {System.out.println(String.format("currentThreadName:%s. nextVal: %d", Thread.currentThread().getName(),sequence.nextValue()));}latch.countDown();});}latch.await();System.out.println("Latch end");executor.shutdown();System.out.println("executor shutdown");System.out.println(executor);}}
多数据库实例的批量获取
实际工程应用中需要构建多数据源集群来保证高可用,可扩展的发号能力。
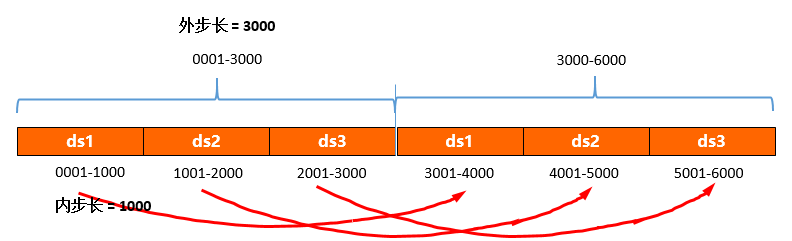
多数据源要解决的问题同样是各个数据源要确保生成互不重叠的ID序列,即将原来的自然数序列分成若干份互不相交的子等差数列。实现原理如下:把一个大批量ID段(外步长)按数据源分成多个小批量ID段(内步长),每个dataSource每次分配一个内步长的ID段,然后按照外步长跃进;通过这种错位交替分配策略,可以使不同dataSource产生的ID段互不相交。
在这种场景下,有多个db里有相同的Sequence表,涉及到内步长innerStep与外步长outStep。
实现代码思路
初始化阶段:
- 配置数据库实例数量
dsCount,内部长innerStep,默认为1000, 计算外步长outStep=dsCount * innerStep. - 自动调节sequence表:
如果sequence里无初始值,则分别初始化每个db实例里的初始值。例如:以内步长为1000,dsCount=2为例,则ds1库里Sequence表里的value序列应该为为0,1000.ds2库里Sequence表里的value序列应该为1000,2000
如果已经存在value,验证当前value是否需要重新需要校正一下。
获取Range阶段
随机从ds里拿取一个value,然后计算一下newValue=value+outStep,在update value为newValue.
单一数据库表自增
创建一个Sequence表,用MySQL的自增Id机制来生成序列。采用replace into 语法加select last_insert_id,由于两个sql预计不是原子的,需要包含在一个事物里。
Sequence表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `sequence` (`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` char(8) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`),UNIQUE KEY `uk_name` (`name`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
事物中获取Id的SQL脚本类似如下:
begin;replace into sequence(`name`) value ('default2');select last_insert_id();commit;
注:Mysql可配置自增起始值(@@auto_increment_increment)与步长(@@auto_increment_offset)来控制Id的生成策略,不同的业务可用不同的序列表来控制对应的Id序列。
JDBC实现代码
import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;/*** 单一数据库表自增Id实现序列服务* 实现思路为:事物中执行replace into && select last_insert_id()** @author xiele.xl* @date 2020-05-19 11:04*/public class SingleSequenceService implements SequenceService {private static final String jdbc_url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_demo";private static final String user = "root";private static final String password = "Xiele";private static ThreadLocal<Connection> localConn = new ThreadLocal<>();static {try {Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");}}public static Connection getConnection() {try {Connection conn = localConn.get();if (conn == null) {conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbc_url, user, password);localConn.set(conn);}return conn;} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("can not get connection, e=" + e);}}@Overridepublic long nextId() {Connection con = getConnection();try {// 设置事物为非自动提交,并开启事物con.setAutoCommit(false);final PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("replace into `sequence` (name) values ('default')");ps.executeUpdate();final ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery("select LAST_INSERT_ID()");rs.next();long nextId = rs.getLong(1);con.commit();return nextId;} catch (SQLException e) {try {con.rollback();} catch (SQLException ex) {}throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public static void main(String[] args) {SingleSequenceService uss = new SingleSequenceService();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(uss.nextId());}}}
其他方案
Redis原子命令实现递增
Redis提供一些自增原子命令,可以对KEY的值进行原子的增量操作,把返回值作为新的ID。Redis自增命令有:
INCRBY :给key对应的value加上1,value必须是数值类型。
INCR :为key对应的value加上指定的增量值。
HINCRBY :给HASH key中的field指定的域加上指定的增量值。
方案总结
- Redis方案和基于数据库的方案本质是一样的,只是发号源由数据库换成了Redis、事务由Redis的单线程机制来保证;也可以类似数据库批量方式,一次生成一批ID。
- Redis的ID是一个64 bit signed integer,容量可以充分保证。
- 可以保证ID的趋势递增,适用于主键字段
- 不足之处:Redis的AOF、RDB两种持久化方式都无法绝对保证数据不丢失,重启Redis有可能产生重复ID。
Zookeeper顺序节点实现递增
Zookeeper作为分布式协调服务框架,提供多种类型的ZNode来存储数据,其中顺序节点(Sequence Node)可以用来生成单调自增序列。它的机制如下:
在同一个路径中创建任意顺序节点(不需要同名),Zookeeper都会在节点名称中追加一个单调增长的计数值,格式是左补0的10位数字,如:”0000000001”、”0000000002”等
Zookeeper集群能保证多个客户端并发创建顺序节点时,只有一个会争抢成功,保证并发的一致性。
顺序节点可以是持久化的,需要应用自行删除;也可以是临时的,创建该节点的客户端断开后,ZK会自动删除。两种方式都不会影响序列的增长。
方案总结
- 操作简单,ID单调递增
- ID上限:顺序节点的序号生成是由其父节点维持的一个计数器生成的,计数器是一个4字节的signed整数,因此ID的最大值是2147483647,超出就会溢出。
- ZooKeeper只能顺序发号,无法批量创建ID,交易性能存在瓶颈,不适用于高并发的发号场景。

