Nginx配置文件
Nginx 服务启动时会读入配置文件,后续的行为则按照配置文件中的指令进行。Nginx 的配置文件是 纯文本文件,默认安装 Nginx 后,其配置文件均在 /usr/local/nginx/conf/ 目录下。其中,nginx.conf
为主配置文件。配置文件中以 # 开始的行,或者是前面有若干空格或者 TAB 键,然后再跟 # 的行,都被 认为是注释。这里只是了解主配置文件的结构。
Nginx 配置文件是以 block(块)形式组织,每个 block 都是以一个块名字和一对大括号 “{}” 表示 组成,block 分为几个层级,整个配置文件为 main 层级,即最大的层级;在 main 层级下可以有 event、http 、mail 等层级,而 http 中又会有 server block,server block中可以包含 location block。即块之间是可以嵌套的,内层块继承外层块。最基本的配置项语法格式是“配置项名 配置项值1配置项值2 配置项值3 … ”;
每个层级可以有自己的指令(Directive),例如 worker_processes 是一个main层级指令,它指定 Nginx 服务的 Worker 进程数量。有的指令只能在一个层级中配置,如worker_processes 只能存在于 main 中,而有的指令可以存在于多个层级,在这种情况下,子 block 会继承 父 block 的配置,同时如果 子block配置了与父block不同的指令,则会覆盖掉父 block 的配置。指令的格式是“指令名 参数1 参数2 … 参数N;”,注意参数间可用任意数量空格分隔,最后要加分号。
下图是 Nginx 配置文件通常结构图示。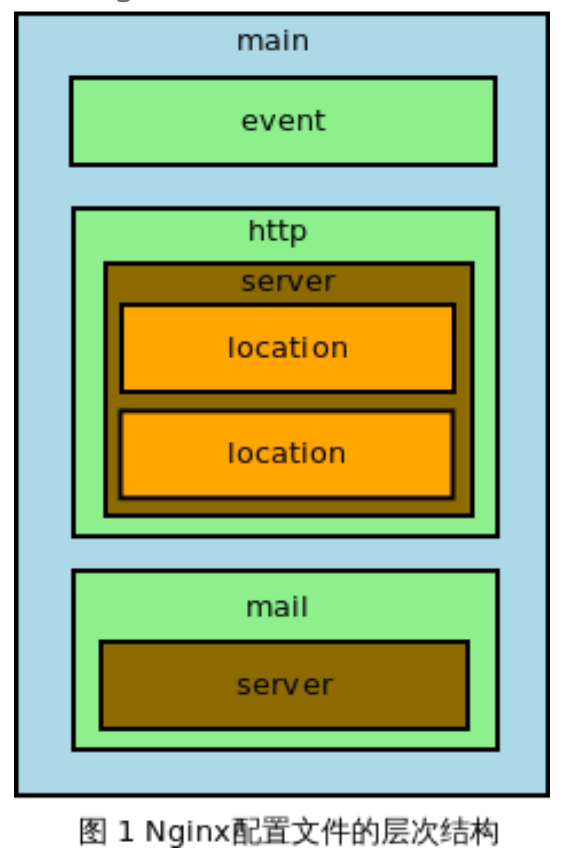
Nginx基本配置项
Nginx 服务运行时,需要加载几个核心模块和一个事件模块,这些模块运行时所支持的配置项称为基 本配置;基本配置项大概可分为以下四类:
- 用于调试、定位的配置项;
- 正常运行的必备配置项;
- 优化性能的配置项;
- 事件类配置项;
各个配置项的具体实现如下:用于调试、定位的配置项
#以守护进程 Nginx 运行方式#语法:daemon off | on;#默认:daemon on;#master / worker 工作方式#语法:master_process on | off;#默认:master_process on;#error 日志设置#路径 错误级别#语法:error_log /path/file level;#默认:error_log logs/error.log error;#其中/path/file是一个具体文件;level是日志的输出级别,其取值如下:#debug info notice warn error crit alert emerg#从左至右级别增大;若设定一个级别后,则在输出的日志文件中只输出级别大于或等于已设定的级别;
正常运行的配置项
#定义环境变量#语法:env VAR | VAR=VALUE; #VAR 是变量名,VALUE 是目录;#嵌入其他配置文件#语法:include /path/file;#include 配置项可以将其他配置文件嵌入到 Nginx 的 nginx.conf 文件中;#pid 的文件路径#语法:pid path/file;#默认:pid logs/nginx.pid;#保存 master 进程 ID 的 pid 文件存放路径;#Nginx worker 运行的用户及用户组#语法:user username [groupname]; #默认:user nobody nobody;#指定 Nginx worker进程可打开最大句柄个数#语法:worker_rlimit_nofile limit;#限制信号队列#语法:worker_rlimit_sigpending limit; #设置每个用户发给 Nginx 的信号队列大小,超出则丢弃;
优化性能配置项
#Nginx worker 进程的个数#语法:worker_process number; #默认:worker_process 1;#绑定 Nginx worker 进程到指定的 CPU 内核#语法:worker_cpu_affinity cpumask [cpumask...]#SSL 硬件加速 #语法:ssl_engine device;#系统调用 gettimeofday 的执行频率#语法:timer_resolution t;##Nginx worker优先级设置##语法: worker_priority nice (最高到最低: -20 ~ 19)#默认:worker_priority 0;
事件类配置项
#一般有以下几种配置:#1、是否打开accept锁# 语法格式:accept_mutex [on | off];#2、lock文件的路径#语法格式:lock_file path/file;#3、使用accept锁后到真正建立连接之间的延迟时间 # 语法格式:accept_mutex_delay Nms;#4、批量建立新连接#语法格式:multi_accept [on | off];#5、选择事件模型#语法格式:use [kqueue | rtisg | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll | eventport];#6、每个worker进行的最大连接数#语法格式:worker_connections number;
HTTP 核心模块的配置(http块)
虚拟主机与请求分发:server块
#监听端口#语法:listen address:port[default | default_server | [backlog=num | rcvbuf=size | sndbuf=size |# accept_filter | deferred | bind | ipv6only=[on | off] | ssl]];# 默认:listen 80;#说明:#default或default_server:将所在的server块作为web服务的默认server块;当请求无法匹配配置文件中的 所有主机名时,就会选择默认的虚拟主机;#backlog=num:表示 TCP 中backlog队列存放TCP新连接请求的大小,默认是-1,表示不予设置;#rcvbuf=size:设置监听句柄SO_RCVBUF的参数;#sndbuf=size:设置监听句柄SO_SNDBUF的参数;#accept_filter:设置accept过滤器,只对FreeBSD操作系统有用;#deferred:设置该参数后,若用户发起TCP连接请求,并且完成TCP三次握手,但是若用户没有发送数据, 则不会唤醒worker进程,直到发送数据;#bind:绑定当前端口 / 地址对,只有同时对一个端口监听多个地址时才会生效; # ssl:在当前端口建立的连接必须基于ssl协议;#主机名称#语法:server_name name[...]; 正则匹配规则:首先选择完全匹配(www.e.com),其次选择前缀批量(*.e.com),然后选择后缀匹配(www.e.*), 最后选择~^\.e\.com$#默认:server_name "";#server name 是使用散列表存储的, 每个散列桶占用内存大小#语法:server_names_hash_bucket_size size;#默认:server_names_hash_bucker_size 32|64|128;#location语法:location[= | ~ | ~* | ^~ | @] /uri/ {} #配置块范围:server#location尝试根据用户请求中的URI来匹配 /uri表达式,若匹配成功,则执行{}里面的配置来处理用户请求, 说明如下:#1. = 表示把URI当做字符串,以便于参数中的uri作完全匹配,如 location = / { 当请求为/,则使用该配置 }#2. ~ 表示匹配URI时是字母大小写敏感的#3. ~* 表示匹配URI时忽略字母大小写#4. ^~ 表示匹配URI时只需要其前半部分与uri参数匹配即可,如 location ^~ images {以image开头的请求都会匹配上}#5. @ 表示仅用于Nginx服务内部请求之间的重定向,带@符号的location不直接处理用户请求#6. 支持正则表达式, 如 location ~* \.(gif|jpg|png)$ { 匹配以gif,jpg,png结尾的请求 }#7. location是有顺序的,当以个请求能匹配多个location时,则被第一个location处理#上述规则语义为:如果匹配,则执行。若需匹配所有的http请求,参数部分直接使用/, 如:location / {#匹配所有请求}location /path {#匹配path开头的请求}#文件路径定义#1. 以root设置资源路径#语法: root path#配重块:http server location if#定义资源文件相对于Http请求的根目录, 如:请求为/download/test.htm, 返回html/test.htmlocation /download/ {root html;}#以alias方式设置资源路径#语法:alias path; #配置块范围:location#访问主页#语法:index file...;#默认:index index.html;#配置块范围:http、server、location#根据HTTP返回码重定向页面#语法:error_page code [code...] [= | =answer-code] uri | @named_location;#配置块范围:server、http、location、if#对应某个请求返回错误码时,如果匹配error_page中设置的code,则重定向到新的URI中,如:error_page 404 404.htmlerror_page 502 503 504 50x.htmlerror_403 http://err.example.com/error.htmlerror_page 404 @fetch#返回重定向后实际处理的真实结果: error_page 404 /404.html#请求返回的错误code想让另一个location处理, 如返回404的请求会被反向代理到后端处理:location / {error_page 404 @fallback}location @fallback {proxy_pass http://backend;}#try_files#语法:try_files path1 [path2] uri;#配置块范围:server、location
内存及资源分配与网络连接设置
#HTTP 包体只存储在磁盘文件中#语法:client_body_in_file_only on | clean | off;#默认:client_body_in_file_only off;#配置块范围:http、server、location#存储 HTTP 头部的内存buffer大小#语法:client_header_buffer_size size;#默认:client_header_buffer_size 1k; #配置块范围:http、server#存储超大 HTTP 头部的内存buffer大小#语法:large_client_header_buffer_size#默认:large_client_header_buffer_size#配置块范围:http、server#存储 HTTP 包体的内存buffer大小#语法:client_body_buffer_size size;#默认:client_body_buffer_size 8k/16k;#配置块范围:http、server、location#HTTP 包体的临时存放目录#语法:client_body_temp_path dir-path#默认:client_body_temp_path client_body_temp;#配置块范围:http、server、location#存储 TCP 成功建立连接的内存池大小#语法:connection_pool_size size;#默认:connection_pool_size 256;#配置块范围:http、server#存储 TCP 请求连接的内存池大小#语法:request_pool_size size;#默认:request_pool_size 4k; #配置块范围:http、server#读取 HTTP 头部的超时时间#语法:client_header_timeout time;#默认:client_header_timeout 60;#配置块范围:http、server、location#读取 HTTP 包体的超时时间#语法:client_body_timeout time; # 默认:client_body_timeout 60;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# 发送响应的超时时间# 语法:send_timeout time;# 默认:send_timeout 60;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# TCP 连接的超时重置# 语法:reset_timeout_connection on | off; # 默认:reset_timeout_connection off;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# 控制关闭 TCP 连接的方式# 语法:lingering_close off | on | always;# 默认:lingering_close on;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# always 表示关闭连接之前无条件处理连接上所有用户数据; # off 表示不处理;on 一般会处理;# lingering_time# 语法:lingering_time time;# 默认:lingering_time 30s;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# lingering_timeout# 语法:lingering_timeout time;# 默认:lingering_time 5s;# 配置块范围:http、server、location
MIME 类型设置
# MIME type 与文件扩展的映射# 语法:type{...}# 配置块范围:http、server、location# 多个扩展名可映射到同一个 MIME type# 默认 MIME type# 语法:default_type MIME-type;# 默认:default_type text/plain;# 配置块范围:http、server、location
客户端请求相关
# 按 HTTP 方法名限制用户请求# 语法:limit_except method...{...}# 配置块:location# method 的取值如下:# GET、HEAD、POST、PUT、DELETE、MKCOL、COPY、MOVE、OPTIONS、 # PROPFIND、PROPPATCH、LOCK、UNLOCK、PATCH# HTTP 请求包体的最大值# 语法:client_max_body_size size; # 默认:client_max_body_size 1m;# 配置块范围:http、server、location# 对请求限制速度# 语法:limit_rate speed;# 默认:limit_rate 0;# 配置块范围:http、server、location、if # 0 表示不限速# 忽略不合法的 HTTP 头部# 语法:ignore_invalid_headers on | off; # 默认:ignore_invalid_headers on;# 配置块:http、server# HTTP 头部是否允许下划线# 语法:underscores_in_headers on | off; # 默认:underscores_in_headers off;# 配置块:http、server# If_Modified_Since 头部的处理策略# 语法:if_modified_since [off | exact | before]# 默认:if_modified_since exact;# 是否合并相邻的“/”# 语法:merge_slashes on | off; # 默认:merge_slashes on;# 配置块:http、server、location# DNS解析的超时时间# 语法:resolver_timeout time; # 默认:resolver_timeout 30s; # 配置块:http、server、location# 返回错误页面是否在server中注明Nginx版本 # 语法:server_tokens on | off;# 默认:server_tokens on;# 配置块:http、server、location
配置示例(沙箱配置)
user admin;#worker_processes auto;#worker_cpu_affinity auto;worker_rlimit_nofile 100000;error_log "pipe:/opt/taobao/install/cronolog/sbin/cronolog /home/admin/cai/logs/cronolog/%Y/%m/%Y-%m-%d-error_log" warn;pid /home/admin/cai/logs/nginx-proxy.pid;events {use epoll;worker_connections 20480;}http {include mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;root /home/admin/cai/htdocs;sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;server_tokens off;keepalive_timeout 0;client_header_timeout 1m;send_timeout 1m;client_max_body_size 3m;client_body_timeout 3600s;#error_page 400 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 403 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 404 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 405 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 408 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 410 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 411 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 412 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 413 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 414 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 415 http://err.taobao.com/error1.html;#error_page 500 http://err.taobao.com/error2.html;#error_page 501 http://err.taobao.com/error2.html;#error_page 502 http://err.taobao.com/error2.html;#error_page 503 http://err.taobao.com/error2.html;#error_page 506 http://err.taobao.com/error2.html;index index.html index.htm;log_format proxyformat "$remote_addr $request_time_usec $http_x_readtime [$time_local] \"$request_method http://$host$request_uri\" $status $body_bytes_sent \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" \"$md5_encode_cookie_unb\" \"$md5_encode_$cookie_cookie2\" \"$eagleeye_traceid\"";# if want to do A/B test, please set the log format to abtest, and umcomment the include line#include gray_conf/resource/gray-log-format.conf;access_log "pipe:/opt/taobao/install/cronolog/sbin/cronolog /home/admin/cai/logs/cronolog/%Y/%m/%Y-%m-%d-taobao-access_log" proxyformat;log_not_found off;gzip on;gzip_http_version 1.0;gzip_comp_level 6;gzip_min_length 1024;gzip_proxied any;gzip_vary on;gzip_disable msie6;gzip_buffers 96 8k;gzip_types text/xml text/plain text/css application/javascript application/x-javascript application/rss+xml application/json;server {listen 80;server_name alink.smart.tbsandbox.com;location / {proxy_pass http://100.69.196.80:7001;}location /api {proxy_pass http://alink_api_vip;}location /login/oauth2 {proxy_pass http://11.163.209.52:80;}}upstream alink_api_vip {server 11.162.252.212:80;server 11.163.209.52:80;}server {listen 443;ssl on;server_name alink.smart.tbsandbox.com;ssl_certificate /home/admin/cai/conf/ssl/alink.smart.tbsandbox.com.cer;ssl_certificate_key /home/admin/cai/conf/ssl/alink.smart.tbsandbox.com.key;ssl_session_timeout 5m;ssl_session_cache shared:NXSSL:256M;log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /home/admin/logs/nginx/access.log main;ssl_protocols SSLv3 TLSv1;ssl_ciphers ALL:!aNULL:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:!LOW:!SSLv2:+EXP:!eNULL:!MD5:!EXPORT40;location / {proxy_pass http://100.69.196.80:7001;}location /api {proxy_pass http://alink_api_vip;}}

