神经网络通常依赖反向传播求梯度来更新网络参数,求梯度过程通常是一件非常复杂而容易出错的事情。而深度学习框架可以帮助我们自动地完成这种求梯度运算。
Pytorch一般通过反向传播 backward 方法实现这种求梯度计算。该方法求得的梯度将存在对应自变量张量的grad属性下。除此之外,也能够调用torch.autograd.grad 函数来实现求梯度计算。
这就是Pytorch的自动微分机制。
利用backward方法求导数
backward 方法通常在一个标量张量上调用,该方法求得的梯度将存在对应自变量张量的grad属性下;如果调用的张量非标量,则要传入一个和它同形状的gradient参数张量,相当于用该gradient参数张量与调用张量作向量点乘,得到的标量结果再反向传播。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44179269/article/details/124573992
- 标量的反向传播 ```python import numpy as np import torch
f(x) = ax**2 + bx + c的导数
x = torch.tensor(0.0,requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导 a = torch.tensor(1.0) b = torch.tensor(-2.0) c = torch.tensor(1.0) y = atorch.pow(x,2) + bx + c
y.backward() dy_dx = x.grad print(dy_dx)
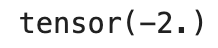2. 非标量的反向传播```pythonimport numpy as npimport torch# f(x) = a*x**2 + b*x + cx = torch.tensor([[0.0,0.0],[1.0,2.0]],requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导a = torch.tensor(1.0)b = torch.tensor(-2.0)c = torch.tensor(1.0)y = a*torch.pow(x,2) + b*x + cgradient = torch.tensor([[1.0,1.0],[1.0,1.0]])print("x:\n",x)print("y:\n",y)y.backward(gradient = gradient)x_grad = x.gradprint("x_grad:\n",x_grad)

- 非标量的反向传播可以用标量的反向传播实现 ```python import numpy as np import torch
f(x) = ax**2 + bx + c
x = torch.tensor([[0.0,0.0],[1.0,2.0]],requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导 a = torch.tensor(1.0) b = torch.tensor(-2.0) c = torch.tensor(1.0) y = atorch.pow(x,2) + bx + c print(y.shape)
gradient = torch.tensor([[1.0,1.0],[1.0,1.0]]) z = torch.sum(y*gradient) #这里是对应位置元素相乘,不是矩阵乘法!
print(“x:”,x) print(“y:”,y) z.backward() x_grad = x.grad print(“x_grad:\n”,x_grad)
也可以这样写
y.sum().backward print(x.grad)

---
<a name="JomyB"></a>
## 利用autograd.grad方法求导数
```python
import numpy as np
import torch
# f(x) = a*x**2 + b*x + c的导数
x = torch.tensor(1.0,requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导
a = torch.tensor(1.0)
b = torch.tensor(-2.0)
c = torch.tensor(1.0)
y = a*torch.pow(x,2) + b*x + c
# create_graph 设置为 True 将允许创建更高阶的导数
dy_dx = torch.autograd.grad(y,x,create_graph=True)[0]
print(dy_dx.data)
# 求二阶导数
dy2_dx2 = torch.autograd.grad(dy_dx,x)[0]
print(dy2_dx2.data)

import numpy as np
import torch
x1 = torch.tensor(1.0,requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导
x2 = torch.tensor(2.0,requires_grad = True)
y1 = x1*x2
y2 = x1+x2
# 允许同时对多个自变量求导数
(dy1_dx1,dy1_dx2) = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=y1,inputs = [x1,x2],retain_graph = True)
print(dy1_dx1,dy1_dx2)
# 如果有多个因变量,相当于把多个因变量的梯度结果求和
(dy12_dx1,dy12_dx2) = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=[y1,y2],inputs = [x1,x2])
print(dy12_dx1,dy12_dx2)

利用自动微分和优化器求最小值
import numpy as np
import torch
# f(x) = a*x**2 + b*x + c的最小值
x = torch.tensor(0.0,requires_grad = True) # x需要被求导
a = torch.tensor(1.0)
b = torch.tensor(-2.0)
c = torch.tensor(1.0)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=[x],lr = 0.01)
def f(x):
result = a*torch.pow(x,2) + b*x + c
return(result)
for i in range(500):
optimizer.zero_grad()
y = f(x)
y.backward()
if i%50==0:
print(x.grad)
optimizer.step()
print("y=",f(x).data,";","x=",x.data)


