Title
Guided Image Filtering
Summary
作者基于bilateral filter提出guided filter,更好地在保护边缘的同时平滑图像,可用于降噪,上色,消色,去雾,HDR压缩等多方面
Research Objective
提出一个更好的保护边缘的平滑方法
Background and Problems
降噪或提取图像有效结构有广泛应用。一些explicit linear translation-invariant(LTI) filters(Gaussian filter, Laplacian filter, and Sobel filter)被广泛应用在模糊/锐化,边缘检测,特征提取,high dynamic range(HDR)压缩,图像拼接和图像消光。
潜在的问题:
- 滤波时引入给定的引导图像的信息,比如亮度通道有一致的边缘,保护细的结构如头发信息。
- 方法一:优化二次函数,基于引导图像对未知输出加以约束,通过求解引导图的稀疏矩阵获得解。这种方法被广泛用在着色,消光,除雾,多尺度分解。效果不错,计算时间长。
- 方法二:基于引导图构建滤波器。bilateral filter应该是其中最流行的。它的输出是周围像素的加权平均,而权重来自引导图像中强度、颜色相似度。这种卷积可以平滑小波动,保留边缘,但可能造成伪影,无法快速实现。当时有很多加速这个方法的研究。
- 方法一和方法二高度相关,方法一是隐式滤波,方法二是显式滤波,通常显式滤波会比基于优化的方法更简单更快。
Method(s)
- 新的explicit image filter,称之为guided filter。卷积的输出是引导图的线性变化参数。这种卷积和bilateral filter一样能保护边缘地平滑,但不会受到梯度反转伪影的影响。同时它也和matting laplacian matrix相关。
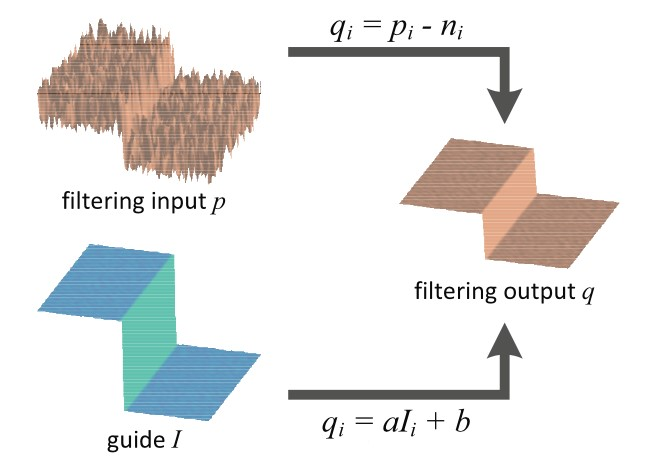
- 引导滤波的重要假设是输出图和引导图在滤波窗口上存在局部线性关系。
- 输入图和输出图的差值应视为噪声
- 优化目标是使噪声最小,用最小二乘最优化方法(岭回归)求解线性关系的参数
- 对多个卷积窗口的输出图结果求均值(推导时是这么推的,实际应用的时候是整图操作)

参考:
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43194305/article/details/88959183
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/36813673
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/161666126 这篇写得特别好,也提到了fast版本,推荐重点看这个
Evaluation
作者做了些实验,列举了大量图片的细节,证明guided filter在细节增强、HDR压缩、降噪、消光/引导羽毛、去雾、上采样、上色等方面做的非常好。
Conclusion
- guided filter能在平滑时保护边缘,计算有效快速(O(N))
- guided filter有超越降噪的多方面应用,
- guided filter有所有explicit filter的共有限制:会在边缘有光晕,因为滤波器无法区分哪些要平滑哪些要保护,但是瑕不掩瑜,这仍然是个好方法
Reference
- Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. ICCV (1998)
- Non-linear gaussian filters performing edge preserving diffusion.(1995)
- Digital photography with flash and no-flash image pairs(2004) joint bilateral filter
Code
提供两个pytorch版本的,原始代码来自:https://github.com/wuhuikai/DeepGuidedFilter
torch 基础版本
import torchfrom torch import nnimport cv2import numpy as npfrom torch.autograd import Variabledef cv2tensor(x, is01=False):if is01:x = x / 255. # x: [0, 1]else:x = x / 255. * 2 - 1 # x: [-1, 1]x = torch.from_numpy(x.transpose((2, 0, 1))).float().unsqueeze(0)return xdef save_tensor_img(tensor, save_path, is01=False):img_numpy = tensor.detach().cpu().numpy().transpose((1,2,0))if is01:img_numpy = img_numpy * 255.0else:img_numpy = (img_numpy * 0.5 + 0.5) * 255.0img_numpy = np.clip(img_numpy, 0., 255.)img_output = img_numpy.astype(np.uint8)img_output = cv2.cvtColor(img_output, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)#img_output = cv2.resize(img_output, (512, 512))cv2.imwrite(save_path, img_output)def diff_x(input, r):assert input.dim() == 4left = input[:, :, r:2 * r + 1]middle = input[:, :, 2 * r + 1: ] - input[:, :, :-2 * r - 1]right = input[:, :, -1: ] - input[:, :, -2 * r - 1: -r - 1]output = torch.cat([left, middle, right], dim=2)return outputdef diff_y(input, r):assert input.dim() == 4left = input[:, :, :, r:2 * r + 1]middle = input[:, :, :, 2 * r + 1: ] - input[:, :, :, :-2 * r - 1]right = input[:, :, :, -1: ] - input[:, :, :, -2 * r - 1: -r - 1]output = torch.cat([left, middle, right], dim=3)return outputclass BoxFilter(nn.Module):def __init__(self, r):super(BoxFilter, self).__init__()self.r = rdef forward(self, x):assert x.dim() == 4# numpy.cumsum给定轴上的和return diff_y(diff_x(x.cumsum(dim=2), self.r).cumsum(dim=3), self.r)class GuidedFilter(nn.Module):def __init__(self, r, eps=1e-8):super(GuidedFilter, self).__init__()self.r = rself.eps = epsself.boxfilter = BoxFilter(r)def forward(self, x, y):n_x, c_x, h_x, w_x = x.size()n_y, c_y, h_y, w_y = y.size()assert n_x == n_yassert c_x == 1 or c_x == c_yassert h_x == h_y and w_x == w_yassert h_x > 2 * self.r + 1 and w_x > 2 * self.r + 1# NN = self.boxfilter(Variable(x.data.new().resize_((1, 1, h_x, w_x)).fill_(1.0)))# mean_xmean_x = self.boxfilter(x) / N# mean_ymean_y = self.boxfilter(y) / N# cov_xycov_xy = self.boxfilter(x * y) / N - mean_x * mean_y# var_xvar_x = self.boxfilter(x * x) / N - mean_x * mean_x# 这里是求A和b的重点# AA = cov_xy / (var_x + self.eps)# bb = mean_y - A * mean_x# mean_A; mean_bmean_A = self.boxfilter(A) / Nmean_b = self.boxfilter(b) / Nreturn mean_A * x + mean_b
torch 优化版本
把好多除法给删除了,把N当作权重,只在初始化的时候算一次(这样的话需要指定好宽高)
class GuidedFilter2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, r, eps=1e-8, height=512, width=512):
super(GuidedFilter2, self).__init__()
self.r = r
self.eps = eps
self.boxfilter = BoxFilter(r)
self.N = 1/self.boxfilter(torch.ones((1, 3, height, width)))
def forward(self, x, y):
n_x, c_x, h_x, w_x = x.size()
n_y, c_y, h_y, w_y = y.size()
assert n_x == n_y
assert c_x == 1 or c_x == c_y
assert h_x == h_y and w_x == w_y
assert h_x > 2 * self.r + 1 and w_x > 2 * self.r + 1
# mean_x
self.N = self.N.to(x.device)
mean_x = self.boxfilter(x) * self.N
# mean_y
mean_y = self.boxfilter(y) * self.N
# cov_xy
cov_xy = self.boxfilter(x * y) * self.N - mean_x * mean_y
# var_x
var_x = self.boxfilter(x * x) * self.N - mean_x * mean_x
# 这里是求A和b的重点
# A
A = cov_xy / (var_x + self.eps)
# b
b = mean_y - A * mean_x
# mean_A; mean_b
mean_A = self.boxfilter(A) * self.N
mean_b = self.boxfilter(b) * self.N
out = mean_A * x + mean_b
return out
输入同一张图的torch优化版本
我将guided filter当作保边滤波使用,引导图也是输入图,因此进一步做了相应的改进
class GuidedFilter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, r, eps=1e-8, height=512, width=512):
super(GuidedFilter, self).__init__()
self.r = r
self.eps = eps
self.boxfilter = BoxFilter(r)
self.N = 1/self.boxfilter(torch.ones((1, 3, height, width)))
def forward(self, x):
n_x, c_x, h_x, w_x = x.size()
assert h_x > 2 * self.r + 1 and w_x > 2 * self.r + 1
# mean_x
self.N = self.N.to(x.device)
mean_x = self.boxfilter(x) * self.N
# cov_xy,也即var_x
cov_xy = self.boxfilter(x * x) * self.N - mean_x * mean_x
# 这里是求A和b的重点
# A
A = cov_xy / (cov_xy + self.eps)
# b
b = (1.0 - A) * mean_x
# mean_A; mean_b
mean_A = self.boxfilter(A) * self.N
mean_b = self.boxfilter(b) * self.N
out = mean_A * x + mean_b
return out

