1.前言
路哥要学习SpringSecurity,我就跟随他的脚步重温一下SpringSecurity。
这次要学习看SpringSecurity的文档学习。。。。
2.文档整体浏览

文档的整体逻辑:
①介绍SpringSecurity框架
②使用SpringSecurity框架的环境要求
③SpringSecurity5.4的新增功能
④如何使用SpringSecurity
⑤各个模块的依赖介绍
⑥使用实例:Servlet 和 Reactive 两种应用使用样例
重点章节:
3.Getting Spring Security
文档中介绍了各种引入方式,我们关注的就是SpirngBoot如何引入SpringSecurity框架。
引入方式:
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
完了,这一节最有用的信息就是这个依赖了。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
4.Servlet Application Sample
这一章中介绍的就是SpringSecurity如何应用于Servlet程序中,SpringSecurity集成到Servlet程序中的方式就是使用过滤器的方式。
4.1HelloWorld
1.引入依赖包
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency>
2.编写一个index.html页面放在如下目录下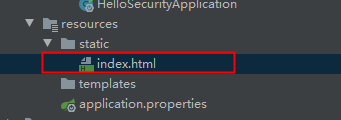
3.启动程序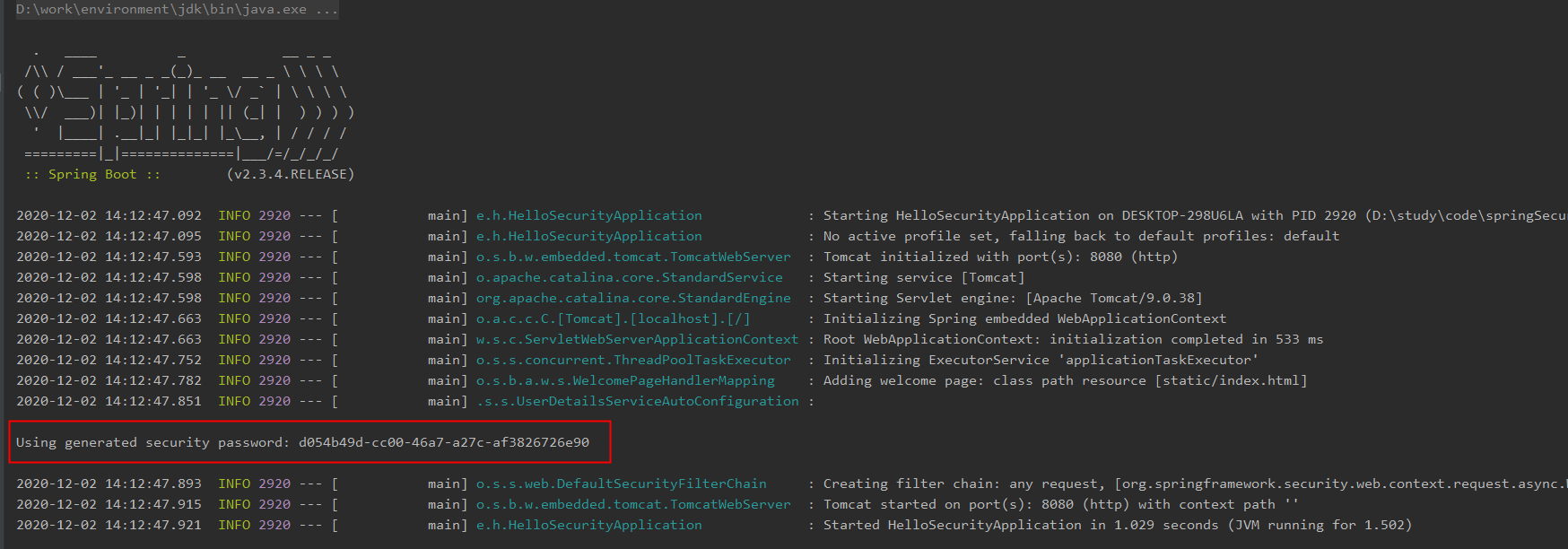
4.浏览器输入localhost:8080,输入用户名,输入控制台上的密码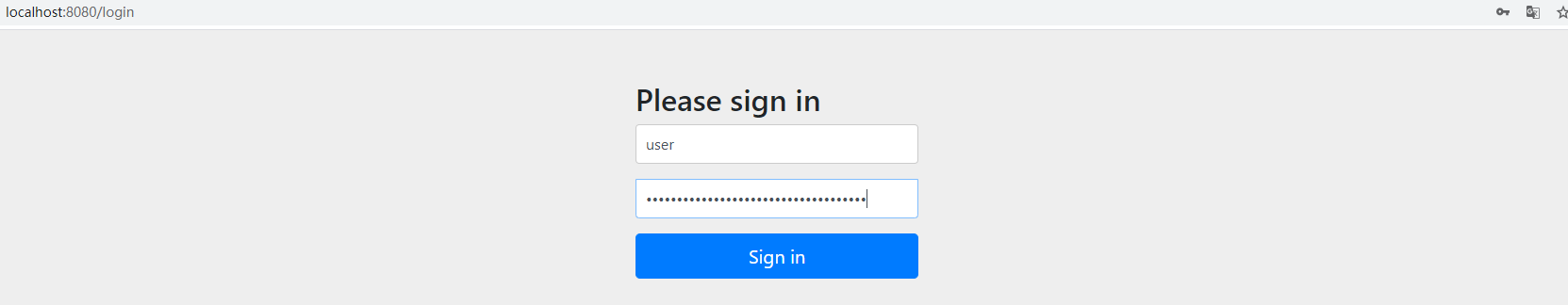
5.点击Sign in成功登录到自己index.html页面
4.2SpringBoot帮我们配置了啥?
引入SpringSecurity后,SpringBoot会帮我自动配置,于是,我们可以快速的使用SpringSecurity,那么,SpringBoot帮我们配置了哪些东西呢?
1.SpringBoot将一个filter注册到Spring的Bean容器中,名字为:springSecurityFilterChain 他负责的就是所有安全相关的内容:保护我们的程序的各个接口、校验用户的账号和密码、跳转登录页等。
2.SpringBoot创建了一个UserDetailsService的Bean,这个Bean拥有一个用户名为 :user ,密码为随机生成的用户,且密码会打印在控制台上。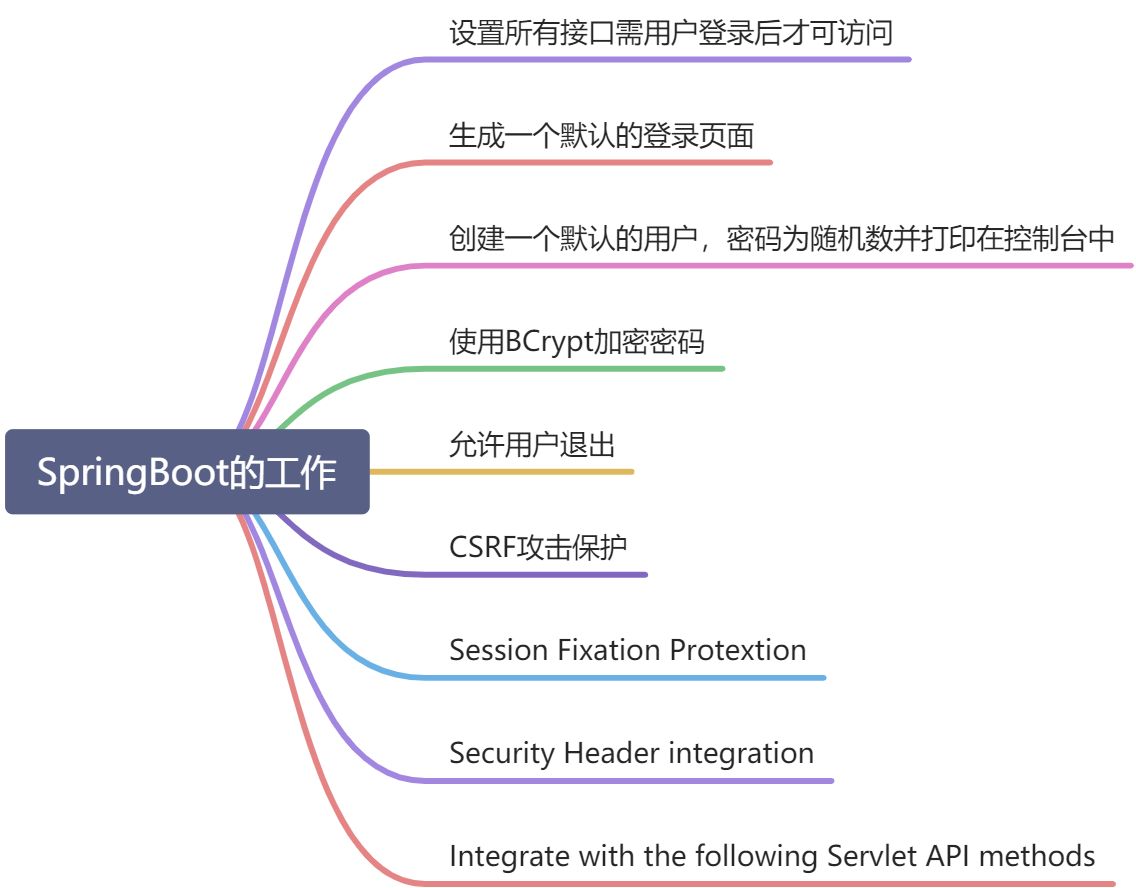
4.3SpringSecurity的宏观设计
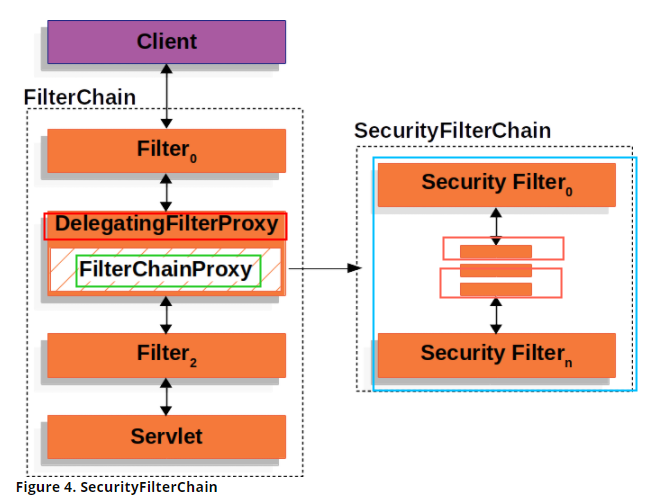
4.3.1过滤器代理 DelegatingFilterProxy
这个类的作用是注册为Servlet容器的过滤器,将具体的工作委托给其他的Spring容器Bean。这个Bean的名称就叫做:FilterChainProxy 它决定使用哪个 SecurityFilterChain (包含一堆具体的过滤器)。使用FilterChaninProxy的好处是: 可以在这个类中打断点调试。可以执行一些必须执行的操作。可以选择使用那一个 SecurityFilterChain(一组Filter)
4.3.2关系图
4.4各个过滤器的工作原理
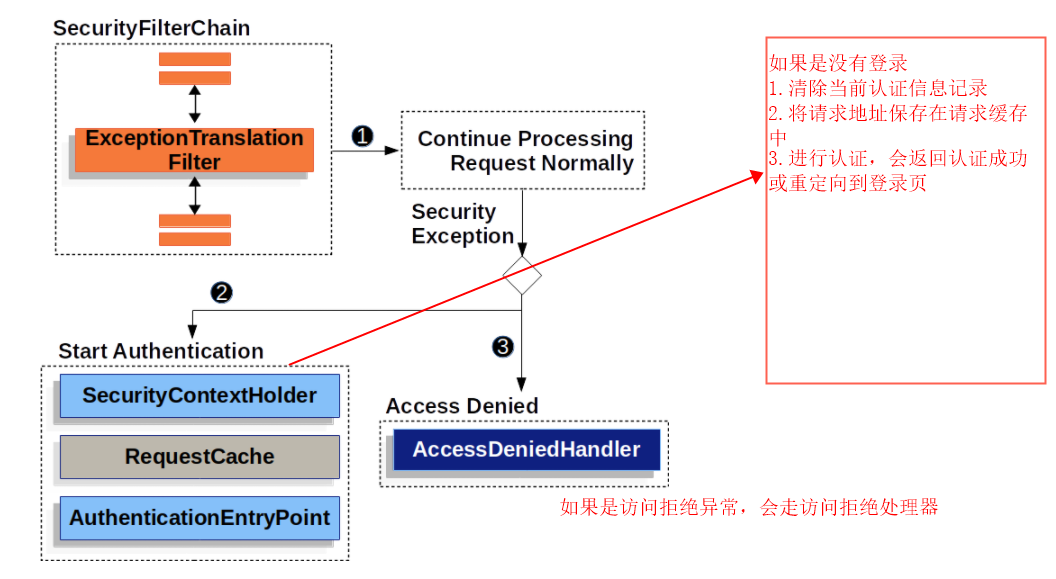
4.4.1ExceptionTranslationFilter 过滤器
权限异常或者认证异常会返回响应。
5.SpringSecurity的认证流程
| 修改记录 | 日期 |
|---|---|
| 第一次修改 | 2021/11/13 |
Spring提供了全面的支持。身份认证就是验证访问者是谁,通常的方式是通过 用户名和密码的方式。认证结束后就可以进行授权。
5.1PasswordStorage 密码存储
用户名密码方式的身份验证方式,一个问题就是,系统如何保存用户设置的密码。使用明文的方式。如果数据库数据被盗取,密码将被泄露。
解决方式:将密码加密后存储在数据库中,这样即使数据被盗取,这样侵略者就算得到了数据,也无法得到密码。
在SpringSecurity框架中,PasswordEncoder接口被用作进行密码的转换以至于密码可以安全的存储。PasswordEncoder对密码的转换时单向的,只能加密不可解密。因此,用户输入的密码会通过PasswordEncoder再次加密后与数据库中加密后的密码比较。
5.1.1密码存储方式的变化
①使用明文存储在数据库中
②使用hash散列 SHA-256 方式加密密码,用户输入明文后也散列后比较数据库中的值。这样通过一个叫RainBow table 可以破解
③引入盐值,用户设置的密码+salt(随机字符)之后加密后存入密码。同时保存盐值,登录时,用户输入密码,系统将密码拼接盐值后加密,并与数据库中的密码进行比较。
如今的计算机运行速度快,这种SHA-256的加密手段已经很容易破解了
④现在使用自适应-单向函数,SpringSecurity提供了 bcrypt、等
5.1.2密码加密器代表
在SpringSecurity5.0之前的版本,默认的密码加密器是NoOpPasswordEncoder,就是不加密的。但是在5.0版本时,我们期待的是默认加密方式就是BCrypt这种方式。但是我们忽略了现实情况。如果贸然的改动后,许多项目的用户密码信息都需要迁移。于是,SpringSecurity推荐使用DelegatingPasswordEncoder。在SpringBoot使用SpringSecurity框架时,这个类被默认创建了 。
这个类其实是多个密码加密器的一个门面、代理。内部初始化多个加密方式,通过Map的方式保存起来。然后根据密码上的id,来判断使用哪种加密器。
其密码加密结果如下:
{bcrypt}$2a$10$dXJ3SW6G7P50lGmMkkmwe.20cQQubK3.HZWzG3YB1tlRy.fqvM/BG{noop}password{pbkdf2}5d923b44a6d129f3ddf3e3c8d29412723dcbde72445e8ef6bf3b508fbf17fa4ed4d6b99ca763d8dc{scrypt}$e0801$8bWJaSu2IKSn9Z9kM+TPXfOc/9bdYSrN1oD9qfVThWEwdRTnO7re7Ei+fUZRJ68k9lTyuTeUp4of4g24hHnazw==$OAOec05+bXxvuu/1qZ6NUR+xQYvYv7BeL1QxwRpY5Pc={sha256}97cde38028ad898ebc02e690819fa220e88c62e0699403e94fff291cfffaf8410849f27605abcbc0
默认的如果进行密码匹配时,不指定 {加密方式id} 会报异常,解决方式可以通过DelegatingPasswordEncoder.setDefaultPasswordEncoderForMatches(PasswordEncoder) 设置默认的加密器。
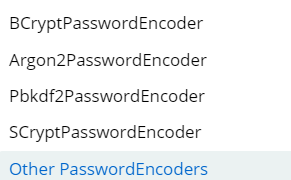
5.1.3加密器类别有哪些
5.1.4SpringBoot如何配置密码加密器
默认的是使用 DelegatingPasswordEncoder ,如果想自定义使用其他的加密器可以通过以下方式:
@Beanpublic static NoOpPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();}
5.2认证有关的组件
①SecurityContextHolder:记录着所有登录用户的认证信息
②SecurityContext:记录当前访问者的登录信息
③Authentication:是一个用于封装用户认证输入信息的类作为AuthenticationManager的入参,也可能是从SecurityContext中取得的用户认证信息
④GrantedAuthority:是赋予登录人的角色功能信息,被复制到 Authentication的principle中
⑤AuthenticationManager :定义SpringSecurity如何认证一套接口
⑥ProviderManager:是AuthenticationManager的一种实现方式
⑦AuthenticationProvider :被ProviderManager使用,去执行具体的一种认证方式
⑧AuthenticationEntryPoint :用于发送验证成功的响应和验证失败重定向到登录页面的操作
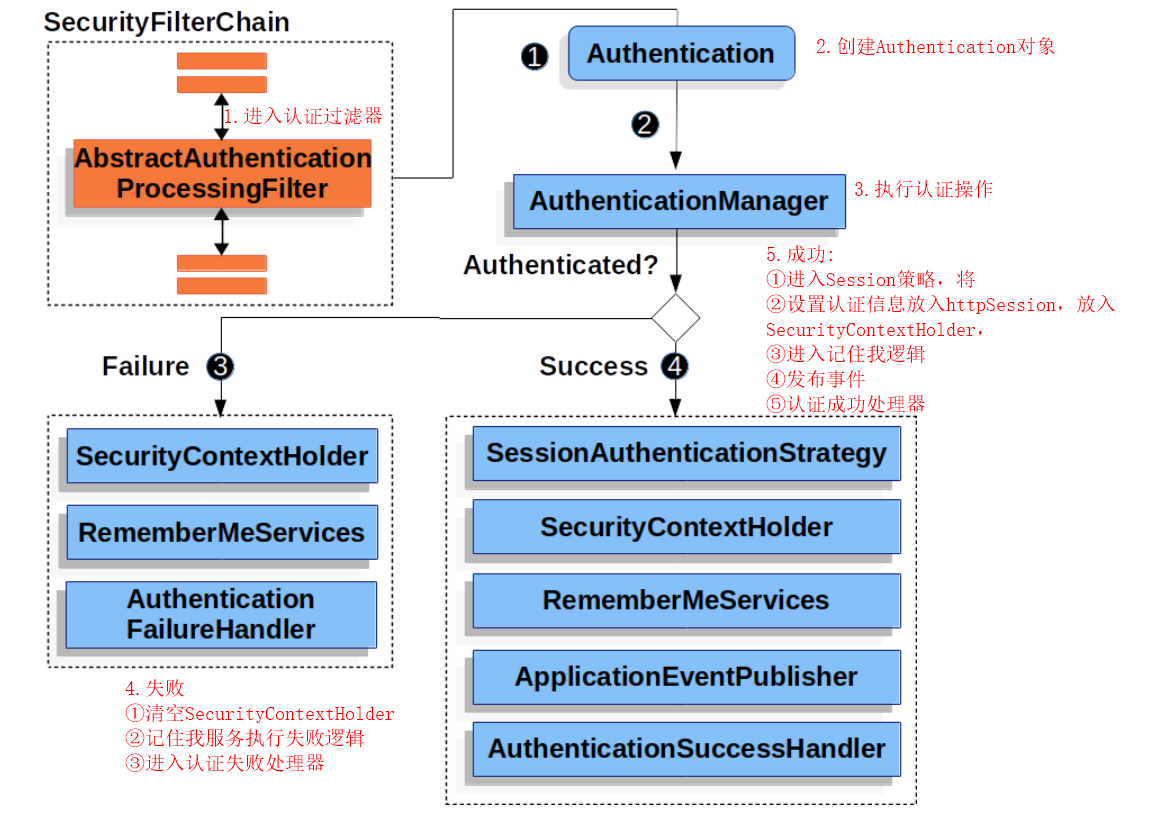
⑨AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter:是一个过滤器,控制整个认证流程,规定以上组件如何协同工作共同完成认证工作。
5.2.1SecurityContextHolder

SecurityContext记录这SecurityContext,使用ThreadLocal存储用户认证信息。可以切换存储模式。
5.2.2 SecurityContext
可以从SecurityContextHolder中获取里面包含Authentication信息
5.2.3Authentication
在未认证前,作为用户认证数据的封装参数,可以调用 isAuthenticated()方法校验是否被认证
包含:
principle:用户的身份信息,用户密码认证方式通常是userDetail
credentials:通常是密码,在认证结束后通常清除
authorities:通常是权限、角色。
5.2.4GrantedAuthority
可以获得通过Authentication的 getAuthorities() 方法 ,用户密码登录方式通常是在userDetailService中国被授予的
5.2.5AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManger规划如何执行认证,返回的Authentication被设置到SecurityContextHolder中。也就是说你可以直接设置一个Authentication到SecurityContextHolder。这样也代表完成了认证。
5.2.6ProviderManager
是AuthenticationManger的一种常见实现方式。它将认证任务委托给其手下的AuthenticationProvider们,每一个手下都可以回答认证是否成功,或者说不能做。如果没手下能够认证则会报一个 ProviderNotFoundException 也是 AuthenticationException的一种(这样就会到4.4.1的一个过滤器中了)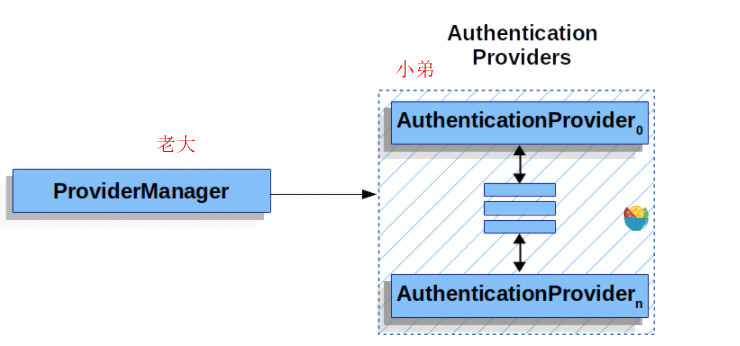
可以指定父 AuthenticationManager。用于处理无法处理认证任务的情况
5.2.7AuthenticationProvider
主要有DaoAuthenticationProvider 和 JwtAuthenticationProvider
5.2.8 AuthenticationEntryPoint
5.2.9AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
5.3用户名密码认证流程
5.3.1表单登录流程
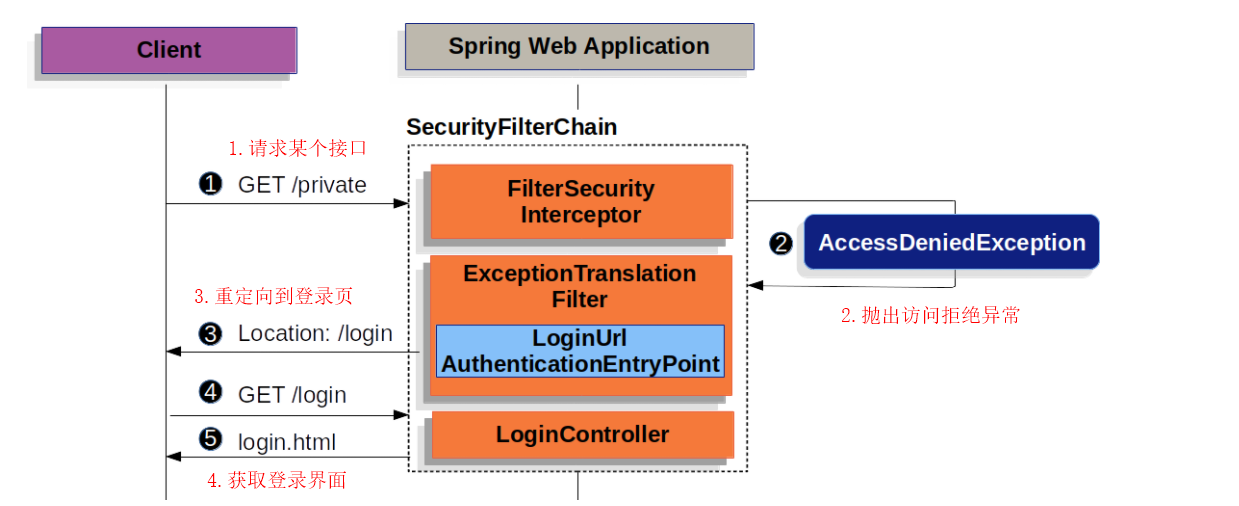
如果配置没有被提供,则默认是formlogin,但是一旦被提供,则需要做简单配置
如何配置,文档没有说清楚,就给了一个配置,草我去哪配置?MD 。因此此时先看JavaConfiguration(说实话没学过前,看这篇文档,鬼能看懂???),也许以后学习新的Spring相关框架就默认有一个配置方式。
我草,文档中的配置没有一个是对的,可能是我没配置对吧。
经过我的尝试以下配法是可以的:
@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {super.configure(http);http// ....formLogin(form -> form.loginPage("/login").permitAll());; }
整体这篇讲的的就是:
①如何配置formPage登录方式
②如何自定义登录页面。完了。。
5.3.2基本认证
会返回一个有 WWW-Authentication:Basic realm=”Realm”的头的响应。
会弹出一个认证框 alert
5.4基于内存数据库等的用户认证
基于内存或者说基于数据库的用户认证方式,就是将用户的信息存储在数据库或者内存中
5.4.1存储在内存中的配置方式
InmemoryUserDetailManager 实现了 UserDetailService (是啥之后再说,就是一个执行认证逻辑的类)允许从内存中获取用户信息并执行认证逻辑。这个类 InmomeryUDM 实现了UserDetailManager接口 可以管理 UserDetails 。(具体是啥,回头再讲)
配置方式:
@Beanpublic UserDetailsService users() {UserDetails user = User.builder().username("user").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER").build();UserDetails admin = User.builder().username("admin").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER", "ADMIN").build();return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user, admin);}
可以发现密码是密文。
如果使用明文,登录时会报下面的错误:
如果想设置成明文的话需要指定默认的加密方式
@Beanpublic UserDetailsService users() {//添加下面一行即可完成指定默认加密方式User.UserBuilder users = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder();UserDetails user = users.username("user").password("password").roles("USER").build();UserDetails admin = users.username("admin")//指定默认加密方式就不能再 {}xxxxxxx 这样了.password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER", "ADMIN").build();return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user, admin);}
5.4.2基于数据库的认证
JdbcDaoImpl实现了UserDetialService,JdbcUserDetailManager 管理UserDetails。
既然支持Jdbc的话,就又数据表喽,SpringSecurity提供默认表结构,其sql语句在路径
The default schema is also exposed as a classpath resource named org/springframework/security/core/userdetails/jdbc/users.ddl. |
|---|
官方例子需要引入的依赖包 h2依赖包。。。。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.h2database</groupId><artifactId>h2</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId></dependency>
代码,官方丢了一行要哟
@BeanDataSource dataSource() {return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder().setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2).addScript("classpath:org/springframework/security/core/userdetails/jdbc/users.ddl").build();}@BeanUserDetailsManager users(DataSource dataSource) {UserDetails user = User.builder().username("user").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER").build();UserDetails admin = User.builder().username("admin").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER", "ADMIN").build();JdbcUserDetailsManager users = new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource);users.createUser(user);users.createUser(admin);return users;}
其实基于的是数据库了,但是h2这个是不是还是基于 内存的呀。。哈哈。。。
自定义数据源
1.在本机数据库执行脚本
create table users(username varchar(50) not null primary key,password varchar(500) not null,enabled boolean not null);create table authorities (username varchar(50) not null,authority varchar(50) not null,constraint fk_authorities_users foreign key(username) references users(username));create unique index ix_auth_username on authorities (username,authority);
2.导入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId></dependency>
3.配置文件
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_security?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTCspring.datasource.username=rootspring.datasource.password=888888spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
4.代码
@BeanUserDetailsManager users(DataSource dataSource) {UserDetails user = User.builder().username("user").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER").build();UserDetails admin = User.builder().username("admin").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER", "ADMIN").build();UserDetails user2 = User.builder().username("user2").password("{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW").roles("USER").build();JdbcUserDetailsManager users = new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource);users.createUser(user);users.createUser(admin);users.createUser(user2);return users;}
数据库就到这了。。。。
5.5UserDetail和UserDetailService
前两天上班偷偷的刷leetcode,今天不想刷了,就偷偷的说一下 这俩个东西。
UserDetail:
①被UserDetailService返回的一个对象
②DaoAuthenticationProvider ,它将 返回的UserDetail放入 Authentication的 principle字段中。
UserDetailService:
①被DaoAuthenticationProvider使用,用来获取相关登录人的登录信息,UserDetail。
可以暴露一个 自定义的UserDetailService ,暴露方式如下:
@BeanCustomUserDetailsService customUserDetailsService() {return new CustomUserDetailsService();}
customUserDetailService必须继承 UserDetailService。
5.6PasswordEncoder
自定义PasswordEncoder的方式:
@Beanpublic static NoOpPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();}
5.7DaoAuthenticationProvider
它使用UserDetailService和PasswordEncoder进行认证一个用户名和密码。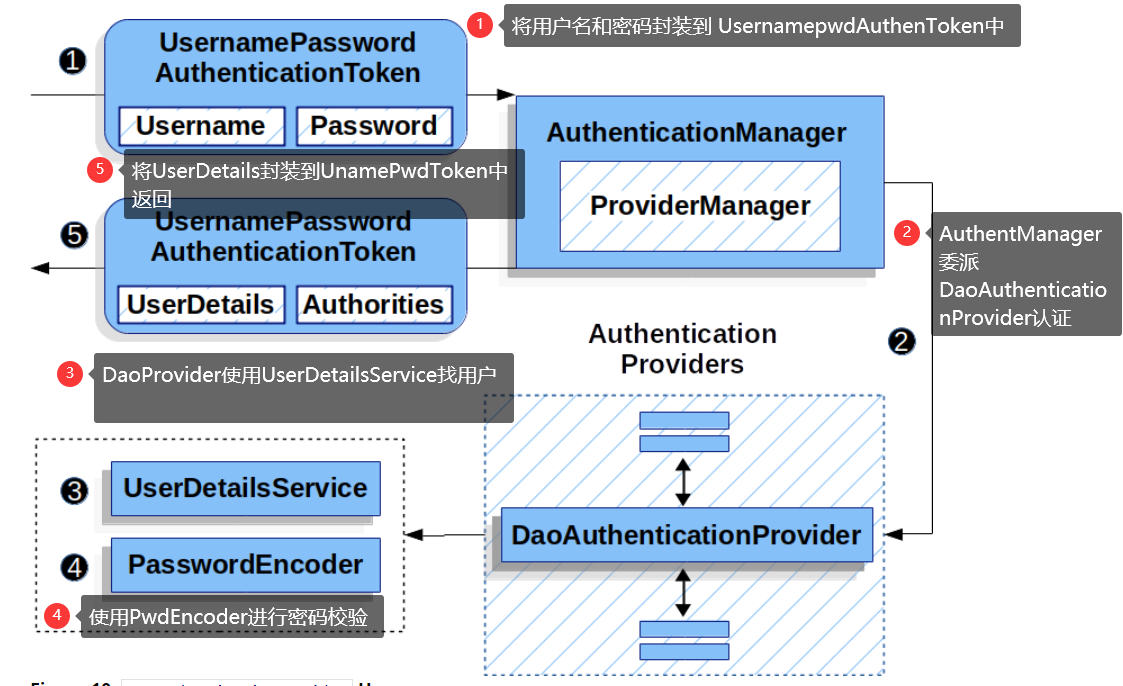
5.8SessionManagement
认证完成后,认证的信息默认是存储在Session中的。
Session的相关功能是 SessionManagementFilter和SessionAuthenticationStrategy接口联合实现。
典型的应用:
①防护session被攻击
②检测session的超时。
③定义一个用户可以拥有几个登录认证session信息
5.8.1SessionManagementFilter
它检查SecurityContextRepository的内容在SecurityContextHolder去决定是否用户被认证之前。如果说有在SecuirtyContextRepo中有被认证的信息,这个过滤器啥都不做,如果没有,但是SecurityContext是个非匿名的认证信息,它会认为别的过滤器已经认证这个人,需要我存储这个人的认证信息。于是触发 SessionStrategy。
用户未登录,过滤器将检查是否是一个不合法的sessionId,如果是返回配置的 一个策略。
5.8.2SessionAuthenticationStrategy
有两处用到它,SessionManagementFilter和AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilte,如果自定义这两类,需要在这自定的类中引入他们俩。
5.9记住我认证方式
6.SpringSecurity的配置方式
SpringSecurity引入项目后,考虑简单的用户名密码校验,我框架怎么知道你们公司有哪些用户。
第一步:配置过滤器
配置的目的就是配置一个 SpringSecurityFilterChain,也就是一组过滤器。
配置方式:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.*;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.*;@EnableWebSecuritypublic class WebSecurityConfig {@Beanpublic UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("password").roles("USER").build());return manager;}}
第二步:注册过滤器
使用SpringMVC的话就以下代码注释
import org.springframework.security.web.context.*;public class SecurityWebApplicationInitializerextends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {}
6.1一个默认的配置类
我们的配置类仅仅包含了系统有哪些用户,那么使用表单认证还是基础认证。其他的一些配置,没有配置如何帮我们配置的呢?其实背后还有一个叫 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter ,它偷偷的帮我们配置了。
默认的配置是下面这样的:
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http//1.所有的接口认证后访问.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated())//允许表单登录.formLogin(withDefaults())//允许Basic登录.httpBasic(withDefaults());}
6.2配置一个自定义过滤器
自定义过滤器
public class MyCustomDsl extends AbstractHttpConfigurer<MyCustomDsl, HttpSecurity> {private boolean flag;@Overridepublic void init(H http) throws Exception {// any method that adds another configurer// must be done in the init methodhttp.csrf().disable();}@Overridepublic void configure(H http) throws Exception {ApplicationContext context = http.getSharedObject(ApplicationContext.class);// here we lookup from the ApplicationContext. You can also just create a new instance.MyFilter myFilter = context.getBean(MyFilter.class);myFilter.setFlag(flag);http.addFilterBefore(myFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);}public MyCustomDsl flag(boolean value) {this.flag = value;return this;}public static MyCustomDsl customDsl() {return new MyCustomDsl();}}
这是使用SpringSecurity的常规配置方式
@EnableWebSecuritypublic class Config extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.apply(customDsl()).flag(true).and()...;}}
eeee,这张写的不好哦。。。。。。