原文: https://javatutorial.net/breadth-first-search-example-java
当涉及从给定数据结构访问数据时,搜索或遍历非常重要。 在这些数据结构中,例如图和树,有多种遍历/搜索元素的方法。

广度优先搜索是这些方法的一个示例。 BFS 是一种遍历树或图形的算法,它从树的根(树中的最高节点)开始或仅从顶部开始,并在当前深度扫描所有相邻节点,然后再继续移动到节点或元素。 下一个深度级别。
简而言之,BFS 必须完成一层,然后继续进行下一层直到没有剩余的任何层。
BFS 使用与深度优先搜索完全相反的工作流程,反之亦然。
在 BFS 和 DFS 之间的实现方面,一个很大的不同是 BFS 使用队列,而 DFS 使用栈。
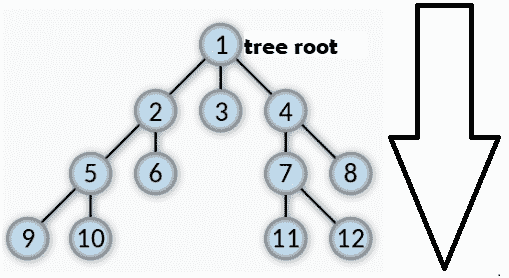
BFS 的工作流程
BFS 的实现
实现 BFS 时要遵循两个简单的规则:
- 访问给定层上的每个元素
- 移至下一层
一个例子:
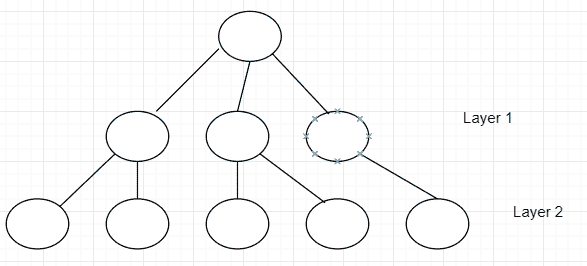
在继续进行第 2 层之前,必须先通过第 1 层。
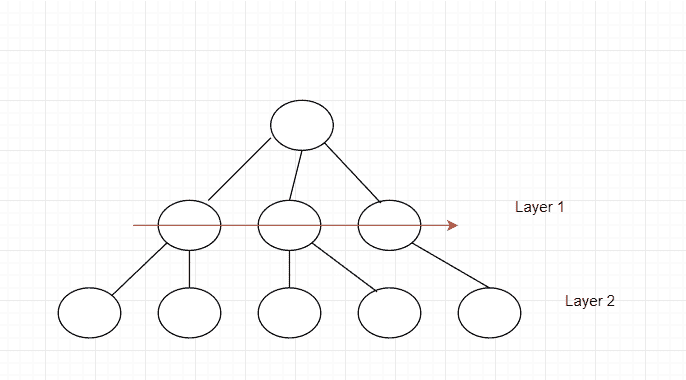
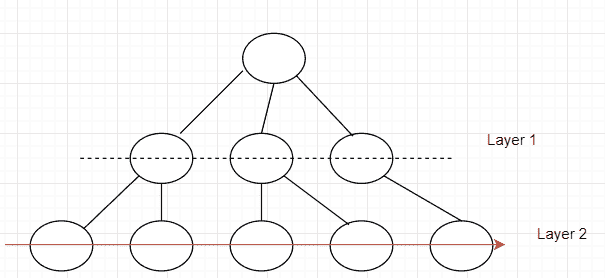
在那之后,这是应该怎么做的:
伪代码
public void breadthFirstSearch(Graph G, Object S)// G => Graph ; S => Source node{define a queue named as Queue;insert the source node in the Qmark s as visitedperform a while loop that keeps looping until the queue is not emptyremoving the current element from the queue as it will be visited nowperform a for loop that goes through all neighbours of the current elementif condition that checks if the current element/node/vertex is not visitedif it has not been visited, enqueue it and mark it as visited}
实际代码实现
public void BFS(int s, int l){// create an array that holds boolean values that will have length 'l'boolean visited[] = new boolean[l];// create a queueLinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();// mark the current node as visited and add it to the queuevisited[s]=true;q.add(s);while (q.size() != 0){// dequeuing a vertex from queues = q.poll();// get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex if a adjacent has not// been visited, then mark it visited and enqueue itIterator<Integer> k = adj[s].listIterator();while (k.hasNext()){int j = k.next();if (!visited[j]){visited[j] = true;q.add(j);}}}}

