Java ArrayList类是实现List接口的可调整大小的数组。 它允许所有元素(包括null),并且实现所有可选列表操作。 可以在ArrayList上运行的大多数操作,例如size,isEmpty,get,set,iterator和listIterator都是恒定时间。 但是,add操作的复杂度为O(n)时间。与LinkedList相比,常数因子低。

ArrayList的优点
- 动态添加或删除元素的能力。
ArrayList使用数组作为其基础实现,这使ArrayList类可以更快地访问元素。- 灵活性。
ArrayList是面向对象的,因此您可以从中扩展并添加功能(如果需要)。- 向
ArrayList添加自定义行为是可能的,甚至很容易实现。
ArrayList的局限性
- 添加元素需要
O(n)时间。 ArrayList将数据顺序存储在内存中,因此,如果列表很大,则将需要大量连续的内存块。ArrayList的初始容量为 10,如果不指定容量,则将受到性能限制。 每当ArrayList达到其自身容量时,数据将以 50% 以上的容量从旧空间复制到新空间。
ArrayList的简单说明
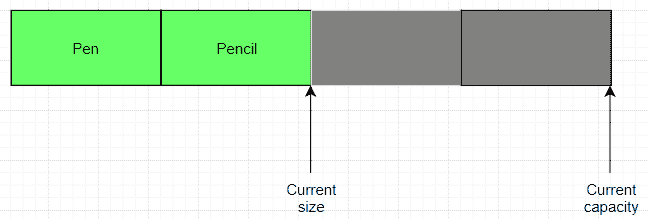
Java 中的ArrayList
从上图可以看到,ArrayList中当前有 2 个元素,可以添加的最大元素数量(容量)为 8(或 6 个以上)。
ArrayList中的构造方法
ArrayList()– 构造一个初始容量为 10 的空列表。ArrayList(Collection <? extended E> c)– 构造一个列表,该列表包含指定集合的元素,并按集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序。ArrayList(int initialCapacity)– 构造一个具有指定初始容量的空列表。
ArrayList类中的方法
boolean add(E e):将指定的元素附加到列表的末尾。void add(int index, E element):将指定的元素插入列表中的指定位置。boolean addAll(Collection <? extends E> c):将指定集合中的所有元素附加到列表的末尾,以指定集合的Iterator返回它们的顺序。boolean addAll(int index, Collection <? extends E> c):从指定位置开始,将集合中的所有元素插入列表。void clear():从列表中删除所有元素。boolean contains(Object o):如果列表包含指定的元素,则返回true;否则返回false。void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity):如果有必要确保列表可以容纳最小容量参数指定的所有元素,则增加列表的容量。void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action):对已循环通过的每个元素执行给定的动作。int indexOf(Object o):如果列表不包含元素,则返回 -1。 但是,如果元素存在于列表中,则它返回此列表中指定元素首次出现的索引。boolean isEmpty():如果列表不包含任何元素,则返回true。Iterator<E> iterator():以适当的顺序返回列表中元素的迭代器。int lastIndexOf(Object o):返回列表中指定元素最后一次出现的索引;如果列表中不存在该元素,则返回 -1。boolean remove(Object o):从列表中删除第一次出现的指定对象。boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c):从列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素。boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter):移除此集合中所有满足给定谓词的元素。void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex):删除列表中fromIndex和toIndex之间的所有元素。(fromIndex–包括在内,toIndex–排除在外)void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator):使用将运算符应用于该元素的结果替换列表中的每个元素。boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c):仅返回指定集合中包含的列表中的元素。int size():返回列表的大小。void sort(Comparator<? super E> c):根据Comparator指定的顺序对列表进行排序。Object[] toArray():返回包含列表中包含的元素的数组。
有关所有方法的文档,请访问 Oracle 官方文档页面。
使用add()在ArrayList中添加元素
import java.util.* ;public class ArrayListEgTwo{public static void main ( String[] args){// Create an ArrayList that consists of StringsArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();// Capacity starts at 10, but size starts at 0System.out.println("initial size: " + animals.size());// Populating some of the arraylistanimals.add("Elephant");animals.add("Tiger");animals.add("Lion");System.out.println("new size: " + animals.size());}
输出:
size: 0new size: 3
使用remove()移除ArrayList中的元素
import java.util.* ;public class RemoveExample{public static void main ( String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();animals.add( "Elephant" );animals.add( "Tiger" );animals.add( "Lion" );names.remove(1);for ( int i=0; i < animals.size(); i++ )System.out.println( i + ": " + animals.elementAt(j) );}}
输出:
0: Elephant1: Lion
使用isEmpty()检查ArrayList是否包含元素
import java.util.* ;public class isEmptyExample{public static void main ( String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();System.out.println( "Case 0:" + animals.isEmpty());animals.add("Tiger");System.out.println( "Case 1:" + animals.isEmpty() );nobby.clear();System.out.println( "Case 2:" + animals.isEmpty() );}}
输出:
Case 0: trueCase 1: falseCase 2: true
使用indexOf(Object o)在ArrayList中搜索元素
import java.util.* ;public class IndexOfExample{public static void main (String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();animals.add("Elephant");animals.add("Tiger");animals.add("Lion");System.out.println("Index of 'Elephant': " + animals.indexOf("Elephant" ));System.out.println("Index of 'Lion': " + animals.indexOf("Lion"));}}
输出:
Index of 'Elephant': 0Index of 'Lion': 2
使用Iterator()遍历ArrayList中的元素
import java.util.* ;public class IteratorExample{public static void main ( String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();animals.add("Elephant");animals.add("Tiger");animals.add("Lion");// Initializing an iteratorIterator<String> iterator = animals.iterator();// Using the iterator to visit each elementwhile(iterator.hasNext())System.out.println(iterator.next());}}
输出:
ElephantTigerLion
使用增强的For循环遍历ArrayList中的元素
import java.util.* ;public class ForLoopExample{public static void main ( String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();animals.add("Elephant");animals.add("Tiger");animals.add("Lion");for (String animal : animals)System.out.println(animal);}}
输出:
ElephantTigerLion
使用size()获取ArrayList的大小
import java.util.* ;public class ForLoopExample{public static void main ( String[] args){ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<String>();animals.add("Elephant");animals.add("Tiger");animals.add("Lion");System.out.println("Size of ArrayList: " + animals.size());}}
输出:
Size of ArrayList: 3

