在本教程中,我将向您展示如何在 Java 中创建和使用数组
数组是同一类型的变量的集合。 数组有多种用途。 例如,您可能希望将所有价格存储在一个数组中。 但是使数组真正有用的是可以使用存储在数组中的值的方式。
在 Java 中声明新数组的一般形式如下:
type arrayName[] = new type[numberOfElements];
其中type是基本类型(请在教程中了解有关基本类型的更多信息)或对象。numberOfElements是将存储到数组中的元素数。 此值不能更改。 Java 不支持动态数组。 如果需要灵活,动态的结构来保存对象,则可能需要使用某些 Java 集合。 有关更多详细信息,请参见 Java 集合教程。
总览
Java 支持一维或多维数组。
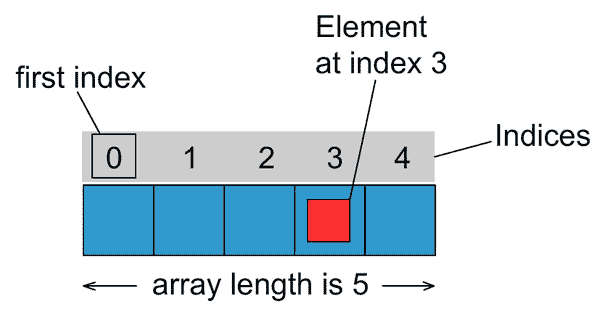
数组中的每个项目都称为元素,并且每个元素都通过其数字索引进行访问。 如上图所示,编号从 0 开始。例如,第 4 个元素将在索引 3 处访问。
初始化数组
让我们创建一个数组来存储一个 5 人的小公司中所有雇员的薪水。
int salaries[] = new int[5];
数组的类型(在本例中为int)适用于数组中的所有值。 您不能在一个数组中混合类型。
将值放入数组
现在我们已经初始化了salaries数组,我们想要在其中添加一些值。 我们可以在初始化期间执行以下操作:
int salaries[] = {50000, 75340, 110500, 98270, 39400};
或稍后再执行以下操作:
int salaries[] = new int[5];salaries[0] = 50000;salaries[1] = 75340;salaries[2] = 110500;salaries[3] = 98270;salaries[4] = 39400;
遍历数组
您可以像这样调用特定元素的值来使用它:
System.out.println("The value of the 4th element in the array is " + salaries[3]);
这将产生输出:
The value of the 4th element in the array is 98270
也可以使用for循环或while循环遍历数组中所有元素的值。 在我们先前的教程 Java 循环中进一步了解循环
public class ArrayExample {public static void main(String[] args) {int salaries[] = {50000, 75340, 110500, 98270, 39400};for(int i=0; i<salaries.length; i++) {System.out.println("The element at index " + i + " has the value of " + salaries[i]);}}}
上面程序产生的输出是:
The element at index 0 has the value of 50000The element at index 1 has the value of 75340The element at index 2 has the value of 110500The element at index 3 has the value of 98270The element at index 4 has the value of 39400
注意salaries.length的使用。 Java 中的数组具有length属性,该属性返回数组的长度。

