- 覆盖的默认实现:
HashMap之间的效率比较">ConcurrentMap和HashMap之间的效率比较ConcurrentMap中的方法- 使用上述某些方法的示例程序
即使Map 由许多类实现,但其中许多不是线程安全的,或者其中一些效率不高。 这就是为什么在 Java 1.5 中引入ConcurrentMap的原因。 它是线程安全且高效的。

覆盖的默认实现:
countreplaceAllforEachgetOrDefaultcomputerIfAbsentcomputerIfPresent
ConcurrentMap由表示为表存储桶的节点数组组成,它们在第一次插入后初始化。
ConcurrentMap和HashMap之间的效率比较
- 如果要尽快处理数据,则必须使用所有线程,因此这意味着
ConcurrentMap在这里更有效。 - 如果只需要单线程访问,则
HashMap更快。 - 如果由
HashMap实现,则添加方法的速度快 3 倍。 - 如果由
ConcurrentMap实现,则 get 方法会更快。
如果程序需要多个线程访问,则ConcurrentMap是更好的选择。 但是,如果程序仅使用 1 个线程,则HashMap将是更好的选择。
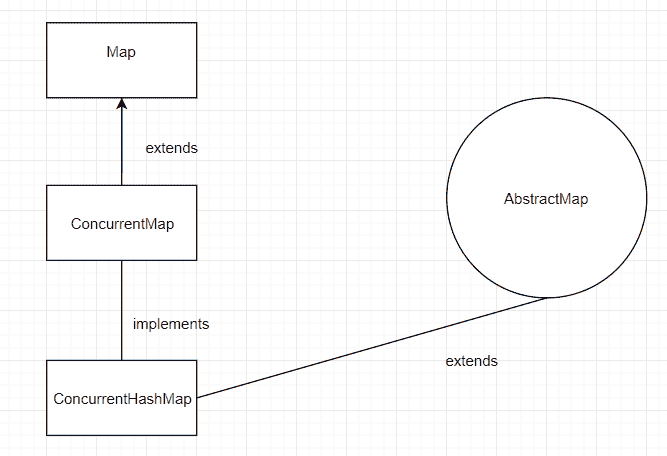
ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentMap中的方法
default V compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction):尝试计算指定键及其当前映射值的映射。default V computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction):如果作为参数给出的键与值不相关(或为null),则尝试计算其值并输入 进入此映射,除非为null。default V computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction):如果指定键的值存在且非空,则尝试计算新映射,给定键及其当前映射值。default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action):对当前映射中的每个条目执行给定的操作,直到所有条目都已处理。default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue):返回指定键所映射到的值或如果映射不包含该键的映射关系,则返回defaultValue(作为第二个参数)。default V merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction):如果键尚未与值关联或与null关联,则它将关联指定的非null值。V putIfAbsent(K key, V value):如果指定的键尚未与值关联,则将其与给定的值关联。boolean remove(Object key, Object value):仅当当前映射到给定值时,才删除键的条目。V replace(K key, V value):仅当当前映射到某个值时才替换键的条目。boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue):仅当当前映射到给定值时才替换项的条目。
有关 EnumSet 主要方法的更多信息,请随时访问原始 Oracle 文档。
使用上述某些方法的示例程序
import java.util.concurrent.*;class ConcurrentHashMapExample {public static void main(String[] args){ConcurrentHashMap conCurrHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();conCurrHashMap.put(100, "Elephant");conCurrHashMap.put(101, "Tiger");conCurrHashMap.put(102, "Lion");conCurrHashMap.put(103, "Cow");// since 103 already exists, this won't workconCurrHashMap.putIfAbsent(103, "Goat");conCurrHashMap.remove(103, "Goat");System.out.println("After removal: " + conCurrHashMap);// since 103 was removed, this now worksconCurrHashMap.putIfAbsent(103, "Leopard");System.out.println("After put: " + conCurrHashMap);// changing Goat to CheetahconCurrHashMap.replace(103, "Leopard", "Cheetah");System.out.println("Final: " + conCurrHashMap);}}
输出:
After removal: {100=Elephant, 101=Tiger, 102=Lion, 103=Cow}After put: {100=Elephant, 101=Tiger, 102=Lion, 103=Cow}Final: {100=Elephant, 101=Tiger, 102=Lion, 103=Cow}

