Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routingkey 的时候使用通配符!Routingkey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以**.**分割,例如: item.insert
通配符规则:
#:匹配一个或多个词*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
举例:item.#:能够匹配item.spu.insert 或者 item.spuitem.*:只能匹配item.spu
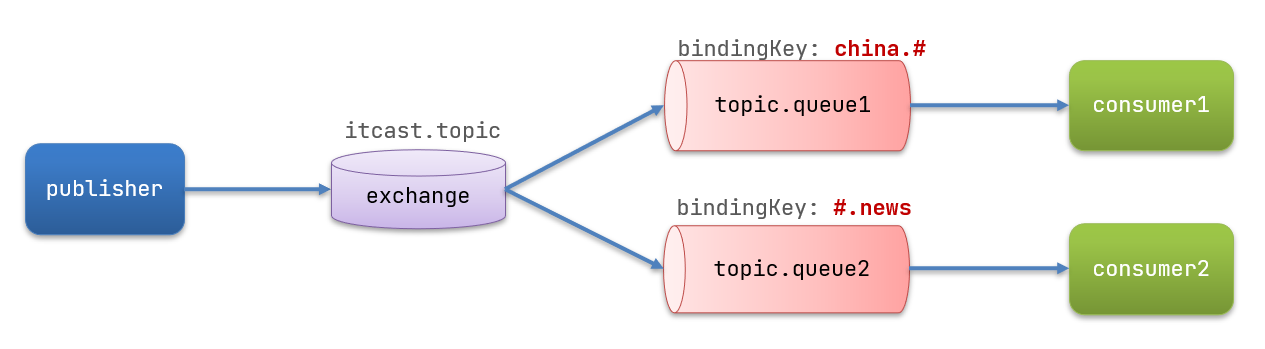
图示:

解释:
- Queue1:绑定的是
china.#,因此凡是以china.开头的routingkey 都会被匹配到。包括china.news和china.weather - Queue2:绑定的是
#.news,因此凡是以.news结尾的 routingkey 都会被匹配。包括china.news和japan.news案例
- 并利用@RabbitListener声明Exchange、Queue、RoutingKey
- 在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听topic.queue1和topic.queue2
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向itcast. topic发送消息
1.引入依赖
2.基于注解声明交换机和队列并接收消息
package cn.itcast.mq.listener;import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class SpringRabbitListener {@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = "china.#"))public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");}@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),key = "#.news"))public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");}}
3.发送消息
/*** topicExchange*/@Testpublic void testSendTopicExchange() {// 交换机名称String exchangeName = "itcast.topic";// 消息String message = "喜报!孙悟空大战哥斯拉,胜!";// 发送消息rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", message);}
因为发送者带的key china.news两个队列的key china.#和 #.news 都匹配,所以两个消费者都拿到了消息