Knuth-Morris-Pratt 字符串查找算法,简称为 “KMP算法”,常用于在一个文本串str1内查找一个模式串str2 的出现位置,这个算法由Donald Knuth、Vaughan Pratt、James H. Morris三人于1977年联合发表,故取这3人的姓氏命名此算法
暴力匹配代码
用暴力匹配算法解决的话就会有大量的回溯问题 ,浪费了大量的时间。从而有一种算法能高效的解决问题
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Globalization;using System.IO;using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string str1 = "wehskhkjsdhsdiuussjsjshshsshkskhshsgskhdhhskshsdgkaub";string str2 = "shsd";int i = violenceMatch(str1, str2);Console.WriteLine(i);}//暴力匹配算法public static int violenceMatch(string str1,string str2){char[] s1 = str1.ToCharArray();char[] s2 = str2.ToCharArray();int s1len = s1.Length;int s2len = s2.Length;int i = 0;//i指向s1int j = 0;//j指向s2while (i < s1len & j < s2len)//保证检索时不越界{if (s1[i] == s2[j])//匹配到了某个字符{i++;j++;}else//没有匹配到某个字符{//s1的指针指向从匹配成功后开始的下一个//s2的指针就清空i = i - (j - 1);j = 0;}}//判断是否成功if (j == s2len)return i - j;elsereturn -1;}}}
字符串前后缀
对于字符串ABCDABD来说
他的前缀有不包括最后一个字符的从头连续字符串的集合:A,AB,ABC,ABCD,ABCDA,ABCDAB
他的后缀有不包括第一个字符的从尾开始到第二个字符的连续正序字符串的集合:D,BD,ABD,DABD,CDABD,BCDABD
前后缀的最大公共元素
如上这个字符串,他的各个子字符串的前后缀分别如下图。
最大公共元素就是前缀和后缀集合里面相同的字符串的最大长度,如下图红色的字A的长度为1,AB的长度为2
部分匹配表
然后可以整理成一张表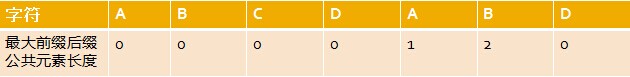
因为模式串中首尾可能会有重复的字符,故可得出下述结论:
失配时,模式串向右移动的位数为:**已匹配字符数 - 失配字符的上一位字符所对应的最大长度值**
KMP算法思想步骤
因为模式串第一个字符A和文本串前面的BBC空格一开始就不匹配,直接将模式串不断的右移一位即可,直到模式串中的字符A跟文本串的第5个字符A匹配成功
继续往后匹配,当模式串最后一个字符D跟文本串匹配时失配,显而易见,模式串需要向右移动。
但向右移动多少位呢?因为此时已经匹配的字符数为6个(ABCDAB),然后根据《部分匹配表》可得失配字符D的上一位字符B对应的长度值为2,所以根据之前的结论,可知需要向右移动6 - 2 = 4 位。
模式串向右移动4位后,发现C处再度失配,因为此时已经匹配了2个字符(AB),且上一位字符B对应的最大长度值为0,所以向右移动:2 - 0 =2 位。
A与空格失配,向右移动1 位。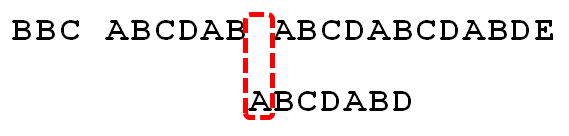
继续比较,发现D与C 失配,故向右移动的位数为:已匹配的字符数6减去上一位字符B对应的最大长度2,即向右移动6 - 2 = 4 位。
经历第5步后,发现匹配成功,过程结束
代码
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Globalization;using System.IO;using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string str1 = "BBC ABCDAB ABCDABCDABDE";string str2 = "ABCDABD";int[] next = kmpNext(str2);foreach(int n in next){Console.Write(n+" ");}Console.WriteLine("index"+kmpSearch(str1,str2,next));}//获取到一个子串的部分匹配表public static int[] kmpNext(string dest){//创建一个next数组保存部分匹配值int[] next = new int[dest.Length];next[0] = 0;//如果字符串的长度为1部分匹配值就是0for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < dest.Length; i++){/*kmp核心* 当不匹配时就改变j的值* 公式:已匹配字符数 - 失配字符的上一位字符所对应的最大长度值* j是已经匹配的字符数,j-1就是上一位字符,next就是部分匹配 表,对应的最大长度* 这段理解可以看笔记的图解部分*/while (j > 0 && dest[i] != dest[j])j = next[j - 1];//当这个条件满足时,部分匹配值+1if (dest[i] == dest[j]){j++;}next[i] = j;}return next;}//kmp搜索算法public static int kmpSearch(string str1,string str2,int[] next){//遍历str1for(int i =0,j=0;i<str1.Length; i++){//需要处理str1[i]!=str2[j],这是kmp算法的核心点while (j > 0 && str1[i] != str2[j])j = next[j - 1];if (str1[i] == str2[j])j++;if (j == str2.Length) //找到了return i - j + 1;}return -1;}}}

