二叉树介绍
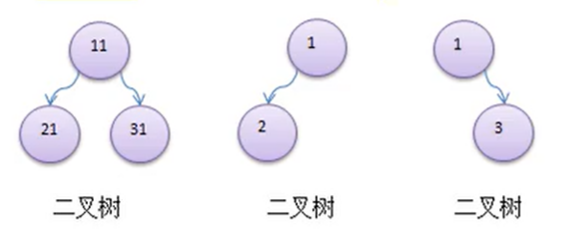
- 树有很多种,每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树。
- 二叉树的子节点分为 左节点 和 右节点。
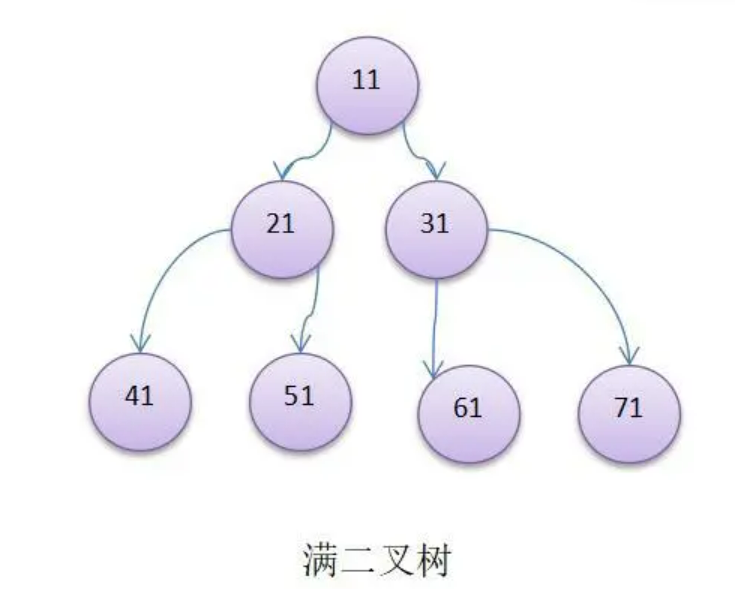
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且节点总数为2**n**-1,n为层数,则我们称为满二叉树
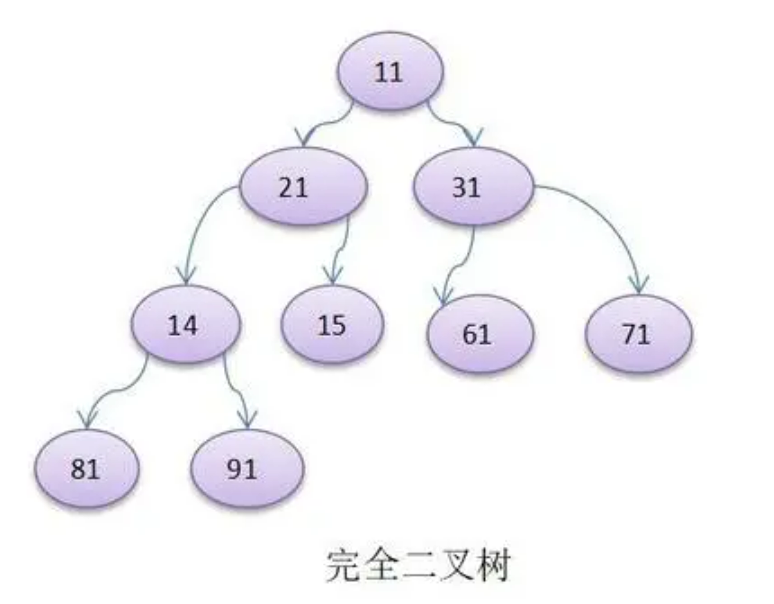
- 如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二成的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树
-
遍历节点
前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
- 先输出当前节点(初始的时候是root节点)
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续中序遍历
- 输出当前节点
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续中序遍历
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,在遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续后序遍历
- 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续后序遍历
- 输出当前节点
总结:看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前中后序
代码
就跟链表一个路子,单链表每个节点指向一个next,二叉树每个节点指向两个节点left和right
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{public class BinaryTree{public BTNode root;//前序遍历public void preOrder(){if (this.root != null)this.root.preOrder();elseConsole.WriteLine("当前二叉树为空");}//中序遍历public void infixOrder(){if (this.root != null)this.root.infixOrder();elseConsole.WriteLine("当前二叉树为空");}//后序遍历public void postOrder(){if (this.root != null)this.root.postOrder();elseConsole.WriteLine("当前二叉树为空");}}//二叉树节点public class BTNode{public int id;public string name;public BTNode left;public BTNode right;public BTNode(int id,string name){this.id = id;this.name = name;}//前序遍历public void preOrder(){//1.先输出当前节点Console.WriteLine(this.id+this.name);//2.如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历if (this.left != null)this.left.preOrder();//3.如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历if (this.right != null)this.right.preOrder();}//中序遍历public void infixOrder(){//1.如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续中序遍历if (this.left != null)this.left.infixOrder();//2.输出当前节点Console.WriteLine(this.id+this.name);//3.如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续中序遍历if (this.right != null)this.right.infixOrder();}//后续遍历public void postOrder(){//1.如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归继续后序遍历if (this.left != null)this.left.postOrder();//2.如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归继续后序遍历if (this.right != null)this.right.postOrder();//3.输出当前节点Console.WriteLine(this.id+this.name);}}}
查找节点
代码
思路就跟前中后序遍历大致相同,不过找到就返回,要注意,比如我左边节点返回了,就要在它执行下一段代码的时候判断有没有找到数据,如果找到了,不用执行另外分支的递归了,直接返回。如果没有这个判断的话,哪怕前面分支已经找到了结果,依旧去找后面的分支。两递归函数也不要用else if判断,哪怕一条分支返回为null,只能说明这条分支没找到,还有其他的分支呢,用else if其他的分支直接不执行了
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{public class BinaryTree{public BTNode root;public void preOrder(){};//前序遍历public void infixOrder(){}//中序遍历public void postOrder(){};//后序遍历//前序查找public BTNode preFind(int id){if (root != null)return this.root.preFind(id);elsethrow new Exception("二叉树为空");}//中序查找public BTNode infixFind(int id){if (root != null)return this.root.infixFind(id);elsethrow new Exception("二叉树为空");}//后序查找public BTNode postFind(int id){if (root != null)return this.root.postFind(id);elsethrow new Exception("二叉树为空");}}public class BTNode{public int id;public string name;public BTNode left;public BTNode right;public BTNode(int id,string name){this.id = id;this.name = name;}public void preOrder(){};//前序遍历public void infixOrder(){};//中序遍历public void postOrder(){};//后续遍历//前序查找public BTNode preFind(int id){//1.定义一个辅助节点,这个节点用来装递归的结果,默认为null,如果都没有找到就返回默认的BTNode temp = null;//2.先比较当前节点,如果找到了就返回if (this.id == id)return this;//3.没找到就前序查找左节点if (this.left != null)temp = this.left.preFind(id);//3.1.只要找到了这个节点,temp不为空了就立马返回if (temp != null)return temp;//4.右边节点也前序查找if (this.right != null)temp = this.right.preFind(id);if (temp != null)return temp;//5.都没找到说明真没有这个要查找的值,返回temp,默认值为nullreturn temp;}//中序查找public BTNode infixFind(int id){//中序遍历一样的思路,前序查找一样的写法BTNode temp = null;if (this.left != null)temp = this.left.infixFind(id);if (temp != null)return temp;if (this.id == id)return this;if (this.right != null)temp = this.right.infixFind(id);if (temp != null)return temp;return temp;}//后序查找public BTNode postFind(int id){//如上BTNode temp = null;if (this.left != null)temp = this.left.postFind(id);if (temp != null)return temp;if (this.right != null)temp = this.right.postFind(id);if (temp != null)return temp;if (this.id == id)return this;if (this.id == id)return this;return temp;}}}
删除节点
思路
- 因为这个二叉树是单向的,所以我们要判断当前节点的子节点是否需要被删除,而不是判断当前节点,和单链表删除一样
- 当前节点的子节点又分为左右两个子节点,需要都判断左子节点和右子节点是不是这个要被删除的节点,如果是,就把当前节点对应的子节点赋值为null,然后返回(结束递归)
- 如果第2步没有删除节点,就继续向左子数递归删除
- 如果第2步也没有删除节点,则应当向右子树进行递归删除
代码
```csharp using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApp1 { public class BinaryTree { public BTNode root;
public void preOrder(){};//前序遍历public void infixOrder(){};//中序遍历public void postOrder(){};//后序遍历public BTNode preFind(int id){};//前序查找public BTNode infixFind(int id){};//中序查找public BTNode postFind(int id){};//后序查找//删除节点public void delNode(int id){if (root != null){if (root.id == id){root = null;return;}else{root.delNode(id);}}else{Console.WriteLine("空树");}}}public class BTNode{public int id;public string name;public BTNode left;public BTNode right;public BTNode(int id, string name){this.id = id;this.name = name;}public void preOrder(){};//前序遍历public void infixOrder(){};//中序遍历public void postOrder(){};//后序遍历public BTNode preFind(int id){};//前序查找public BTNode infixFind(int id){};//中序查找public BTNode postFind(int id){};//后序查找//删除节点public void delNode(int id){if (this.left != null && this.left.id == id){this.left = null;return;}if (this.right != null && this.right.id == id){this.right = null;return;}//当前节点的左右节点都不是要删除的节点,就要向左右树递归删除if (this.left != null){this.left.delNode(id);}if (this.right != null){this.right.delNode(id);}}}
}
<a name="qaLkk"></a># 顺序存储二叉树从数据存储来看,数组存储方式和树的存储方式可以相互转换,即数组可以转换成树,树也可以转换成数组。<br />可以用二叉树前中后序遍历的方式遍历数组。顺序存储二叉树有如下特点1. 顺序存储二叉树只考虑完全二叉树1. 第n个元素的左子节点为`2*n+1`1. 第n个元素的右子节点为`2*n+2`1. 第n个元素的父节点为`(n-1)/2`1. n表示二叉树中第几个元素,从0开始(为了跟数组保持一致)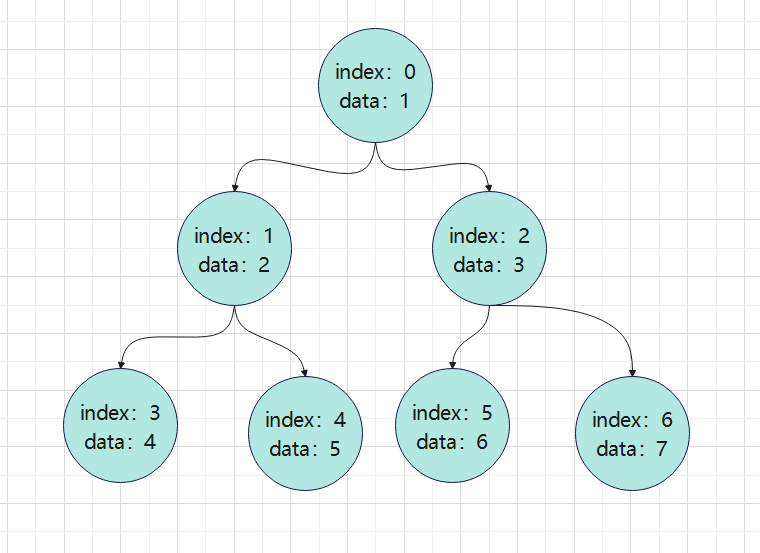<br />上图对应的数组就是`[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]`<a name="bewHh"></a>## 代码```csharpusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{public class ArrayBinaryTree{int[] array = null;public ArrayBinaryTree(int[] array){this.array = array;}//前序public void preOrder(int index){if (array == null || array.Length == 0){Console.WriteLine("数组为空");return;}//1.输出当前元素Console.WriteLine(array[index]);//2.向左递归遍历if (2 * index + 1 < array.Length)preOrder(2 * index + 1);//3.向右递归遍历if (2 * index + 2 < array.Length)preOrder(2 * index + 2);}//中序public void infixOrder(int index){if (array == null || array.Length == 0){Console.WriteLine("数组为空");return;}if (2 * index + 1 < array.Length)infixOrder(2 * index + 1);Console.WriteLine(array[index]);if (2 * index + 2 < array.Length)infixOrder(2 * index + 2);}//后序public void postOrder(int index){if (array == null || array.Length == 0){Console.WriteLine("数组为空");return;}if (2 * index + 1 < array.Length)postOrder(2 * index + 1);if (2 * index + 2 < array.Length)postOrder(2 * index + 2);Console.WriteLine(array[index]);}}}
线索二叉树
线索化二叉树思路
n个节点的二叉树中含有n+1个(公式2n-(n-1)=n+1)个空指针域。利用二叉树中这些空指针域,存放指向该节点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继节点指针(这种附加的指针称为 “线索”)。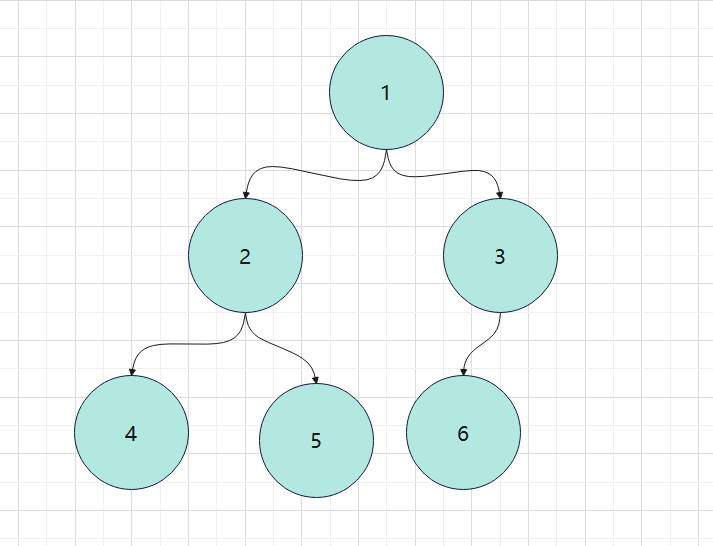
这种加上了线索的二叉树称为线索二叉树。根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可以分为前序线索二叉树,中序线索二叉树,和后序线索二叉树三种。
一个节点的前一个节点,称为前驱节点。
一个节点的有一个结点,称为后继节点。
如上图的二叉树,3,4,5,6节点的指针域并没有使用完。3的右子节点为空,4,5,6的左右节点都为空,所以空的指针节点有7个。
根据上图公式2n-(n-1)=n+1得到 2*6-(6-1)=6+1=7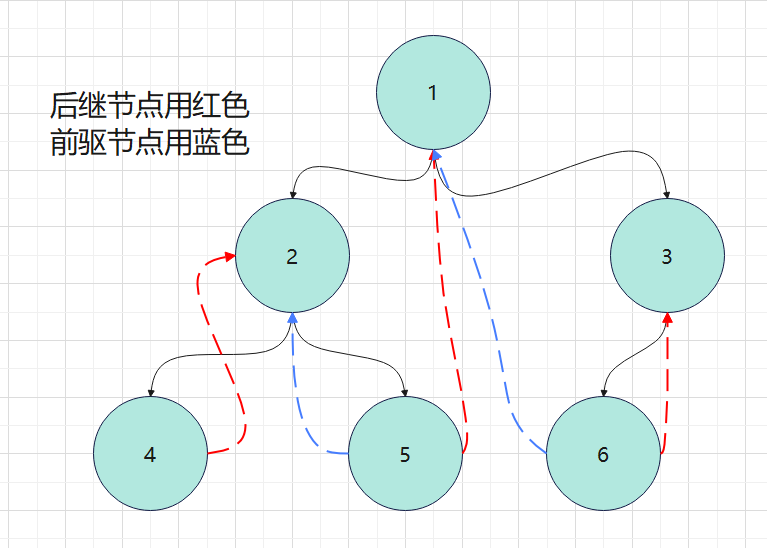
根据中序遍历,结果为
4,2,5,1,6,3输出4后,下一个节点应该是输出2,这时候就用4的右指针指向2(2是4的后继节点)。这时候4的左指针还是空的,4是第一个输出,因此没有前驱节点。 5的后继节点是1,就用5的右指针指向1,而5的左指针还是空的,就指向前驱节点2。 6的后继节点是3,右指针指向3,左指针是空的,就指向6的前驱节点1。 3没有后继节点,左指针又不为空,就不动。 以此类推。这就是附加线索
这里举例是前序,中后序同理。
说明:当线索化二叉树后节点的left和right有如下情况。
- left指向的是左子树,也有可能指向前驱节点,如上图,1节点的left就指向左子树,而4节点的left指向的就是前驱节点
- right指向的是右子数,也有可能指向后继节点,如上图,1节点的right就指向右子树,而4节点的right指向的就是后继节点
因此需要给每个节点的left和right设置一个属性,来判断他是子树还是线索节点
线索化代码
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{public class ThreadedBinaryTree{public TBTNode root;//为了实现线索化,需要创建要给指向当前节点的前驱节点的指针//在递归进行线索化时,pre总是保留前一个节点public TBTNode pre;//前序线索化二叉树public void preThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){//思路如中序线索化if (node == null)return;if (node.left == null){node.left = pre;node.lefttype = 1;}if (pre != null && pre.right == null){pre.right = node;pre.righttype = 1;}pre = node;if(node.lefttype==0)preThreadedNodes(node.left);if(node.righttype==0)preThreadedNodes(node.right);}//中序线索化二叉树,node就是需要线索化的节点public void infixThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){if (node == null)//不能线索化return;//(一).先线索化左子树infixThreadedNodes(node.left);//(二).线索化当前节点//先处理当前节点的前驱节点if (node.left == null){node.left = pre;//让当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点node.lefttype = 1;//修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱节点}//处理后继节点,其实是在下次递归的时候处理当前节点的后继节点//也就是说当前这次是处理上一节点的后继节点与当前节点的前驱节点if(pre!= null && pre.right==null){pre.right = node;//让前驱节点的右指针指向当前节点pre.righttype = 1;//修改前驱节点的右指针类型//这样就处理好了 上一个节点 的后继节点}pre = node;//前一个节点进行迭代//(三).线索化右子树infixThreadedNodes(node.right);}//后序线索化二叉树public void postThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){if (node == null)return;postThreadedNodes(node.left);postThreadedNodes(node.right);if (node.left == null){node.left = pre;node.lefttype = 1;}if (pre != null && pre.right == null){pre.right = node;pre.righttype = 1;}pre = node;}}public class TBTNode{public int id;public string name;public TBTNode left;public TBTNode right;//说明//1.如果lefttype==0,表示指向的是左子树,如果1表示指向前驱节点//2.如果righttype==0,表示指向是右子树,如果1表示指向后继节点public int lefttype;public int righttype;public TBTNode(int id, string name){this.id = id;this.name = name;}}}
遍历线索化二叉树
因为线索化了之后,各个节点指向有变化,因此原来的遍历方式不能使用,这时需要使用新的方式遍历线索化二叉树,各个节点可以通过线型方式遍历,因此无需使用递归方式,这样提高了遍历的效率。遍历的次序和使用的线性化的次序一致。
遍历线索化二叉树代码
需要注意的是,后序遍历线索二叉树,需要每个节点添加一个父节点,在创建二叉树时每个节点就指向了父节点
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;namespace ConsoleApp1{public class ThreadedBinaryTree{public TBTNode root;//为了实现线索化,需要创建要给指向当前节点的前驱节点的指针//在递归进行线索化时,pre总是保留前一个节点public TBTNode pre;public void preThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){};//前序线索化二叉树public void infixThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){};//中序线索化二叉树public void postThreadedNodes(TBTNode node){};//后序线索化二叉树//前序遍历线索二叉树public void preThreadedList(){TBTNode node = root;while (node != null){//前序遍历,先输出当前节点//如果lefttype==0,说明left是左子树while (node.lefttype == 0){Console.WriteLine(node.id + node.name);node = node.left;}Console.WriteLine(node.id + node.name);node = node.right;}}//中序遍历线索二叉树public void infixThreadedList(){//定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始TBTNode node = root;while (node != null){//循环的找到lefttype==1的节点//因为是中序遍历,左边的节点先输出//所以第一个输出的节点本身指针为null,线索化后,lefttype==1,该节点是按照线索化处理的有效节点while (node.lefttype==0){node = node.left;}Console.WriteLine(node.id+node.name);//如果当前节点的右指针指向的是后继节点就一直输出while (node.righttype == 1){//改变当前节点为下一个节点node = node.right;Console.WriteLine(node.id+node.name);}//退出了上面的循环,就说明遇到了下一个节点不是后继节点的节点,直接替换它node = node.right;}}//后序遍历线索二叉树public void postThreadedList(){TBTNode node = root;TBTNode pre = null;//后序的第一个值是左边的叶子节点,所以当lefttype==1时,说明这个节点就是第一个输出的点,用循环先定位到这个点while (node != null&&node.lefttype == 0){node = node.left;}//然后开始遍历节点while (node != null){//如果当前节点有后继节点if (node.righttype == 1){Console.WriteLine(node.id + node.name);pre = node;node = node.right;}else//没有后继节点,想象三角形顶上的那个点,左右节点都是子节点{//如果上一个处理的节点是当前节点的右节点(当前节点来到了三角形的顶端节点,想想后序遍历的顺序)if (pre == node.right){Console.WriteLine(node.id+node.name);if (node == root)//根节点是后序遍历的最后一个点return;pre = node;node = node.parent;//往父节点迭代}else//已经退回了root节点,上一个处理的节点不是当前节点(root)的右节点{//开始往根节点的右边遍历node = node.right;//同样的找到最左边的点开始while (node != null && node.lefttype == 0){node = node.left;}}}}}}public class TBTNode{public int id;public string name;public TBTNode left;public TBTNode right;public TBTNode parent;//当前节点的父节点,用于后序遍历线索二叉树//说明//1.如果lefttype==0,表示指向的是左子树,如果1表示指向前驱节点//2.如果righttype==0,表示指向是右子树,如果1表示指向后继节点public int lefttype;public int righttype;public TBTNode(int id, string name){this.id = id;this.name = name;}}}
前中后序遍历线索二叉树比较
前序线索化二叉树遍历相对最容易理解,实现起来也比较简单。由于前序遍历的顺序是:根左右,所以从根节点开始,沿着左子树进行处理,当子节点的left指针类型是线索时,说明到了最左子节点,然后处理子节点的right指针指向的节点,可能是右子树,也可能是后继节点,无论是哪种类型继续按照上面的方式(先沿着左子树处理,找到子树的最左子节点,然后处理right指针指向),以此类推,直到节点的right指针为空,说明是最后一个,遍历完成。
中序线索化二叉树的网上相关介绍最多。中序遍历的顺序是:左根右,因此第一个节点一定是最左子节点,先找到最左子节点,依次沿着right指针指向进行处理(无论是指向子节点还是指向后继节点),直到节点的right指针为空,说明是最后一个,遍历完成。
后序遍历线索化二叉树最为复杂,通用的二叉树数节点存储结构不能够满足后序线索化,因此我们扩展了节点的数据结构,增加了父节点的指针。后序的遍历顺序是:左右根,先找到最左子节点,沿着right后继指针处理,当right不是后继指针时,并且上一个处理节点是当前节点的右节点,则处理当前节点的右子树,遍历终止条件是:当前节点是root节点,并且上一个处理的节点是root的right节点。

