当
析构函数``virtual时,几乎没有区别,否则: default时:认为是trivial{}时: 认为是user-defined
区别
如下为trivial class的两种实现:
struct Trivial{int foo;};struct Trivial_Default{int foo;Trivial_Default() = default;};
如下为non-trivial的实现:
struct Non_Trivial{int foo;Non_Trivial(){}};
什么是trivial
The C++ Standard n3337 § 8.5/7 says
To value-initialize an object of type T means: — if T is a (possibly cv-qualified) class type (Clause 9) with a user-provided constructor (12.1), then the default constructor for T is called (and the initialization is ill-formed if T has no accessible default constructor); — if T is a (possibly cv-qualified) non-union class type without a user-provided constructor, then the object is zero-initialized and, if T’s implicitly-declared default constructor is non-trivial, that constructor is called. — if T is an array type, then each element is value-initialized; — otherwise, the object is zero-initialized.
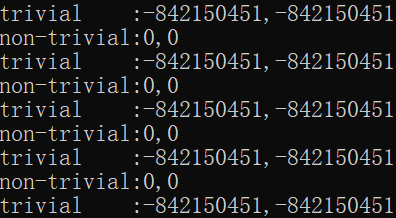
举例如下
#include <iostream>class A {public:A(){}int i;int j;};class B {public:B() = default;int i;int j;};int main(){for( int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {A* pa = new A();B* pb = new B();std::cout << <<pa->i << "," << pa->j << std::endl;std::cout << pb->i << "," << pb->j << std::endl;delete pa;delete pb;}return 0;}
结果如下: