- 第一章 回顾SSM
- 第二章 SpringBoot引言
- http://localhost:8080/hello/hello">注意:springboot的项目启动默认项目名
- 访问路径: http://localhost:8080/hello/hello - 第三章 SpringBoot的使用
- 主配置文件:
- 生产配置文件:
- 测试配置文件:
- 在主配置中指定那个环境生效配置
- 2、通过工厂创建之后可以在使用处注入该对象
- 四、属性注入
- 第四章 SpringBoot整合
- 二、整合Mybatis框架
- 三、本地测试
- 四、热部署工具
- 七、文件上传下载
- 八、拦截器
- 九、war包部署
- 十、Jar包部署(推荐)
- java -jar 对应jar文件名字 nohup &
- 总结 - 1.使用 th:text=”${属性名}” 获取对应数据,获取数据时会将对应标签中数据清空,因此最好是空标签 - 2.使用 th:utext=”${属性名}” 获取对应的数据,可以将数据中html先解析在渲染到页面 - 3.使用 th:value=”${属性名}” 获取数据直接作为表单元素value属性
- 第六章 RestFul
- 第七章 异常处理
- CORS 跨域
- Jasypt 加密
Spring Boot 2.5.0
资料来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411p7cQ?p=2&spm_id_from=pageDriver
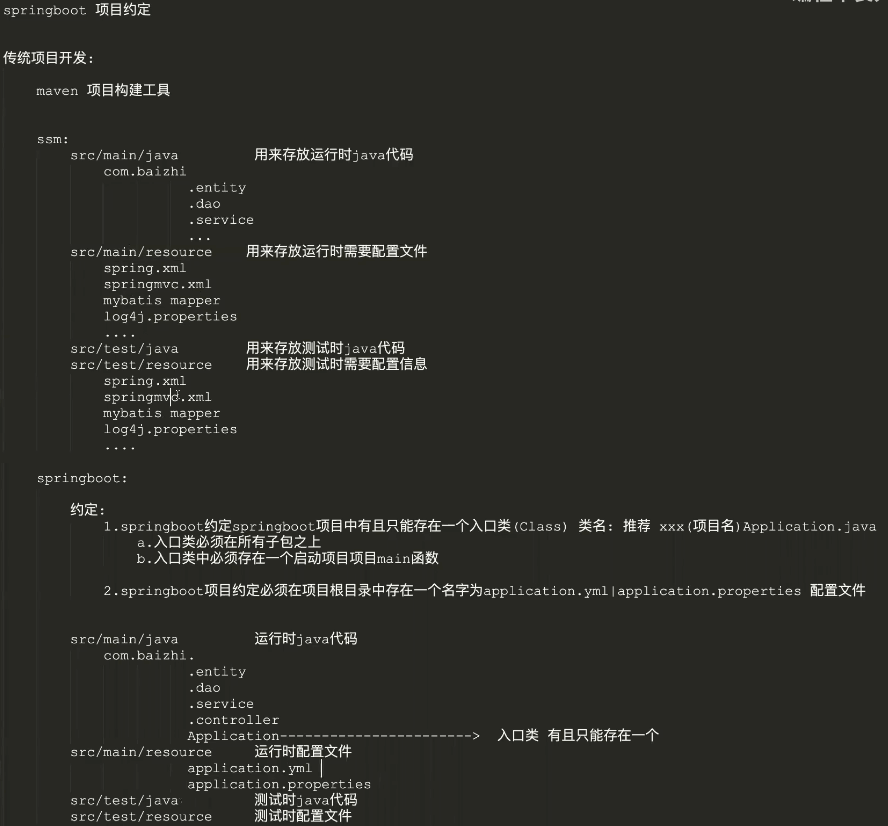
第一章 回顾SSM
一、SSM环境搭建
- spring
- springmvc
- mybatis
- spring springmvc mybatis 简单功能 员工添加 查询 所有
# 项目
- 需求分析 概要设计(库表设计) 详细设计(验证库表正确性) 编码(环境搭建+业务代码) 测试 部署上线
# 员工添加 查询所有功能 SSM
- 库表 库: ssm 数据库:mysql 表: id name birthday salary
# 编码 环境搭建 ssm spring springmvc 一个团队开发 无缝整合
- springmvc spring mybatis
二、引入依赖
<dependencies><!--junit--><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>4.11</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><!--spring--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><!--spring web mvc--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.3.6</version></dependency><!--druid--><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.2.4</version></dependency><!--mysql--><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.38</version></dependency><!--mybatis--><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis</artifactId><version>3.5.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId><version>2.0.6</version></dependency><!-- jackson--><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId><version>2.9.3</version></dependency><!-- aspectj --><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.9.5</version></dependency><!--aspectj--><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId><version>1.9.5</version></dependency></dependencies>
三、创建spring配置
<!--开启注解扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.baizhi.service"><context:exclude-filter type="aspectj" expression="com.baizhi.controller..*"/></context:component-scan><!--创建DataSource--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?characterEncoding=UTF-8"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="root"/></bean><!--创建SQLSessionFactoryBean --><bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/><property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/baizhi/mapper/*.xml"/><property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.baizhi.entity"/></bean><!--创建dao --><bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"><property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/><property name="basePackage" value="com.baizhi.dao"/></bean><!--创建事务管理器--><bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/></bean><!-- 开启注解事务生效--><tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
四、创建springmvc配置
<!--注解扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.baizhi.controller"/><!-- 开启注册驱动--><mvc:annotation-driven/><!-- 配置视图解析器--><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix" value="/"/><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/></bean>
五、配置web.xml
<!--配置工厂配置--><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value></context-param><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><!--配置springmvc--><servlet><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
六、现有SSM开发存在问题
- 大量maven冗余配置
- 每次构建项目都要书写大量相同配置极大浪费了项目开发时间
- 每次整合第三方技术都需要编写相关配置文件
- 项目测试每次都需要部署到tomcat
注意:这就是早期的SSM或者SSH开发存在问题,是不是很麻烦☹️☹️☹️
第二章 SpringBoot引言
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的 初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不 再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,SpringBoot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应 用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
SpringBoot全新框架的作用:简化spring应用初始搭建和开发过程
如何简化:开发人员使用springboot只要基于特定方式进行配置 ,简化spring使用
SpringBoot 微框架:5分钟 完成之前ssm中环境
springboot(微框架) = springmvc(控制器) + spring core(项目管理)
一、SpringBoot的优势
- 创建完整的独立的Spring应用程序 spring springmvc 只有一个容器
- 嵌入的Tomcat,无需部署WAR文件 springboot 内嵌tomcat 应用跑在内嵌服务器
- 简化Maven配置,自动配置Spring Springmvc,没有XML配置 几个依赖
- 使用springboot,spring应用再无xml
二、SpringBoot的约定
- springboot项目中必须在src/main/resources中放入application.yml(.properties)核心配置文件 名字必须为:application
- springboot项目中必须在src/main/java中所有子包之外构建全局入口类型,xxApplication,入口类一个springboot项目只能有一个
三、环境搭建
1、环境要求
# 1.System RequirementsJDK1.8+MAVEN3.2+Spring Framework 5.x+# 2.ServletContainers:Tomcat 9.0+# 3.开发工具IDEA 2021版本
2、新建项目中引入依赖
<!--继承springboot的父项目 便于维护版本 2.3.x.RELEASE 2.4.x 数字命令--><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.5.0</version></parent><dependencies><!--引入springboot的web支持--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
3、引入配置文件
项目中新建src/main/resources/application.yml
4、编写入口类
//在项目中如下的包结构中创建入口类 Application/*com+| baizhi*/// 修饰范围: 用在类上 只能用在入口类上 只能出现一次// 作用: 标识这个类是一个springboot入口类 启动整个springboot项目总入口// 总结: 1、pom文件引入依赖 2、resources生成application.yml 3、创建入口类加入@SpringBootApplication注解,在main中启动应用@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringBootDay1Application {public static void main(String[] args) {//启动springboot应用 参数1: 指定入口类的类对象 .class 参数2: main函数参数SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDay1Application.class,args);}}
5、运行main启动项目
o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Registering beans for JMX exposure on startups.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http)com.baizhi.Application : Started Application in 2.152 seconds (JVM running for 2.611)//说明: 出现以上日志说明启动成功
注意:到这里项目环境已经搭建成功了,看看仅仅需要5分钟😄😁😁
6、建包并创建控制器
// 在项目中创建指定的包结构package com.baizhi.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestControllerpublic class HelloController {//测试控制器 测试地址: http://localhost:端口号/项目名/请求路径//注意: springboot项目默认启动没有项目名 http://localhost:8080/hello@RequestMapping("hello")public String hello(){System.out.println("hello springboot.....");return "hello springboot";}}
7、访问项目
注意:springboot的项目启动默认项目名
- 访问路径: http://localhost:8080/hello/hello
8、修改内嵌服务器端口
# application.ymlserver:port: 8989
9、修改应用名称
# application.ymlserver:servlet:context-path: /springboot_day1 #修改项目名 注意:项目名必须 "/" 开头
第三章 SpringBoot的使用
一、相关注解说明
# 入口类 SpringApplication- SpringBootApplication: 全局入口类 有且只能有一个- mian:函数参数可以在启动时指定jvm参数覆盖默认配置# @SpringBootApplication 注解(组合注解)等价于:- @SpringBootConfiguration 标识这是一个springboot的配置类,这个注解就是用来自动配置spring springmvc(初始化 servlet ..)相关环境- @EnableAutoConfiguration 开启自动配置,自动配置核心注解,自动配置spring相关环境自动与项目中引入第三方技术自动配置其环境、如mybatis-springboot、redis-springboot 、es-springboot 、rabbitmq第三技术- @ComponentScan 组件扫描,根据注解发挥注解作用,默认扫描当前包及其子包
二、配置文件
1、配置文件的拆分
说明:在实际开发过程中生产环境和测试环境有可能是不一样的 因此将生产中的配置和测试中的配置拆分开,是非常必要的在springboot中也提供了配置文件拆分的方式. 这里以生产中项名名称不一致为例:
- 生产中项目名为:springboot
- 测试中项目名为:springboot_day1
- 端口同时为:8080
```java
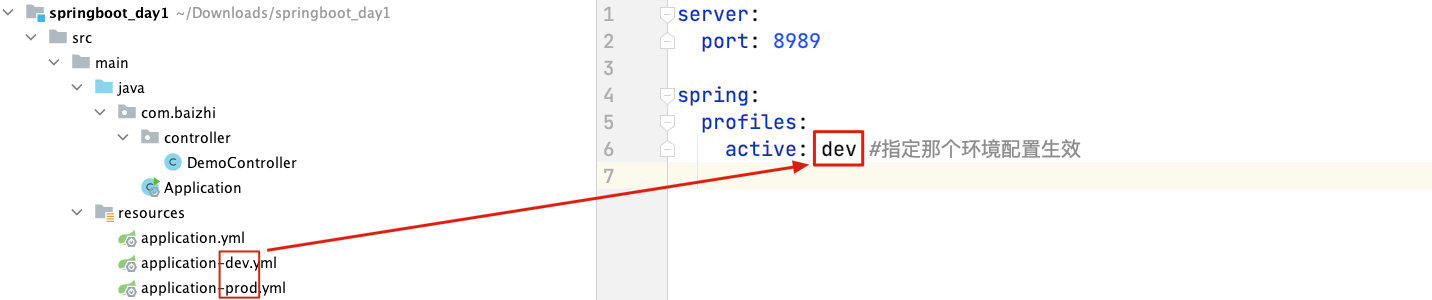
主配置文件:
- application.yml #用来书写相同的的配置
server:port: 8080 #生产和测试端口一致
生产配置文件:
- application-pord.yml #prod为配置文件简名
server:context-path: /cmfz
测试配置文件:
- application-dev.yml #dev为配置文件简名
server:context-path: /springboot
在主配置中指定那个环境生效配置
spring: profiles: active: dev #指定那个环境配置生效 dev为环境配置文件的简名
<br /><a name="ciokZ"></a>##### 2、启动指定配置文件说明:往往在企业级开发过程中为SpringBoot应用启动时指定一个完整外部配置也是经常用到的,在SpringBoot中也提供这个方式来启动项目如<br />**# 1.创建一个完整的配置文件**<br /><br />**# 2.启动时指定配置文件位置**<br />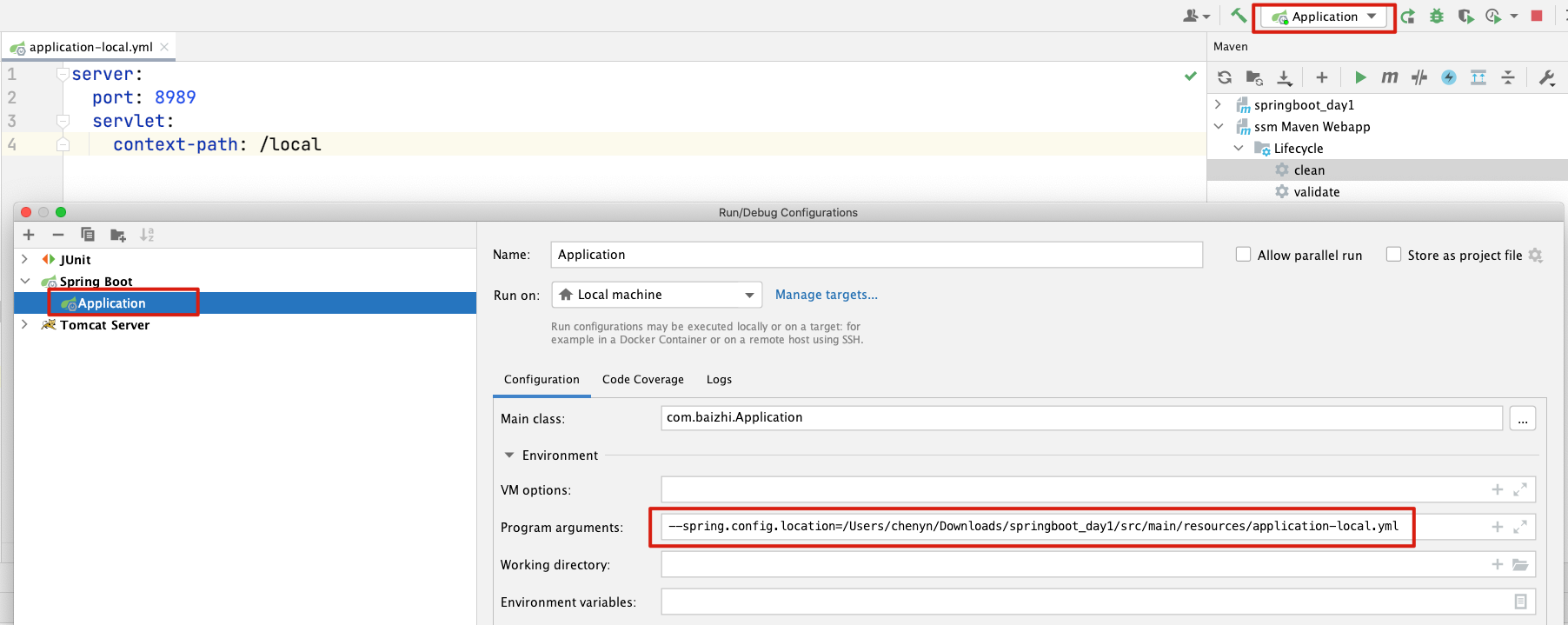<a name="dEyrg"></a>### 三、工厂创建对象<a name="BCigF"></a>#### 1、创建单个对象在springboot中可以管理单个对象,可以直接使用spring框架中注解形式创建。- **@Component** 通用的对象创建注解- @Controller 用来创建控制器对象- @Service 用来创建业务层对象- @Repository 用来创建DAO层对象- 以上注解都有value属性,value属性用来指定工厂中对象名称```java@Servicepublic class DemoServiceImpl implements UserService{//doing....}
2、通过工厂创建之后可以在使用处注入该对象
@Controller@RequestMapping("hello")public class HelloController {@Autowiredprivate DemoService demoService;//doing...}
2、创建多个对象
如何在springboot中像spring框架一样通过xml创建多个对象,在SpringBoot中也提供了相同注解如**@Configuration + @Bean**注解进行创建
- @Configuration 代表这是一个spring的配置类相当于Spring.xml配置文件
- @Bean 用来在工厂中创建这个@Bean注解标识的对象
- 默认使用@Bean创建对象在工厂中唯一标识为方法名称
- 修改在工厂中对象标识可以在使用@Bean(“工厂中名字”)指定一个名字
# 1.管理复杂对象的创建
@Configurationpublic class Beans {@Beanpublic Calendar calendar(){return Calendar.getInstance();}}
# 2.使用复杂对象
@Controller@RequestMapping("hello")public class HelloController {@Autowiredprivate Calendar calendar;......}
# 注意:
1、@Configuration 用来在工厂中一次性创建多个对象
2、@Component 用来创建单个对象
四、属性注入
1、基本属性注入
# 1. @Value 属性注入 [重点]
@RestControllerpublic class HelloController {//基本类型+String类型+日期类型@Value("${name}")private String name;@Value("${age}")private Integer age;@Value("${sex}")private Boolean sex;@Value("${price}")private Double price;@Value("${bir}")private Date bir;//注入数组@Value("${qqs}")private String[] qqs;//注入list@Value("${lists}")private List<String> lists;//注入maps@Value("#{${maps}}")private Map<String,String> maps;}
# 2. 在配置文件中定义注入值
name: 小陈age: 23price: 23.23sex: truebir: 2012/12/12qqs: 123,3434,3434lists: xiaochen,xiaoming,xiaosanmaps: "{'aa':'1234','bb':'2344'}"
-
2、对象方式注入
注意: 这种方式必须提供SET方法
# 1. @ConfigurationProperties(prefix=”前缀”)@Component@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")public class User {private String id;private String name;private Integer age;private String bir;//set 方法一定要提供}
# 2. 编写配置文件
user:id: 24name: xiaoheiage: 23bir: 2012/12/12
# 3. 引入依赖构建自定义注入元数据
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency>
第四章 SpringBoot整合
一、JSP模板集成
在SpringBoot框架中默认模板推荐使用Thymeleaf模板,这里我们优先讲与JSP模板集成
引入jsp的集成jar包
<!--c标签库--><dependency><groupId>jstl</groupId><artifactId>jstl</artifactId><version>1.2</version></dependency><!--让内嵌tomcat具有解析jsp功能--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId><artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId></dependency>
引入jsp运行插件
<build><finalName>springboot_day1</finalName><!--引入springboot插件 可以正确打包 显示jsp--><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId></plugin></plugins></build>
配置视图解析器
#在配置文件中引入视图解析器spring:mvc:view:prefix: / # /代表访问项目中webapp中页面suffix: .jsp
第一种方式使用插件启动访问JSP页面
第二种方式使用idea中指定工作目录启动 访问JSP
启动项目测试
http://localhost:8989/index.jsp
修改jsp无须重启应用
server:servlet:jsp:init-parameters:development: true
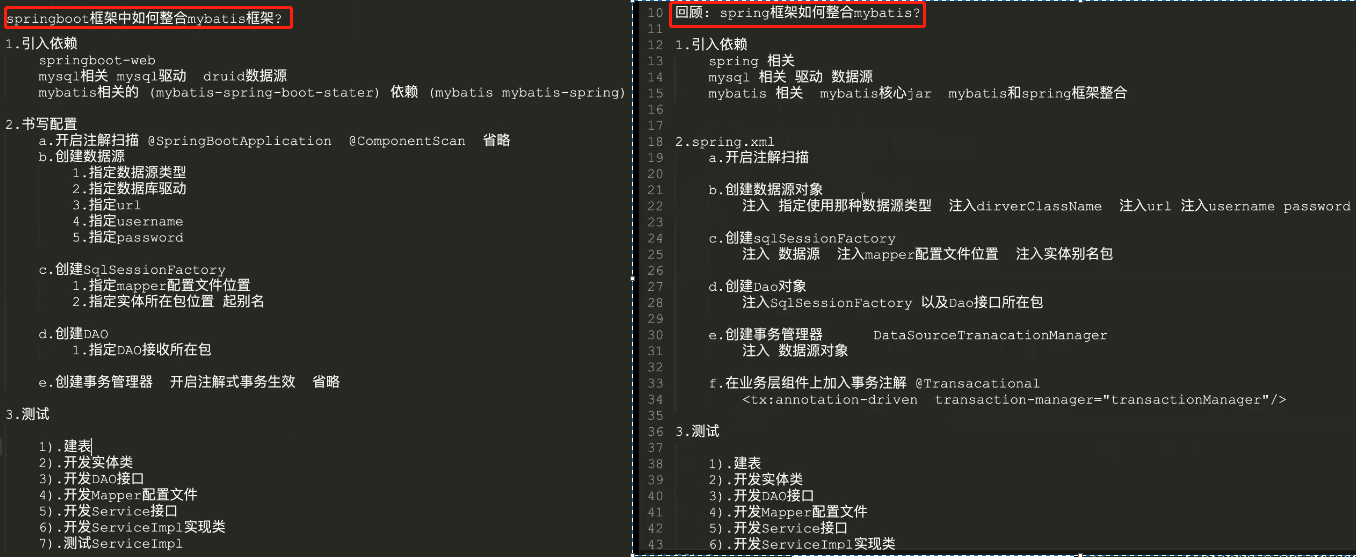
二、整合Mybatis框架
1、引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.2.4</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.38</version></dependency><!--整合mybatis--><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>2.1.4</version></dependency><!--说明:由于springboot整合mybatis版本中默认依赖mybatis因此不需要额外引入mybati版本,否则会出现冲突`-->
2、配置数据源
spring:mvc:view:prefix: /suffix: .jspdatasource:type: org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource #指定连接池类型driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #指定驱动 mysql5.x版本驱动#driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #指定驱动 mysql8.x版本驱动url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?characterEncoding=UTF-8 #指定urlusername: root #指定用户名password: root #指定密码
3、加入mybatis配置
#配置文件中加入如下配置:mybatis:# 指定mapper配置文件位置mapper-locations: classpath:com/baizhi/mapper/*.xml# 指定实体类的包名 默认别名 : 类名 类名首字母小写type-aliases-package: com.baizhi.entity
//入口类中加入如下配置:@SpringBootApplication@MapperScan("com.baizhi.dao") //修饰范围: 用在类上,作用:用来扫描dao接口所在包,同时将所有dao接口在工厂中创建对象//@Mapper注解: 修饰范围: 只能放在Dao接口上 作用:用来在工厂中创建单个dao对象public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);}}
4、建表
CREATE TABLE `t_clazz` (`id` varchar(40) NOT NULL,`name` varchar(80) DEFAULT NULL,`no` varchar(90) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
5、开发实体类
public class Clazz {private String id;private String name;private String no;//get set 方法省略....}
6、开发DAO接口以及Mapper
public interface ClazzDAO {List<Clazz> findAll();}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.baizhi.dao.ClazzDAO"><select id="findAll" resultType="Clazz">select * from t_clazz</select></mapper>
7、开发Service以及实现
//接口public interface ClazzService {List<Clazz> findAll();}//实现@Service@Transactionalpublic class ClazzServiceImpl implements ClazzService {@Autowiredprivate ClazzDAO clazzDAO;@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)@Overridepublic List<Clazz> findAll() {return clazzDAO.findAll();}}
8、开发Controller
@RestControllerpublic class ClazzController {@Autowiredprivate ClazzService clazzService;//查询所有@RequestMapping("findAll")public List<Clazz> findAll(){return clazzService.findAll();}}
9、启动项目访问测试
http://localhost:8989/项目名/findAll
三、本地测试
往往在开发过程中业务代码课程非常复杂频繁启动服务器测试,非常麻烦!这个时候使用本地测试就是一个很好的解决方案,springboot也提供了本地测试解决方案!
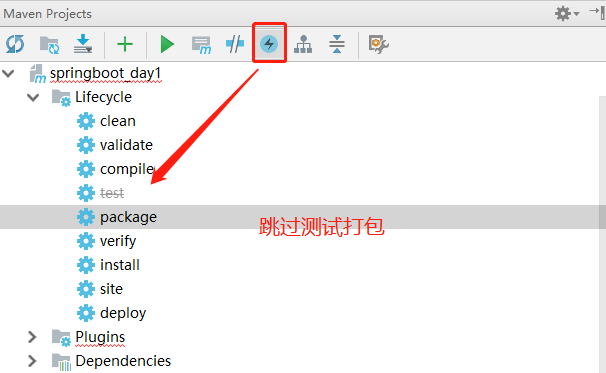
1、引入测试依赖
<!--spring-boot-stater-test junit 单元 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><!--只能在测试时可用,test为包名--><scope>test</scope></dependency>
2、编写测试类
@SpringBootTest
- 修饰范围:用在类上
作用:用来启动本地Spring环境
@SpringBootTestpublic class TestEmpService {@Autowiredprivate EmpService empService;@Testpublic void test(){empService.findAll().forEach(emp-> System.out.println(emp));}}
四、热部署工具
为了进一步提高开发效率,springboot为我们提供了全局项目热部署,日后在开发过程中修改了部分代码以及相关配置文件后,不需要每次重启使修改生效,在项目中开启了springboot全局热部署之后只需要在修改之后等待几秒即可使修改生效。
1、项目中引入依赖
```java
<a name="otvot"></a>
#### 2、设置idea中支持自动编译java
# 只需要设置一次
# 1.开启自动编译
Preferences | Build, Execution, Deployment | Compiler -> 勾选上 Build project automatically 这个选项
# 2.开启允许在运行过程中修改文件
ctrl + alt + shift + / ——>选择1.Registry —-> 勾选 compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running 这个选项
<a name="GdTZA"></a>
#### 3、启动项目检测热部署是否生效
# 1. 启动出现如下日志代表生效java
2019-07-17 21:23:17.566 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] com.baizhi.InitApplication : Starting InitApplication on chenyannandeMacBook-Pro.local with PID 4496 (/Users/chenyannan/IdeaProjects/ideacode/springboot_day1/target/classes started by chenyannan in /Users/chenyannan/IdeaProjects/ideacode/springboot_day1)
2019-07-17 21:23:17.567 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] com.baizhi.InitApplication : The following profiles are active: dev
2019-07-17 21:23:17.612 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext@66d799c5: startup date [Wed Jul 17 21:23:17 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
2019-07-17 21:23:18.782 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8989 (http)
2019-07-17 21:23:18.796 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2019-07-17 21:23:18.797 INFO 4496 —- [ restartedMain] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet Engine: Apache Tomcat/8.5.20
**注意:日志出现restartedMain代表已经生效,在使用热部署时如果遇到修改之后不能生效,请重试重启项目在试**
<a name="cQDhf"></a>
### 五、日志处理
<a name="BEiPU"></a>
#### 1、引言
springboot框架 集成日志 logback 日志 <br /> Logback是由[log4j](https://baike.baidu.com/item/log4j/480673)创始人设计的又一个开源日志组件。目前,logback分为三个模块:logback-core,logback-classic和logback-access。是对log4j日志展示进一步改进!<br /> 总结:logback 也是一个开源日志组件 和 log4j作用一致 都是用来生成日志 logback更加轻量
<a name="HTFt7"></a>
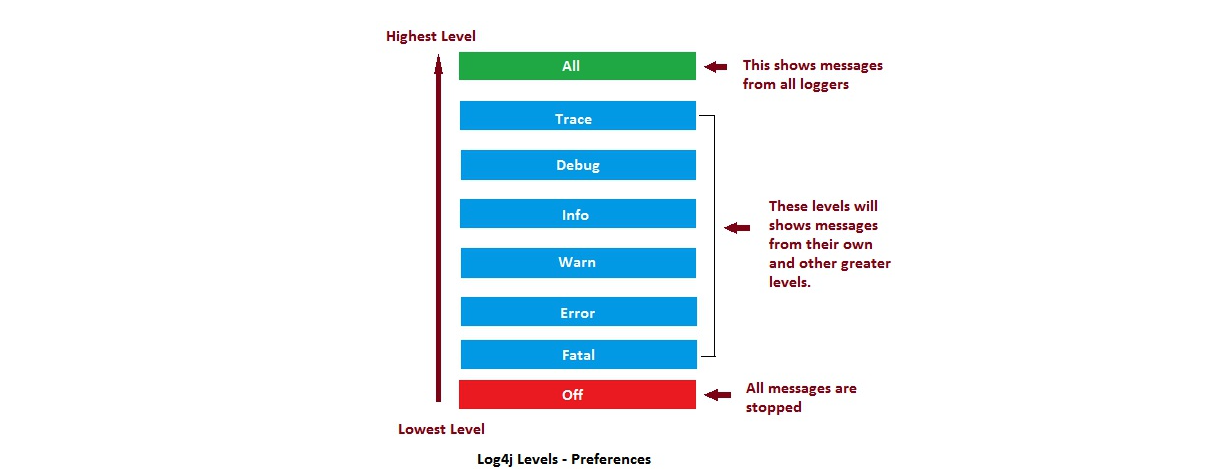
#### 2、日志的级别
java
> All < Trace < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < Fatal < OFF
- OFF | 关闭:最高级别,不打印日志。
- FATAL | 致命:指明非常严重的可能会导致应用终止执行错误事件。
- ERROR | 错误:指明错误事件,但应用可能还能继续运行。
- WARN | 警告:指明可能潜在的危险状况。
- INFO | 信息:指明描述信息,从粗粒度上描述了应用运行过程。
- DEBUG | 调试:指明细致的事件信息,对调试应用最有用。
- TRACE | 跟踪:指明程序运行轨迹,比DEBUG级别的粒度更细。
- ALL | 所有:所有日志级别,包括定制级别。
> 日志级别由低到高: 日志级别越高输出的日志信息越多
<a name="vPfzs"></a>
#### 3、项目中日志分类
# 日志分类: <br />- 一种是rootLogger(根全局日志) : 用来监听项目中所有的运行日志,包括引入依赖jar中的日志 <br />- 一种是logger(指定包级别日志) : 用来监听项目中指定包中的日志信息
<a name="eqCse"></a>
#### 4、配置日志
**注意:SpringBoot框架中默认根日志为INFO**java
logging:
level:
root: debug #指定根日志级别(一般不推荐修改根日志(默认为info),输出信息太多,推荐使用子日志)
com.baizhi.dao: debug #输出指定包的日志
com.baizhi.service: debug #输出指定的包的日志
file:
name: run.log #指定生成日志文件名称
path: ./ #将日志文件生成当前目录 (当前项目(非模块)的目录中)
<a name="YQMJb"></a>
#### 5、项目中使用日志java
@Controller
public class HelloController {
//声明日志成员
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class);
@RequestMapping(“/hello”)
@ResponseBody
public String hello(){
System.out.println(“======hello world=======”);
//若配置文件设置为INFO级别,就不会打印:logger.debug(“DEBUG,{}”,”信息”)
logger.debug(“DEBUG,{}”,”信息”);
logger.info(“INFO,{}”,”信息”);
logger.warn(“WARN,{}”,”信息”);
logger.error(“ERROR,{}”,”信息”);
return “hello”;
}
}
<a name="EH4oG"></a>
### 六、切面编程
<a name="rgeEa"></a>
#### 1、引言
springboot是对原有项目中spring框架和springmvc的进一步封装,因此在springboot中同样支持spring框架中AOP切面编程,不过在springboot中为了快速开发仅仅提供了注解方式的切面编程.java
===================用户业务逻辑=================
用户业务
UserService
void save(User user)
void delete(Integer id);
User queryById(Integer id);
….
UserServiceImpl implement UserService
void save(User user){
sout(“=============”);//业务功能-1
sout(“*“);//业务功能-2
…
userDao.save(user);
}
void delete(Integer id){
sout(“=============”);//业务功能-1
sout(“*“);//业务功能-2
……
userDao.delete(id);
}
User queryById(Integer id){
sout(“=============”);//业务功能-1
sout(“*“);//业务功能-2
…..
return userDao.queryById(id)
}
=================用户业务逻辑======================
加入新的功能:
保存|删除|修改|查询用户之前: 打印输出一句话 “===========”
保存|删除|修改|查询用户之前: 打印输出一句话 “*“
================================================
问题:
1.现有业务层开发存在问题
a.—>额外功能代码存在大量冗余?
b.—>每个方法都需要书写一遍额外功能代码不利于后续项目维护?
**# Spring 框架**java
AOP: Aspect(切面) Oriented(面向) Programmaing 面向切面编程
Aspect (切面) = Advice(通知) + 切入点(Pointcut)
Advice 通知:业务逻辑中一些附加操作称之为通知。前置通知:核心功能执行之前执行 后置通知:核心功能执行之后执行
环绕通知:核心功能执行前后都执行一次 Pointcut 切入点:配置通知应用于项目中那些业务操作 Aspect 切面 = 附加操作(Advice) + 切入点(Pointcut)(配置) 1.类 implement xxAdvice接口 2.XML进行配置
**# SpringBoot框架 现有spring框架 进一步封装**java
1.无xml配置 一切皆java配置
AOP: 面向切面编程
Aspect 切面 = Advice(通知) + 切入点
1.开发附加操作 Advice
2.配置切入点&组装切面
```
# 面向切面编程步骤
1.引入aop切面编程依赖
2.在springboot项目中新建config(配置)包@Configuration //修饰范围: 只能用在类上 作用: 代表这是一个spring的配置类 spring.xml<br /> @Aspect //修饰范围: 只能用在类上 作用:代表这个类是一个切面类 <aop:config><br /> MyAspectConfig(自定义切面类) 配置类{//@Before: 代表这个方法是一个前置附加操作<br /> //@After : 代表这个方法是一个后置附加操作<br /> 注意: 使用@Before 和 @After注解声明方法上加入一个参数 定义一个参数 JointPoint 连接点<br /> //@Around: 代表这个方法是一个环绕附加操作<br /> value属性: 用来书写切入点表达式<br /> 注意: 使用@Around注解 在方法定义时声明一个参数: ProceedingJoinPoint 处理过程中连接点@Before("execution(* com.baizhi.service.*.*(..))")<br /> public void before(){<br /> sout("===========")<br /> }<br /> }
2、引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId></dependency>
3、相关注解
# 切面注解- @Aspect 用来类上,代表这个类是一个切面- @Before 用在方法上代表这个方法是一个前置通知方法- @After 用在方法上代表这个方法是一个后置通知方法- @Around 用在方法上代表这个方法是一个环绕的方法
4、前置切面
@Aspect //代表这个类是一个切面配置类@Configuration //代表当前这个类是一个spring的配置类public class MyAspect {//@Before:代表这是一个核心业务逻辑执行之前附加操作 value:用来书写切入点表达式,配置附加操作在哪里生效@Before("execution(* com.baizhi.service.*.*(..))")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){ //JointPoint:连接点System.out.println("前置通知");joinPoint.getTarget(); //获取目标对象joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); //获取目标对象的方法joinPoint.getSignature(); //获取方法签名joinPoint.getArgs(); //获取方法参数}}
5、后置切面
@Aspect@Configurationpublic class MyAspect {@After("execution(* com.baizhi.service.*.*(..))")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){System.out.println("后置通知");joinPoint.getTarget(); //目标对象joinPoint.getSignature(); //方法签名joinPoint.getArgs(); //方法参数}}
注意:前置通知和后置通知都没有返回值,方法参数都为joinpoint
6、环绕切面
@Aspect@Configurationpublic class MyAspect {@Around("execution(* com.baizhi.service.*.*(..))")//返回值作用: 用来将业务方法返回结果返回给调用者public Object before(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { //ProceedingJoinPoint 处理过程中连接点System.out.println("进入环绕通知");proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget(); //目标对象proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature(); //方法签名proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs(); //方法参数Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); //放行执行目标方法,如果不放行,就只会执行前置、后置通知,不会执行目标方法System.out.println("目标方法执行之后回到环绕通知");return proceed; //返回目标方法返回值}}
注意:环绕通知存在返回值,参数为ProceedingJoinPoint,如果执行放行,不会执行目标方法,一旦放行必须将目标方法的返回值返回,否则调用者无法接受返回数据
7、切入点表达式
//切入点表达式:1.execution:方法级别切入点表达式 save update 运行效率越低2.within:类级别切入点表达式: 控制越粗 运行效率3.基于注解的切入点表达式:@annotation(com.baizhi.annotations.xxx)@Around("execution(* com.baizhi.service.*.*(..))")//@Around("within(com.baizhi.service.*)")//@Around("@annotation(com.baizhi.annotations.MyAdvice)") //扫描有MyAdvice注解的类,切入public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {System.out.println("==========进入环绕的前置操作===========");System.out.println("当前执行类: "+proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget());System.out.println("方法名: "+proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName());//放行目标方法执行Object proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();//继续处理 业务逻辑方法执行System.out.println("==========进入环绕的后置操作===========");return proceed;}
//创建注解,指定运行时生效@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.METHOD)public @interface MyAdvice {}@Servicepublic class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{@Override@MyAdvice //指定注解public String find(String name) {System.out.println("处理find核心业务逻辑,调用DAO~~");return name;}}
七、文件上传下载
1、文件上传
用户访问当前系统,将自己本地计算机中文件通过浏览器上传到当前系统所在的服务器过程中称之为文件的上传
文件上传:用户将自己计算机中文件上传到项目所在服务器过程、文件服务器、OSS 称之为文件上传
2、准备上传页面
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/file/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"><input type="file" name="file"><input type="submit" value="上传"></form><!--1. 表单提交方式必须是post2. 表单的enctype属性必须为multipart/form-data3. 后台接受变量名字要与文件选择name属性一致-->
3、编写控制器
方式一:不推荐
@Controller@RequestMapping("file")public class FileController {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileController.class);/*** 用来测试文件上传 - 这种方式:不能用于jar包部署,不能获取到上传文件的路径,jar包没法访问,war包会解压后再访问* 注意:这种方式存在局限性,不推荐在使用这种方式进行文件上传了* @return*/@RequestMapping("upload")public String upload(MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {//定义:接收文件对象 multipartFile file变量名要与form中input type="file"标签name属性名一致//文件名String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();log.debug("文件名: {}", originalFilename);log.debug("文件大小: {}", file.getSize());log.debug("文件类型: {}", file.getContentType());//1.根据相对 上传 "upload" 获取绝对路径(真实路径) /users/桌面.... 服务器: /home/springboot_day4..String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");log.debug("获取绝对路径: {}", realPath);//2.上传文件 参数1: 将文件写入到那个目录 aa.txt .md xxx.xxx.xxx.md//修改文件名String ext = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));String newFileName = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date()) + ext;file.transferTo(new File(realPath, newFileName));return "redirect:/upload.jsp";}}
方式二:推荐
# 配置文件指定文件上传位置file:upload:dir: /Users/chenyn/imgs # 指定本地测试上传目录@Controller@RequestMapping("file")public class FileController {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileController.class);@Value("${file.upload.dir}")private String realPath; //另外指定服务器上的文件存放位置,不需要读取jar/war包路径/*** 第二种文件上传* 注意: 这种方式适用于任何一种部署方式 推荐使用这种方式* @param file* @return* @throws IOException*/@RequestMapping("uploadByJarDeploy")public String uploadByJarDeploy(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {//文件名String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();log.debug("文件名: {}", originalFilename);log.debug("文件大小: {}", file.getSize());log.debug("文件类型: {}", file.getContentType());//改名String ext = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));String newFileName = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date()) + ext;//上传文件到哪file.transferTo(new File(realPath,newFileName));return "redirect:/upload.jsp";}}
4、修改文件上传大小
#上传时出现如下异常: 上传文件的大小超出默认配置 默认10Mnested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.FileUploadBase$SizeLimitExceededException: the request was rejected because its size (38443713) exceeds the configured maximum (10485760)#修改配置文件上传文件大小:spring:http:multipart:max-request-size: 209715200 #用来控制文件上传大小的限制max-file-size: 209715200 #用来指定服务端最大文件大小spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=500MB #运行请求传递文件大小默认为10Mspring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=500MB #运行服务器可以处理的最大文件大小默认为10M
5、文件下载
**文件下载:将服务器某个资源文件下载到用户本地计算机过程称之为文件下载**<br />
6、提供下载文件链接
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/file/download?fileName=HELP.md">HELP.md</a><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/file/download?fileName=readme.txt">readme.txt</a><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/file/download?fileName=项目介绍.md">项目介绍.md</a>
7、开发控制器
# 配置文件server:port: 8989servlet:context-path: /day6jsp:init-parameters:development: truespring:mvc:view:prefix: /suffix: .jspfile:download:dir: E:/Java/百知教育/springboot-2021-版本资料/codes/springboot_day6/download # 指定下载目录测试环境#dir: /home/download 生产环境
@Controller@RequestMapping("file")public class FileController {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileController.class);@Value("${file.download.dir}") //读取配置文件private String realPath;/*** 文件下载* @param fileName*/@RequestMapping("download")public void download(String fileName, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {log.debug("当前下载文件名为: {}",fileName);log.debug("当前下载文件目录: {}",realPath);//1.去指定目录中读取文件File file = new File(realPath, fileName);//2.将文件读取为文件输入流FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);//2.5 获取响应流之前 一定要设置以附件形式下载 attachment:附件,否则会再浏览器直接打开文件,而不是下载文件response.setHeader("content-disposition","attachment;filename="+ URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8"));//3.获取响应输出流ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();//4.输入流复制给输出流/*int len=0;byte[] b = new byte[1024];while(true){len = is.read(b);if(len==-1)break;os.write(b,0,len);}*///5.释放资源//is.close();FileCopyUtils.copy(is,os); //会自动释放资源}}
8、下载注意点
# 1、必须注入依赖,否则访问download.jsp,页面会弹窗下载框,下载该jsp文件
<!--tomcat解析jsp--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId><artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId></dependency>
# 2、手动新增的webapp包,包上没有小蓝点,需要按以下方式设置,否则访问download.jsp,报404
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43080036/article/details/87273538
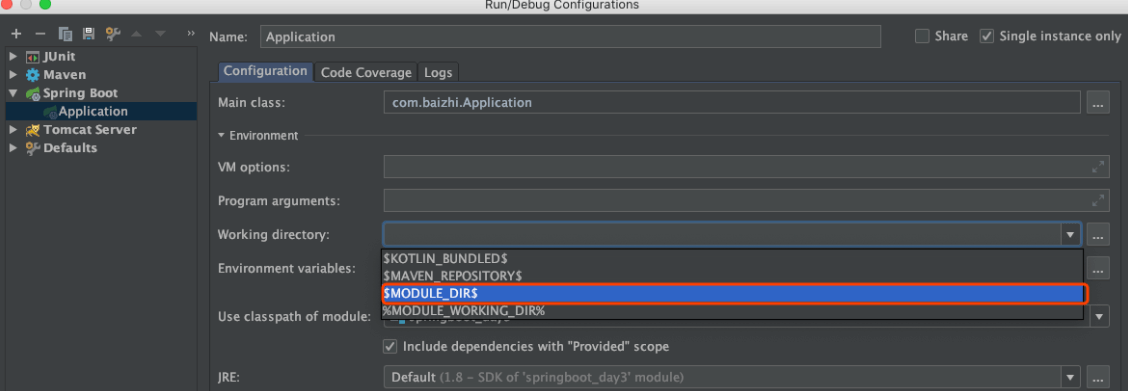
# 3、启动之前需要设置$MODULE_DIR$,否则访问download.jsp,报404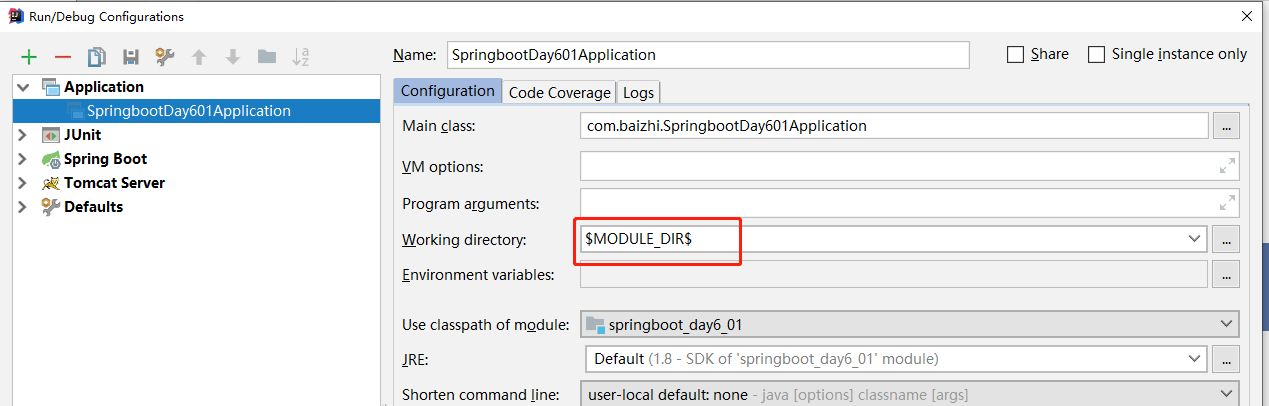
八、拦截器
1、开发拦截器
/*** 自定义拦截器器1*/public class MyInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyInterceptor1.class);//pre handler 最先执行//参数3: handler 当前请求请求的控制器方法对象 比如DemoController的demo方法@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {log.debug("handler: {} ", handler);log.debug("===========1=========");//response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/403.jsp");return true;//true代表放行,false代表中断}//参数3: handler 当前请求请求的控制器方法对象 DemoController#demo//参数4: modelAndView 模型和视图 当前请求访问方法的modelandview对象@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {log.debug("===========2=========");log.debug("view: {}",modelAndView.getViewName());}//参数3: handler 当前请求请求的控制器方法对象 DemoController#demo//参数4: exception 如果控制器出现异常时异常对象//这个方法: finally{}代码块 总是执行 无论请求正确,出现异常@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {log.debug("===========3=========");}}/*** 自定义拦截器2*/public class MyInterceptor2 implements HandlerInterceptor {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyInterceptor2.class);@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {log.debug("===========4=========");return true;}@Overridepublic void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {log.debug("===========5=========");}@Overridepublic void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {log.debug("===========6=========");}}
2、配置拦截器
@Configurationpublic class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {/*** 配置拦截器相关方法* @param registry*/@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor1()) //指定拦截器1.addPathPatterns("/**") //拦截所有.excludePathPatterns("/file/**") //排除哪些路径.order(1); //指定拦截器执行顺序。int 类型数字: 默认按照自然排序执行,数字相同时,按照配置顺序执行registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor2()) //指定拦截器2.addPathPatterns("/login","/user") //拦截指定.excludePathPatterns("/file/**").order(2);//1 4 5 2 6 3}}
注意:order用来执行多个拦截器的执行顺序,order书写是自然数,按照自然数顺序执行
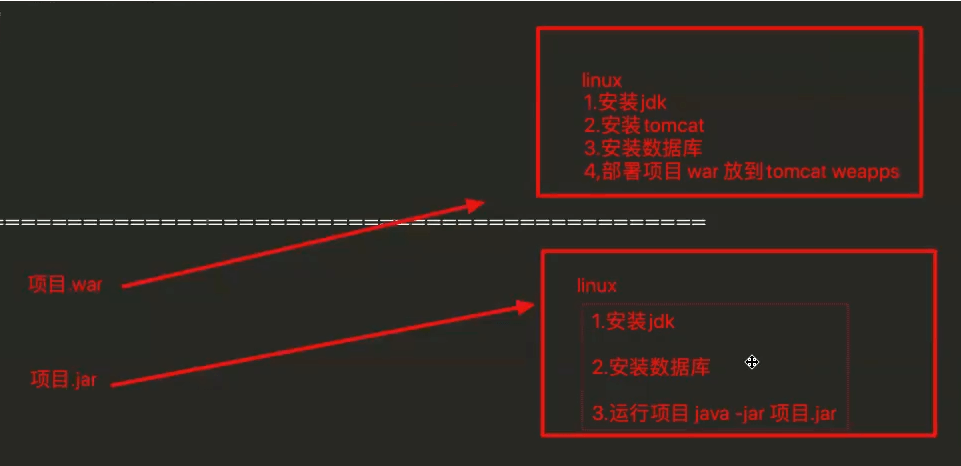
九、war包部署
1、设置打包方式为war
执行项目打包的方式为 “war” 默认创建springboot项目打包都是jar
修改项目pom.xml:
2、在插件中指定入口类
<build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId><!--使用热部署出现中文乱码解决方案--><configuration><fork>true</fork><!--增加jvm参数--><jvmArguments>-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8</jvmArguments><!--指定入口类--><mainClass>com.baizhi.Application</mainClass></configuration></plugin></plugins></build>
3、排除内嵌的tomcat
<!--tomcat解析jsp--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId><artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId><!--provided当前idea环境可用,打包不参与打包--><scope>provided</scope></dependency><!--去掉内嵌的tomcat依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId><scope>provided</scope></dependency>
4、配置入口类
//1.继承SpringBootServletInitializer: 不在使用内嵌容器启动,使用外部tomcat容器启动//2.覆盖configure方法@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringbootDay6Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringbootDay6Application.class, args);}//配置入口类是谁@Overrideprotected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {return builder.sources(SpringbootDay6Application.class);}}
5、打包测试
# 一旦使用war包部署注意:
- 1. application.yml 中配置port、context-path均失效
- 2. 访问时使用打成war包的名字和外部tomcat端口号进行访问项目
十、Jar包部署(推荐)
1、设置打包方式为jar
**<packaging>jar</packaging>**<br />**注意:默认方式也是jar**
2、执行打包
3、测试访问
- 注意:springboot部署jsp时,插件版本必须指定为1.4.2版本,并进行jsp打包配置才可以,其他版本均不支持!!!
4、修改插件版本
在项目的pom.xml配置文件中build标签中修改<plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId><!--打包jsp模板时,必须使用1.4.2插件--><version>1.4.2.RELEASE</version></plugin></plugins>
5、指定jsp打包配置
在项目的pom.xml配置文件中build标签中加入配置<build><!--执行jsp文件打包位置--><resources><!-- 打包时将jsp文件拷贝到META-INF目录下--><resource><!-- 指定resources插件处理哪个目录下的资源文件 --><directory>src/main/webapp</directory><!--指定必须要放在此目录下才能被访问到--><targetPath>META-INF/resources</targetPath><includes><include>**/**</include></includes></resource><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/**</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource></resources></build>
6、启动jar包
java -jar 对应jar文件名字 nohup &
第五章 Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf是一个用于web和独立环境的现代服务器端Java模板引擎。
—摘自官网https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf是跟Velocity、FreeMarker类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代JSP,相较与其他的模板引擎相比, Thymeleaf在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。
集成Thymeleaf模板
引入依赖
编写配置
spring: thymeleaf: cache: false # 关闭缓存 prefix: classpath:/templates/ #指定模板位置 suffix: .html #指定后缀
编写控制器测试
@Controller //一定要是@Controller 不能再使用@RestController注解 @RequestMapping(“hello”) public class HelloController { @GetMapping(“hello”) public String hello(){ System.out.println(“测试与 thymeleaf 的集成”); return “index”; } }
在templates目录中定义模板
测试访问
http://localhost:8989/springboot_day3/hello/hello
查看结果
模板基本语法
展示单个数据
设置数据
model.addAttribute(“name”,”张三”); 或 request.setAttribute(“name”,”小黑”);
获取数据
解析含有html标签数据
model.addAttribute(“name”,”张三“); model.addAttribute(“username”,”小陈”);
- 直接获取原样输出
获取并解析
将数据赋值给表单元素
总结 - 1.使用 th:text=”${属性名}” 获取对应数据,获取数据时会将对应标签中数据清空,因此最好是空标签 - 2.使用 th:utext=”${属性名}” 获取对应的数据,可以将数据中html先解析在渲染到页面 - 3.使用 th:value=”${属性名}” 获取数据直接作为表单元素value属性
展示对象数据
model.addAttribute(“user”,new User(“21”,”xiaochen”,23,new Date())); id: name: age: bir: ==== 日期格式化
条件展示数据
model.addAttribute(“user”,new User(“21”,”xiaochen”,23,new Date()));
青年
青年
# 运算符
gt:great than(大于)>
ge:great equal(大于等于)>=
eq:equal(等于)==
lt:less than(小于)<
le:less equal(小于等于)<=
ne:not equal(不等于)!=
展示多条数据
- 直接遍历集合
遍历时获取遍历状态
- - 获取遍历次数 count 从1开始 index 从0开始
- - 获取当前遍历是否是奇数行
- - 获取当前遍历是否是偶数行
- - 获取当前集合的总条数
引入静态资源
# 使用thymeleaf模板项目中静态资源默认放在resources路径小static目录中
项目中放入对应静态资源
- 页面中引入 注意: @{/}代表通过thymeleaf语法动态获取应用名
在js代码中获取项目名
注意:[[书写thymeleaf语法]],这里[[]]是thymeleaf内嵌表达式
第六章 RestFul
1、引言
REST全称是Representational State Transfer,中文意思是表述(编者注:通常译为表征)性状态转移。 它首次出现在2000年Roy Fielding的博士论文中,Roy Fielding是HTTP规范的主要编写者之一。 他在论文中提到:”我这篇文章的写作目的,就是想在符合架构原理的前提下,理解和评估以网络为基础的应用软件的架构设计,得到一个功能强、性能好、适宜通信的架构。REST指的是一组架构约束条件和原则。” 如果一个架构符合REST的约束条件和原则,我们就称它为RESTful架构。
RestFul:是一种以网络为基础构架一种架构风格,一个架构符合Rest设计原则和约束成这个架构为RestFul。
Rest 词:更新技术 组件 服务,让我们web请求能够利用web中标准和能力更好描述架构
REST本身并没有创造新的技术、组件或服务,而隐藏在RESTful背后的理念就是使用Web的现有特征和能力, 更好地使用现有Web标准中的一些准则和约束。虽然REST本身受Web技术的影响很深, 但是理论上REST架构风格并不是绑定在HTTP上,只不过目前HTTP是唯一与REST相关的实例。 所以我们这里描述的REST也是通过HTTP实现的REST。
2、总结
Restful 一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,只是提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。它主要用于客户端和服务器交互类的软件。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制
web开发:实现所有功能
restful:软件设计风格 标准 简洁 层次 优雅
rest设计原则 和 约束架构称之为restFul
3、URL定义
- 资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
- 一首歌 一张图片 数据库一条记录
资源操作:使用POST(添加)、DELETE(删除)、PUT(修改)、GET(查询),使用不同请求方法对资源进行操作。
- http://127.0.0.1/item/saveUser.action 新增,POST
- http://127.0.0.1/item/updateUser.action 更新,PUT
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteUser.action?id=1 删除,DELETE**注意:传统的操作是没有问题的,大神认为是有问题的,有什么问题呢?你每次请求的接口或者地址,都在做描述,例如查询的时候用了queryUser,新增的时候用了saveUser,修改的时候用了updateUser,其实完全没有这个必要,我使用了get请求,就是查询,使用post请求,就是新增的请求,PUT就是修改,delete就是删除,我的意图很明显,完全没有必要做描述,这就是为什么有了restful。
2)使用RESTful操作资源
【GET】 /users # 查询用户信息列表
- 【GET】 /users/1001 # 查看某个用户信息
- 【POST】 /users # 新建用户信息
- 【PUT】 /users/1001 # 更新用户信息(全部字段)
- 【PATCH】 /users/1001 # 更新用户信息(部分字段)
- 【DELETE】 /users/1001 # 删除用户信息
4、Rest API设计风格原则
# 1. 使用名词而不是动词
- 不要使用,如:
/getAllUsers get /users get /users/002
/createNewUser post /users
/deleteAllUser delete /users/001
# 2. Get方法和查询参数不应该涉及状态改变
- 使用PUT, POST 和DELETE 方法 而不是 GET 方法来改变状态,不要使用GET进行状态改变
# 3. 使用复数名词
- 不要混淆名词单数和复数,为了保持简单,只对所有资源使用复数。
如:
/cars 而不是 /car
/users 而不是 /user
/products 而不是 /product
/settings 而不是 /setting
/orders 而不是 /order
# 4. 使用子资源表达关系
- 如果一个资源与另外一个资源有关系,使用子资源:
如:
GET /cars/711/drivers/ 返回 car 711的所有司机
GET /cars/711/drivers/4 返回 car 711的4号司机
GET /users/11/pets 返回 user 11的所有宠物
GET /users/11/pets/2 返回 user 11的2号宠物
# 5. 使用Http头声明序列化格式
- 在客户端和服务端,双方都要知道通讯的格式,格式在HTTP-Header中指定
如:
Content-Type 定义请求格式
Accept 定义系列可接受的响应格式
# 6. 为集合提供过滤、排序、选择和分页等功能
- Filtering过滤:使用唯一的查询参数进行
GET /cars?color=red 返回红色的cars
GET /cars?seats<=2 返回小于两座位的cars集合
Sorting排序:允许针对多个字段排序
GET /cars?sort=-manufactorer,+model
这是返回根据生产者降序和模型升序排列的car集合Field selection
移动端能够显示其中一些字段,它们其实不需要一个资源的所有字段,给API消费者一个选择字段的能力,这会降低网络流量,提高API可用性。
GET /cars?fields=manufacturer,model,id,color
- Paging分页
使用 limit 和offset.实现分页,缺省limit=20 和offset=0;
GET /cars?offset=10&limit=5
为了将总数发给客户端,使用订制的HTTP头: X-Total-Count.
链接到下一页或上一页可以在HTTP头的link规定,遵循Link规定:
Link: https://blog.mwaysolutions.com/sample/api/v1/cars?offset=15&limit=5; rel=”next”,
https://blog.mwaysolutions.com/sample/api/v1/cars?offset=50&limit=3; rel=”last”,
https://blog.mwaysolutions.com/sample/api/v1/cars?offset=0&limit=5; rel=”first”,
https://blog.mwaysolutions.com/sample/api/v1/cars?offset=5&limit=5; rel=”prev”,
# 7. 版本化你的API 支付宝 v1 v2 v3
- 使得API版本变得强制性,不要发布无版本的API,使用简单数字,避免小数点如2.5.
一般在Url后面使用?v
/blog/api/v1
# 8. 使用Http状态码处理错误
- 如果你的API没有错误处理是很难的,只是返回500和出错堆栈不一定有用
- Http状态码提供70个出错,我们只要使用10个左右:
200 – OK – 一切正常<br />201 – OK – 新的资源已经成功创建
204 – OK – 资源已经成功删除<br />304 – Not Modified – 客户端使用缓存数据
400 – Bad Request – 请求无效,需要附加细节解释如 "JSON无效"<br />401 – Unauthorized – 请求需要用户验证
403 – Forbidden – 服务器已经理解了请求,但是拒绝服务或这种请求的访问是不允许的。<br />404 – Not found – 没有发现该资源
422 – Unprocessable Entity – 只有服务器不能处理实体时使用,比如图像不能被格式化,或者重要字段丢失。<br />500 – Internal Server Error – API开发者应该避免这种错误。
使用详细的错误包装错误: 状态码 数据 header头信息
{"errors": [{"userMessage": "Sorry, the requested resource does not exist","internalMessage": "No car found in the database","code": 34,"more info": "http://dev.mwaysolutions.com/blog/api/v1/errors/12345"}]}
5、Rest API案例
//@RestController: 专用于restful 风格的注解 = @Controller + @ResponseBody @controller:专用于传统开发注解@RestController //代表类中所有的方法均转为json,所以方法上不需要再添加@ResponseBody@RequestMapping("/v1/users") //符合使用复数名词public class UserController {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);// ResponeEntity: springmvc 封装一个专用于restful 响应类 这个类在响应时可以提供响应的状态码,同时还可以自定义响应头信息// HttpStatus: springmvc 封住一个枚举类型类,这个类中都是网络中状态码/*** 查询某个用户详细* @param id* @return*///@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)@GetMapping("/{id}") //@RequestMapping:子类注解,使用GETMapping代表只能使用GET方式访问到当前请求//@ResponseBody //将控制器方法返回值转为json,若类上有注解@RestController,则方法上不需要再添加@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<User> user(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ //注解: PathVariable:代表在路径中获取请求参数log.info("本次id: {}",id);User user = null;try {user = new User(id, "小陈", 2300.23, new Date());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return new ResponseEntity<User>(user,HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);}return new ResponseEntity<>(user,HttpStatus.OK);}/*** 用户列表* @return*/@GetMapping//@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<List<User>> users(){ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();users.add(new User(21,"小王",2300.23,new Date()));users.add(new User(24,"小金豆",3400.23,new Date()));return new ResponseEntity<>(users,HttpStatus.OK);}/*** 添加用户*/@PostMapping//@ResponseBody //@ResponseBody:将方法返回值转为json格式数据并响应请求 @RequestBody: 接收请求json格式数据 将json格式数据转为对象public ResponseEntity<Void> save(@RequestBody User user){log.info("name:{} salary:{} bir:{}",user.getName(),user.getSalary(),user.getBir());//调用业务方法return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT); //没有内容}/*** 更新用户* @param user*/@PutMapping("/{id}")//@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<Void> update(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,@RequestBody User user){log.info("id:{} ",id);log.info("name:{} salary:{} bir:{}",user.getName(),user.getSalary(),user.getBir());//调用业务方法return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT); //没有内容}/*** 删除用户信息* @param id*/@DeleteMapping("/{id}")//@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<Void> delete(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){log.info("本次id: {}",id);return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT); //没有内容}/*** 获取这个人所有宠物*/@GetMapping("/{id}/pets")public ResponseEntity<List<Pet>> pets(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){log.info("查询那个人id: {}",id);List<Pet> pets = Arrays.asList(new Pet(21, "小红帽", 23), new Pet(22, "小猪", 22));return new ResponseEntity<>(pets, HttpStatus.OK);}/*** 获取这个人某个宠物*/@GetMapping("/{id}/pets/{pid}")public ResponseEntity<Pet> pet(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,@PathVariable("pid") Integer petId){log.info("查询那个人id: {}",id);Pet pet = new Pet(21, "小红帽", 23);return new ResponseEntity<>(pet, HttpStatus.OK);}}
第七章 异常处理
1、传统开发的异常处理
@Componentpublic class GlobalExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {//resolveExcpetion: 当控制器中任意一个方法出现异常时,如果该控制器的方法没有自己异常处理(try...catch),则会进入当前方法//注意:在异常处理这个方法中 完成自定义异常处理//参数1: request 当前请求对象//参数2: response 当前请求对应响应对象//参数3: 当前出现错误的方法对象//参数4: 出现异常的异常对象//返回值: modelAndview 模型和视图@Overridepublic ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Object handler,Exception ex) {System.out.println("这是全局异常处理....");System.out.println("当前异常为: "+ex);ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();//针对不同异常类型跳转不同页面if(ex instanceof UserNameNotFoundException){modelAndView.setViewName("error");return modelAndView;}modelAndView.setViewName("500");return modelAndView;}}
2、RestFul的异常处理
/*** 全局异常处理之RestFul*/@ControllerAdvice //作用于所有controllerpublic class GlobalExceptionResolver {//处理指定异常@ExceptionHandler(value = IllegalNumberException.class)@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<String> illegalNumberExceptionHandler(Exception ex) {System.out.println("进入非法参数异常处理");return new ResponseEntity<String>(ex.getMessage(), HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);}// 处理exception子类异常// 用在方法上 作用:用来处理指定异常 value属性:用来指定处理异常类型@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)@ResponseBodypublic ResponseEntity<String> exceptionHandler(Exception ex) {System.out.println("进入自定义异常处理");return new ResponseEntity<>(ex.getMessage(), HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);}}//自定义异常public class IllegalNumberException extends RuntimeException{public IllegalNumberException(String message) {super(message);}}@RestController@RequestMapping("demos")public class DemoController {@GetMapping("/{id}")public ResponseEntity<String> demo(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {System.out.println("demo ok "+id);if(id<0){// 走illegalNumberExceptionHandler异常throw new IllegalNumberException("无效id,请检查!");}if(id==0){System.out.println(1/id); //走exceptionHandler异常}return new ResponseEntity<>("demo ok ", HttpStatus.OK);}}
CORS 跨域
CORS
- CORS是一个W3C标准,全称是”跨域资源共享”(Cross-origin resource sharing)。
- 它允许浏览器向跨源服务器,发出XMLHttpRequest(ajax)请求,从而克服了AJAX只能同源使用的限制
同源策略
- 同源策略[same origin policy]是浏览器的一个安全功能,不同源的客户端脚本在没有明确授权的情况下,不能读写对方资源。 同源策略是浏览器安全的基石。
源
- 源[origin]就是协议、域名和端口号。例如:http://www.baidu.com:80这个URL。
同源
- 若地址里面的协议、域名和端口号均相同则属于同源。
# 同源举例
- 例如判断下面的URL是否与 http://www.a.com/test/index.html 同源
http://www.a.com/dir/page.html ————->同源
http://www.child.a.com/test/index.html ->不同源,域名不相同
https://www.a.com/test/index.html ———>不同源,协议不相同
http://www.a.com:8080/test/index.html —>不同源,端口号不相同
哪些操作不受同源限制
- 页面中的链接,重定向以及表单提交是不会受到同源策略限制的;
- 跨域资源的引入是可以的。如嵌入到页面中的,
,,