资料来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Vf4y127N5?p=1
一、Spring框架概述
1、Spring 是轻量级的开源的 JavaEE 框架
2、Spring 可以解决企业应用开发的复杂性
3、Spring 有两个核心部分: IOC 和 Aop
- IOC:控制反转, 把创建对象过程交给 Spring 进行管理
- Aop:面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强
4、Spring 特点
- 方便解耦,简化开发
- Aop 编程支持
- 方便程序测试
- 方便和其他框架进行整合
- 方便进行事务操作
- 降低 API 开发难度
5、Spring5 入门案例
(1)创建普通 Java 工程
(2)导入 Spring5 相关 jar 包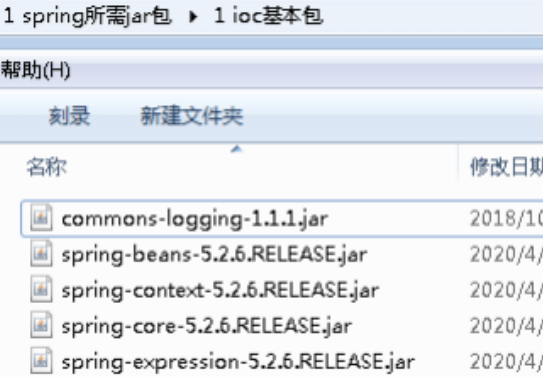
(3)创建普通类,在这个类创建普通方法
public class User {public void add() {System.out.println("add......");}}
(4)创建 Spring 配置文件,在配置文件配置创建的对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!--配置User对象创建--><bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring5.User"></bean></beans>
(5)进行测试代码编写
@Testpublic void testAdd() {//1、加载spring配置文件ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");//2、获取配置创建的对象User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);System.out.println(user);user.add();}
二、IOC 容器
1、IOC概述
(1)控制反转,把对象创建和对象之间的调用过程, 交给 Spring 进行管理
(2)使用 IOC 目的: 为了耦合度降低
(3)入门案例就是 IOC 实现
1、IOC底层原理
2、IOC接口(BeanFactory)
1)IOC 思想基于 IOC 容器完成, IOC 容器底层就是对象工厂
2)Spring 提供 IOC 容器实现两种方式:(两个接口)
① BeanFactory:IOC 容器基本实现,是 Spring 内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员进行使用
- 加载配置文件时候不会创建对象,在获取对象(使用)才去创建对象 ```java //1、加载spring配置文件,此时不会创建对象 BeanFactory context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“bean1.xml”); //2、获取配置时,才创建的对象 User user = context.getBean(“user”, User.class); System.out.println(user);
② **ApplicationContext**:BeanFactory 接口的子接口,提供更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人<br />员进行使用- **加载配置文件时候就会把在配置文件对象进行创建(启动服务器时,加载配置文件,创建对象)**3)ApplicationContext 接口有实现类<br />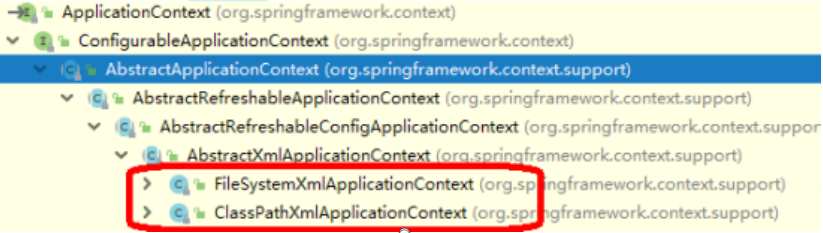<a name="zN2Vr"></a>## 3、IOC操作Bean管理(概念)1)什么是 Bean 管理<br />Bean管理指的是两个操作:Spring 创建对象、Spirng 注入属性<br /> 2)Bean 管理操作有两种方式- 基于 xml 配置文件方式实现- 基于注解方式实现<a name="NMmN3"></a>## 4、IOC操作Bean管理(基于xml)4.1 基于 xml 方式创建对象<br />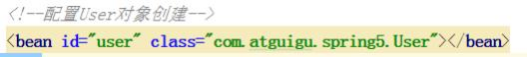<br />① 在 spring 配置文件中,使用 bean 标签,标签里面添加对应属性,就可以实现对象创建<br />② 在bean标签有很多属性,介绍常用的属性<br />* id 属性: 唯一标识<br />* class 属性:类全路径(包类路径)<br />③ 创建对象时候,默认也是执行无参数构造方法完成对象创建<br />4.2 基于 xml 方式注入属性<br />DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性<br />4.3 第一种注入方式:使用set 方法进行注入<br /> 步骤一:创建类,定义属性和对应的 set 方法```java/*** 演示使用set方法进行注入属性*/public class Book {// 创建属性private String bname ;private String bauthor ;// 创建属性对应的 set方法public void setBname(String bname) {this.bname = bname;}public void setBauthor(String bauthor) {this.bauthor = bauthor;}}
步骤二:在 spring 配置文件配置对象创建,配置属性注入
<!--2 set方法注入属性--><bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book"><!--使用property完成属性注入name: 类里面属性名称value:向属性注入的值--><property name="bname" value="易筋经"></property><property name="bauthor" value="达摩老祖"></property></bean>
4.4 第二种注入方式:使用有参数构造进行注入
步骤一:创建类,定义属性, 创建属性对应有参数构造方法
/*** 使用有参数构造注入*/public class Orders {// 属性private String oname ;private String address ;// 有参数构造public Orders(String oname,String address) {this.oname = oname;this.address = address;}}
步骤二:在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<!--3 有参数构造注入属性--><bean id="orders" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Orders"><constructor-arg name="oname" value="电脑"></constructor-arg><constructor-arg name="address" value="China"></constructor-arg></bean>
4.5 p 名称空间注入(了解)
使用 p 名称空间注入,可以简化基于 xml 配置方式
第一步:添加 p 名称空间在配置文件中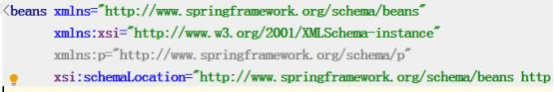
第二步:进行属性注入, 在 bean 标签里面进行操作
<!--2 set方法注入属性--><bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book" p:bname="九阳神功" p:bauthor="无名氏"></bean>
5、IOC操作Bean管理(xml注入其他类型属性)
5.1 字面量
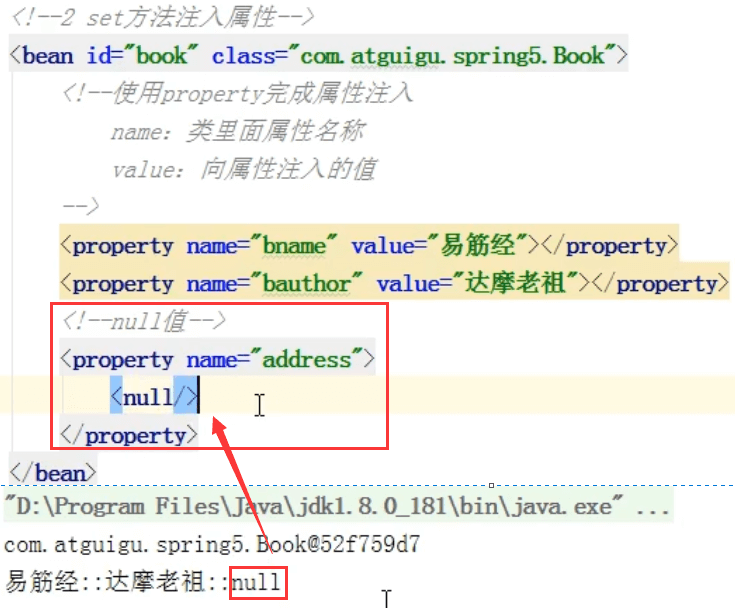
(1)null 值
<!--null值--><property name="address"><null/></property>
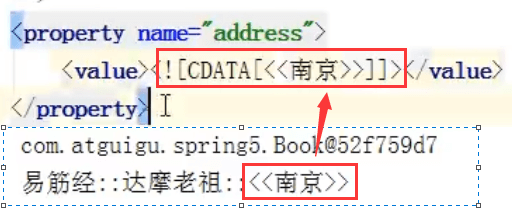
(2)属性值包含特殊符号
<!--属性值包含特殊符号方式一:把<>进行转义:<>方式二:把带特殊符号内容写到CDATA--><property name="address"><value><![CDATA[<<南京>>]]></value></property>
5.2 注入属性 - 外部 bean
(1)创建两个类 service 类和 dao 类
(2)在 service 调用 dao 里面的方法
(3)在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
public class UserService {// 创建UserDao类型属性,生成set方法private UserDao userDao;public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {this.userDao = userDao;}public void add() {System.out.println("service add...............");userDao.update();}}
<!--1 service对象创建--><bean id="userService" class="com.atguigu.spring5.service.UserService"><!--3 注入userDao对象name属性:UserService类里面的属性名称userDaoref属性:创建userDao对象bean标签的id值--><property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl"></property></bean><!--2 dao实现类的对象创建--><bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.atguigu.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
5.3 注入属性 - 内部 bean
(1)一对多关系:部门和员工
一个部门有多个员工, 一个员工属于一个部门
部门是一,员工是多
(2)在实体类之间表示一对多关系,员工表示所属部门,使用对象类型属性进行表示
// 部门类public class Dept {private String dname ;public void setDname(String dname) {this.dname = dname;}}// 员工类public class Emp {private String ename ;private String gender ;// 员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示private Dept dept ;public void setDept(Dept dept) {this.dept = dept;}public void setEname(String ename) {this.ename = ename;}public void setGender(String gender) {this.gender = gender;}}
(3)在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<!--内部bean--><bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp"><!--设置两个普通属性--><property name="ename" value="lucy"></property><property name="gender" value="女"></property><!--设置对象类型属性(此处也可以用外部bean实现)--><property name="dept"><bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept"><property name="dname" value="安保部"></property></bean></property></bean>
5.4 注入属性 - 级联赋值
(1)第一种写法
<!--级联赋值--><bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp"><!--设置两个普通属性--><property name="ename" value="lucy"></property><property name="gender" value="女"></property><!--级联赋值--><property name="dept" ref="dept"></property></bean><bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept"><property name="dname" value="财务部"></property></bean>
(2) 第二种写法
<!--级联赋值--><bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Emp"><!--设置两个普通属性--><property name="ename" value="lucy"></property><property name="gender" value="女"></property><!--级联赋值--><property name="dept" ref="dept"></property><property name="dept.dname" value="技术部"></property><!--此时需要生成getDept方法,否则报错--></bean><bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Dept"><property name="dname" value="财务部"></property></bean>
6、IOC操作Bean管理(xml注入集合属性)
6.1 注入数组类型属性
6.2 注入 List 集合类型属性
6.3 注入 Map 集合类型属性
(1)创建类,定义数组、list、map、set类型属性,生成对应set方法
public class Stu {//1、数组类型属性private String[] courses ;//2、list集合类型属性private List<String> list ;//3、map集合类型属性private Map<String,String> maps ;//4、set集合类型属性private Set<String> sets ;public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {this.sets = sets;}public void setCourses(String[] courses) {this.courses = courses;}public void setList(List<String> list) {this.list = list;}public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {this.maps = maps;}}
(2)在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--1 集合类型属性注入--><bean id="stu" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Stu"><!--数组类型属性注入--><property name="courses"><array><value>java 课程</value><value>数据库课程</value></array></property><!--list类型属性注入--><property name="list"><list><value>张三</value><value>小三</value></list></property><!--map类型属性注入--><property name="maps"><map><entry key="JAVA" value="java"></entry><entry key="PHP" value="php"></entry></map></property><!--set类型属性注入--><property name="sets"><set><value>MySQL</value><value>Redis</value></set></property></bean>

6.4 在集合里面设置对象类型值
// 课程类@ToStringpublic class Course {private String cname; // 课程名称public void setCname(String cname) {this.cname = cname;}}public class Stu {//1 数组类型属性private String[] courses;//2 list集合类型属性private List<String> list;//3 map集合类型属性private Map<String,String> maps;//4 set集合类型属性private Set<String> sets;// 学生所学多门课程private List<Course> courseList;public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) {this.courseList = courseList;}}
<!--创建多个course对象--><bean id="course1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course"><property name="cname" value="Spring5 框架"></property></bean><bean id="course2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Course"><property name="cname" value="MyBatis 框架"></property></bean><!--注入list集合类型,值是对象--><property name="courseList"><list><ref bean="course1"></ref><ref bean="course2"></ref></list></property>
6.5 把集合注入部分提取出来
(1)在 spring 配置文件中引入名称空间 util
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/utilhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
(2)使用 util 标签完成 list 集合注入提取
public class Book {private List<String> list;public void setList(List<String> list) {this.list = list;}public void test() {System.out.println(list);}}
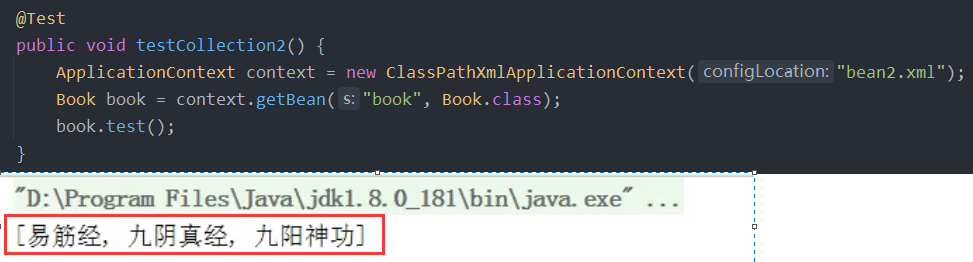
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入--><util:list id="bookList"><value>易筋经</value><value>九阴真经</value><value>九阳神功</value></util:list><!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用--><bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Book"><property name="list" ref="bookList"></property></bean>
7、IOC操作Bean管理(FactoryBean)
1、Spring 有两种类型 bean,一种普通 bean,另外一种工厂 bean(spring内置bean,如FactoryBean)
2、普通 bean:在配置文件中定义 bean 类型就是返回类型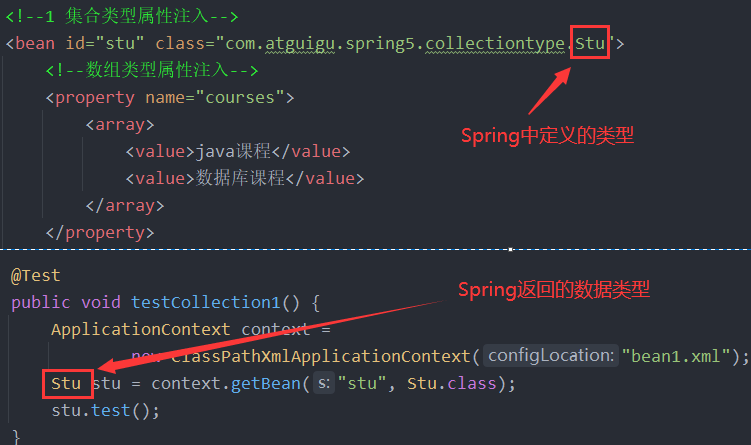
3、工厂 bean:在配置文件定义 bean 类型可以和返回类型不一样
第一步:创建类,让这个类作为工厂 bean,实现接口 FactoryBean
第二步:实现接口里面的方法,在实现的方法中定义返回的 bean 类型
public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<Course> {// 定义返回bean对象。此时返回的对象为Course,而不是MyBean@Overridepublic Course getObject() throws Exception {Course course = new Course();course.setCname("abc");return course;}@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {return null ;}@Overridepublic boolean isSingleton() {return false ;}}
<bean id="myBean" class="com.atguigu.spring5.factorybean.MyBean"> </bean>
@Testpublic void test3() {ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean3.xml");Course course = context.getBean("myBean", Course.class); // 若仍写MyBean.class,执行报错System.out.println(course); // 返回:Course{cname='abc'}}
8、IOC操作Bean管理(bean作用域)
1、在 Spring 里面,设置创建 bean 实例是单实例还是多实例
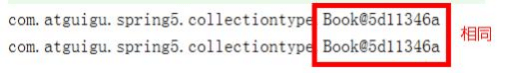
2、在 Spring 里面,默认情况下,bean 是单实例对象
public void testCollection2() {ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");Book book1 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);Book book2 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);System.out.println(book1);System.out.println(book2);}
3、如何设置单实例还是多实例
(1)在 spring 配置文件 bean 标签里面有属性(scope)用于设置单实例还是多实例
(2)scope 属性值
第一个值:singleton,默认值,表示是单实例对象
第二个值:prototype,表示是多实例对象
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入--><util:list id="bookList"><value>易筋经</value><value>九阴真经</value><value>九阳神功</value></util:list><!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用--><bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.collectiontype.Book" scope="prototype"><property name="list" ref="bookList"></property></bean>

(3)singleton 和 prototype 区别
第一:singleton单实例, prototype多实例
第二:设置scope值是singleton时候,加载spring配置文件时候就会创建单实例对象;设置scope值是 prototype时候,不是在加载spring配置文件时候创建对象,在调用getBean方法时候创建多实例对象
9、IOC 操作 Bean 管理(bean生命周期)
1、生命周期
(1)从对象创建到对象销毁的过程
2、bean 生命周期
(1)通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
(2)为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
(3)调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
(4)bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
(5)当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
3、演示 bean 生命周期
public class Orders {// 无参数构造public Orders() {System.out.println("第一步 执行无参数构造创建bean实例");}private String oname ;public void setOname(String oname) {this.oname = oname;System.out.println("第二步 调用set方法设置属性值");}// 创建执行的初始化的方法public void initMethod() {System.out.println("第三步 执行初始化的方法");}// 创建执行的销毁的方法public void destroyMethod() {System.out.println("第五步 执行销毁的方法");}}
<bean id="orders" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.Orders" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"><property name="oname" value="手机"></property></bean>
@Testpublic void testBean3() {// ApplicationContext context = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml");Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);System.out.println("第四步 获取创建bean实例对象");System.out.println(orders);// 手动让bean实例销毁context.close();}

4、bean 的后置处理器,bean 生命周期有七步
(1)通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
(2)为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
(3)把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization
(4)调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
(5)把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessAfterInitialization
(6)bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
(7)当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
5、演示添加后置处理器效果
(1)创建类,实现接口 BeanPostProcessor,创建后置处理器
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("在初始化之前执行的方法");return bean;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("在初始化之后执行的方法");return bean;}}
<!--配置后置处理器,会对xml配置文件中的所有bean实例加上后置处理器--><bean id="myBeanPost" class="com.atguigu.spring5.bean.MyBeanPost"></bean>
10、IOC操作Bean管理(xml自动装配)
1、什么是自动装配
(1)根据指定装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型), Spring 自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
2、演示自动装配过程
(1)根据属性名称自动注入
<!--实现自动装配bean标签属性autowire,配置自动装配autowire属性常用两个值:byName根据属性名称注入,注入值bean的id值和类属性名称一样byType根据属性类型注入--><bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.autowire.Emp" autowire="byName"><!--<propertyname="dept"ref="dept"></property>--></bean><bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.autowire.Dept"></bean>
(2)根据属性类型自动注入
<!--实现自动装配bean标签属性autowire,配置自动装配autowire属性常用两个值:byName根据属性名称注入,注入值bean的id值和类属性名称一样byType根据属性类型注入--><bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.autowire.Emp" autowire="byType"><!--<propertyname="dept"ref="dept"></property>--></bean><bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.autowire.Dept"></bean>
11、IOC 操作 Bean 管理(外部属性文件)
1、直接配置数据库信息
(1)配置德鲁伊连接池
(2)引入德鲁伊连接池依赖 jar 包
<!--直接配置连接池--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDb"></property><property name="username" value="root"></property><property name="password" value="root"></property></bean>
2、引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
(1)创建外部属性文件, properties 格式文件, 写数据库信息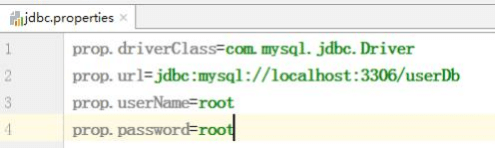
(2)把外部 properties 属性文件引入到 spring 配置文件中
引入 context 名称空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
在 spring 配置文件使用标签引入外部属性文件 ```java
<a name="H80J1"></a>## 12、IOC操作Bean管理(基于注解)1、什么是注解<br />(1)注解是代码特殊标记,格式: @注解名称(属性名称=属性值, 属性名称=属性值..)<br />(2)使用注解,注解作用在类上面,方法上面, 属性上面<br />(3)使用注解目的:简化 xml 配置<br />2、Spring 针对 Bean 管理中创建对象提供注解- @Component- @Service- @Controller- @Repository上面四个注解功能是一样的, 都可以用来创建 bean 实例<br />3、基于注解方式实现对象创建<br />第一步 引入依赖<br /><br />第二步:开启组件扫描```java<!--开启组件扫描:扫描包中的所有类1 如果扫描多个包,多个包使用逗号隔开2 扫描包上层目录--><context :component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan>
第三步:创建类,在类上面添加创建对象注解
// 在注解里面value属性值可以省略不写,// 默认值是类名称,首字母小写// UserService-- userService@Component(value = "userService") //<bean id="userService" class=".."/>public class UserService {public void add() {System.out.println("service add.......");}}
4、开启组件扫描细节配置
<!--示例1use-default-filters="false":表示现在不使用默认filter(默认扫描包中所有的类),此时使用自己配置filtercontext:include-filter,设置扫描哪些内容,此处只扫描带@Controller注解的类--><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu" use-default-filters="false"><context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/></context:component-scan><!--示例2下面配置扫描包所有内容context:exclude-filter:设置哪些内容不进行扫描,此处不扫描带@Controller注解的类--><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"><context :exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/></context:component-scan>
5、基于注解方式实现属性注入
(1)@Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
第一步:把service和dao对象创建,在service和dao类添加创建对象注解
第二步:在service注入dao对象,在service类添加dao类型属性, 在属性上面使用注解
@Servicepublic class UserService {// 定义dao类型属性// 不需要添加set方法// 添加注入属性注解@Autowiredprivate UserDao userDao ;public void add() {System.out.println("service add.......");userDao.add();}}
(2)@Qualifier:根据名称进行注入
这个@Qualifier 注解的使用,和上面@Autowired 一起使用
// 定义dao类型属性// 不需要添加set方法// 添加注入属性注解@Autowired // 根据类型进行注入@Qualifier(value = "userDaoImpl1") // 根据名称进行注入private UserDao userDao;
(3)@Resource:可以根据类型注入,可以根据名称注入
// @Resource // 根据类型进行注入@Resource (name = "userDaoImpl1") // 根据名称进行注入private UserDao userDao ;
(4)@Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "abc")private String name ;
6、完全注解开发
(1) 创建配置类,替代xml配置文件
@Configuration // 作为配置类,替代xml配置文件@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"})public class SpringConfig {}
(2) 编写测试类
@Testpublic void testService2() {// 加载配置类ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);System.out.println(userService);userService.add();}