一、线程回顾
1、初始化线程的4种方式

1)继承 Thread
2)实现 Runnable 接口
3)实现 Callable 接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)
4)线程池
方式1和方式2:主进程无法获取线程的运算结果。不适合当前场景
方式3:主进程可以获取线程的运算结果,但是不利于控制服务器中的线程资源。可以导致服务器资源耗尽。(只要new Thread就立即执行)
方式4:可以控制资源。根据当前系统调配最大线程量(最大线程200,当前1000个任务,就分5次执行。而不是1000个任务全部启动,不会让资源瞬间耗尽),根据通过如下两种方式初始化线程池
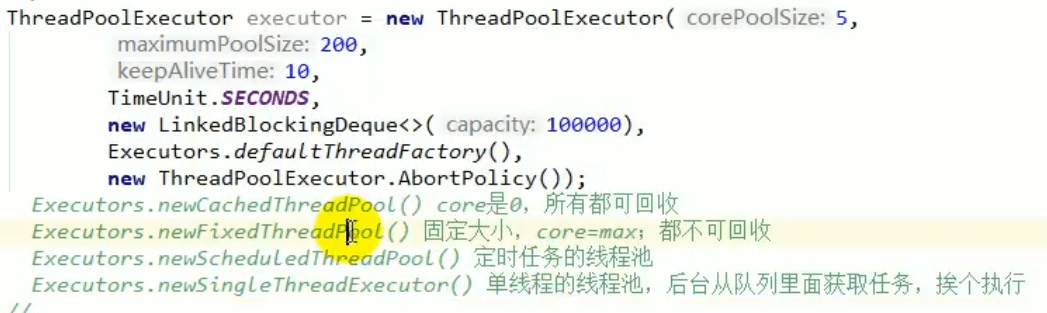
Executors.newFiexedThreadPool(3);//或者new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize,maximumPoolSize,keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,workQueue,threadFactory,handler);
通过线程池性能稳定,也可以获取执行结果,并捕获异常。但是,在业务复杂情况下,一个异步调用可能会依赖于另一个异步调用的执行结果。
2、线程池的七大参数

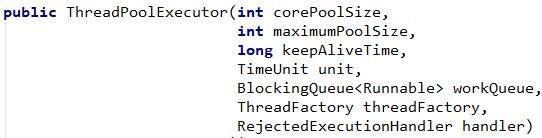
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set池中一直保持的线程的数量, 即使线程空闲。 除非设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the pool池中允许的最大的线程数* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than the core,* this is the maximum time that excess idle threads will wait for new tasks before terminating.当线程数大于核心线程数的时候, 线程在最大多长时间没有接到新任务就会终止释放,最终线程池维持在corePoolSize 大小* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument 时间单位* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.阻塞队列, 用来存储等待执行的任务, 如果当前对线程的需求超过了corePoolSize 大小, 就会放在这里等待空闲线程执行。* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor* creates a new thread创建线程的工厂, 比如指定线程名等* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached拒绝策略, 如果线程满了, 线程池就会使用拒绝策略。
运行流程:
1、线程池创建,准备好 core 数量的核心线程,准备接受任务
2、新的任务进来,用 core 准备好的空闲线程执行。
(1) core 满了,就将再进来的任务放入阻塞队列中。空闲的 core 就会自己去阻塞队 列获取任务执行
(2) 阻塞队列满了,就直接开新线程执行,最大只能开到 max 指定的数量
(3) max 都执行好了。Max-core 数量空闲的线程会在 keepAliveTime 指定的时间后自 动销毁。最终保持到 core 大小
(4) 如果线程数开到了 max 的数量,还有新任务进来,就会使用 reject 指定的拒绝策 略进行处理
3、所有的线程创建都是由指定的 factory 创建的。
面试:
一个线程池 core 7; max 20 ,queue:50 ,100 并发进来怎么分配的;
先有 7 个能直接得到执行,接下来 50 个进入队列排队,在多开 13 个继续执行。现在 70 个 被安排上了。剩下 30 个默认拒绝策略。
3、常见的4种线程池
3.1 newCachedThreadPool
创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若 无可回收,则新建线程。
3.2 newFixedThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
3.3 newScheduledThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
3.4 newSingleThreadExecutor
创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务 按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
4、开发中为什么使用线程池
4.1 降低资源的消耗
通过重复利用已经创建好的线程降低线程的创建和销毁带来的损耗
4.2 提高响应速度
因为线程池中的线程数没有超过线程池的最大上限时,有的线程处于等待分配任务的状态,当任务来时无需创建新的线程就能执行
4.3 提高线程的可管理性
线程池会根据当前系统特点对池内的线程进行优化处理,减少创建和销毁线程带来的系统开销。无限的创建和销毁线程不仅消耗系统资源,还降低系统的稳定性,使 用线程池进行统一分配
二、CompletableFuture异步编排
业务场景:
查询商品详情页的逻辑比较复杂,有些数据还需要远程调用,必然需要花费更多的时间。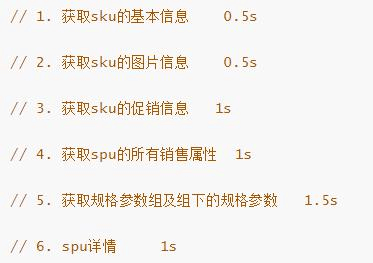
假如商品详情页的每个查询,需要如下标注的时间才能完成
那么,用户需要 5.5s 后才能看到商品详情页的内容。很显然是不能接受的。 如果有多个线程同时完成这 6 步操作,也许只需要 1.5s 即可完成响应。
Future 是 Java 5 添加的类,用来描述一个异步计算的结果。你可以使用isDone方法检查计算是否完成,或者使用get阻塞住调用线程,直到计算完成返回结果,你也可以使用cancel 方法停止任务的执行。
虽然Future以及相关使用方法提供了异步执行任务的能力,但是对于结果的获取却是很不 方便,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。阻塞的方式显然和我们的异步编程的 初衷相违背,轮询的方式又会耗费无谓的 CPU 资源,而且也不能及时地得到计算结果,为什么不能用观察者设计模式当计算结果完成及时通知监听者呢?
很多语言,比如 Node.js ,采用回调的方式实现异步编程。Java 的一些框架,比如 Netty ,自 己扩展了 Java 的 Future接口,提供了addListener等多个扩展方法; Google guava 也提供了通用的扩展Future;Scala 也提供了简单易用且功能强大的 Future/Promise 异步编程模式。
作为正统的 Java 类库,是不是应该做点什么,加强一下自身库的功能呢?
在 Java 8 中, 新增加了一个包含 50 个方法左右的类: CompletableFuture ,提供了非常强大的 Future 的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,提供了函数式编程的能力,可以 通过回调的方式处理计算结果,并且提供了转换和组合 CompletableFuture 的方法。
CompletableFuture 类实现了 Future 接口,所以你还是可以像以前一样通过get方法阻塞或者轮询的方式获得结果,但是这种方式不推荐使用。
CompletableFuture 和 FutureTask 同属于 Future 接口的实现类,都可以获取线程的执行结果。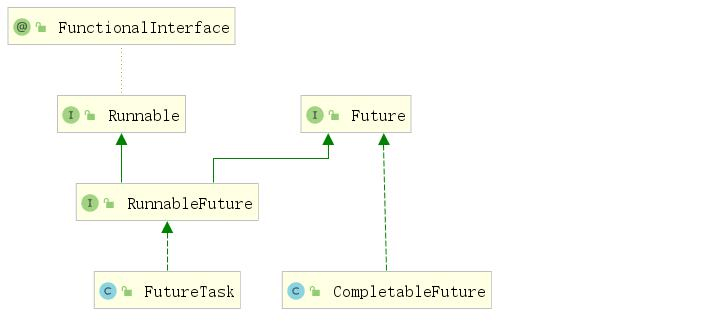
1、创建异步对象
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作(启动一个异步任务)。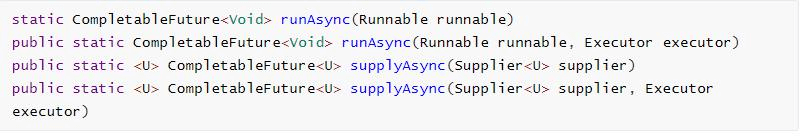
1)runXxxx 都是没有返回结果的,supplyXxx 都是可以获取返回结果的
2)可以传入自定义的线程池,否则就用默认的线程池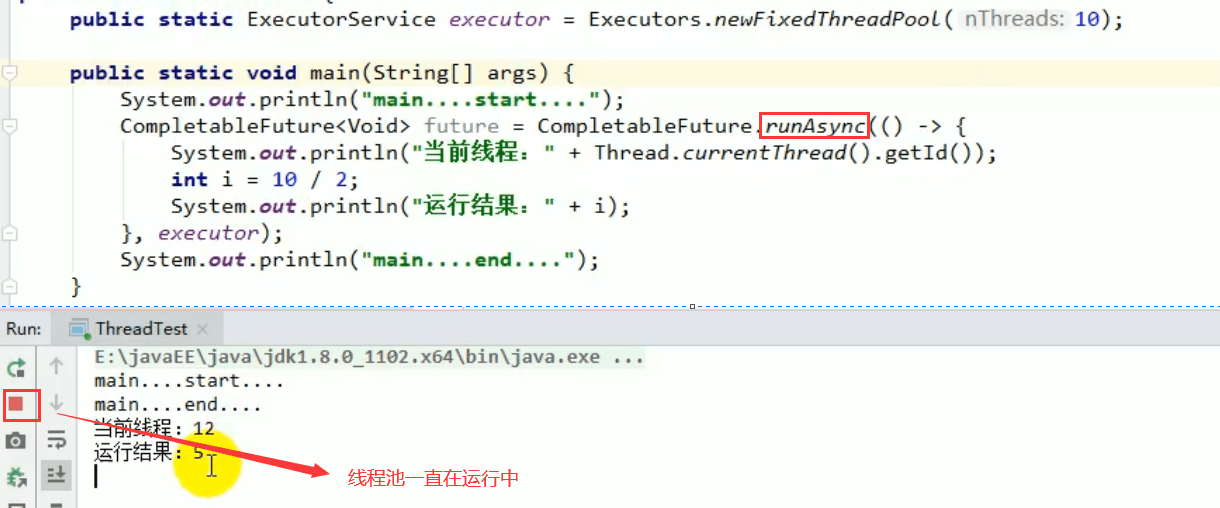
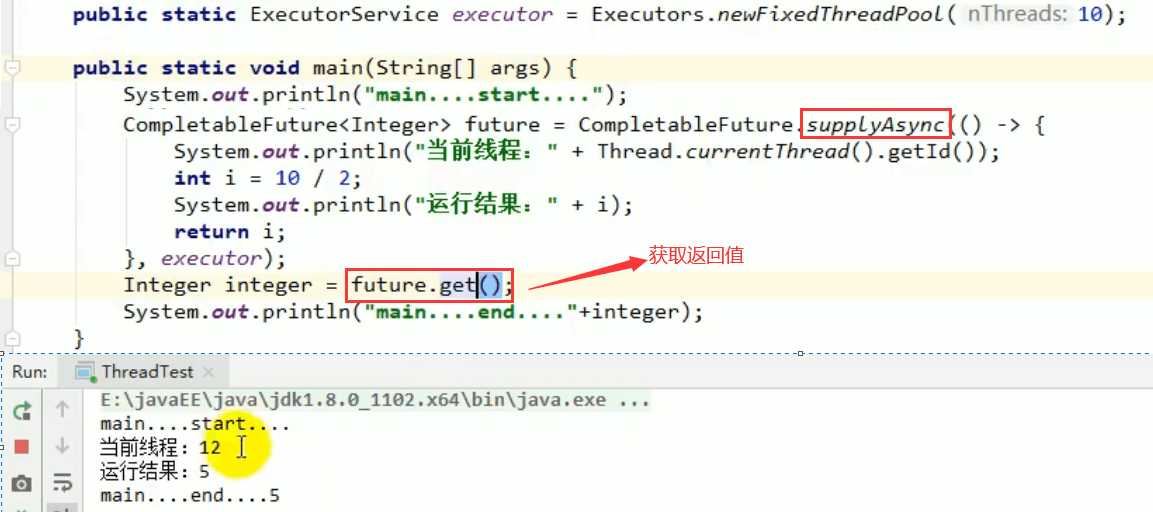
2、计算完成时回调方法
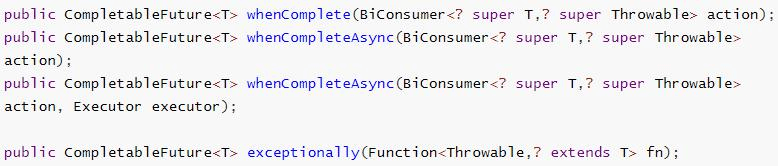
whenComplete(只能感知结果,但不能处理) 可以处理正常和异常的计算结果,exceptionally 处理异常情况。
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。
whenCompleteAsync:是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池 来进行执行。
方法不以 Async 结尾,意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行,而 Async 可能会使用其他线程 执行(如果是使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)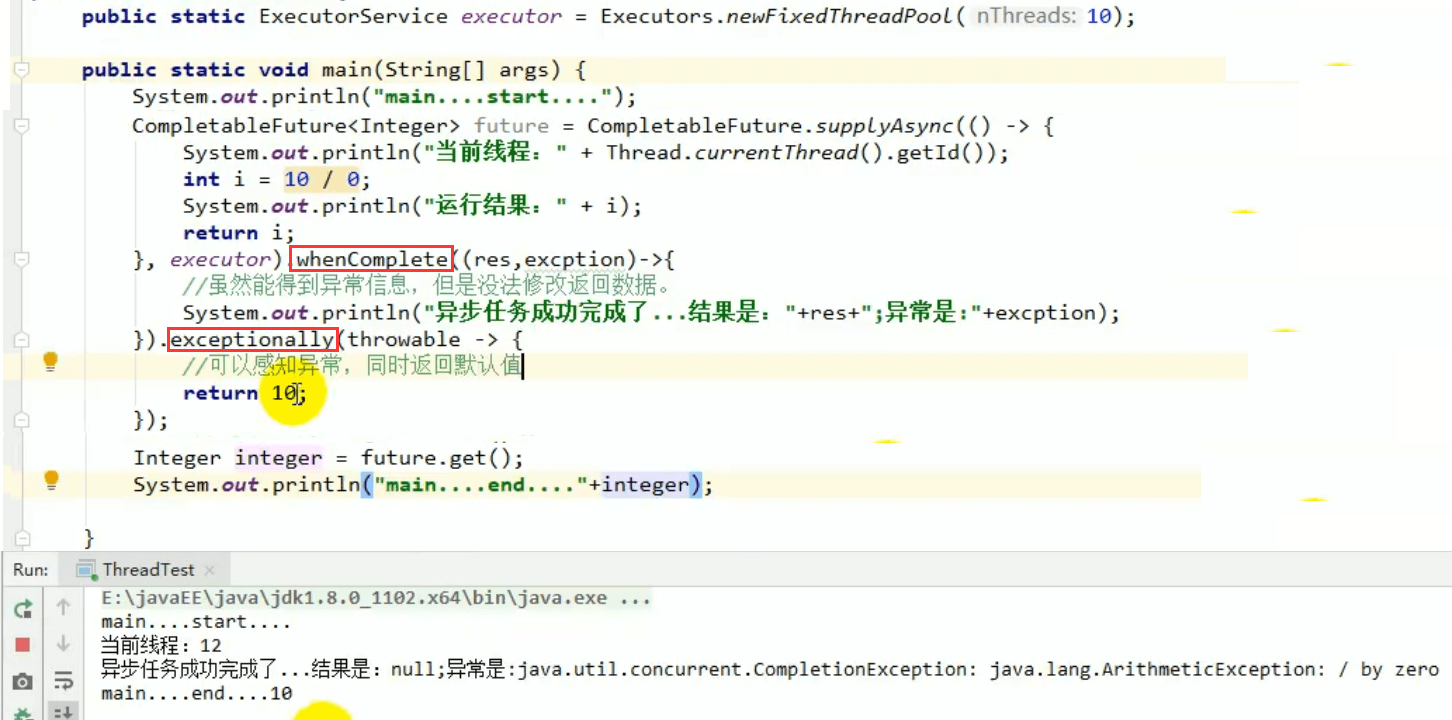
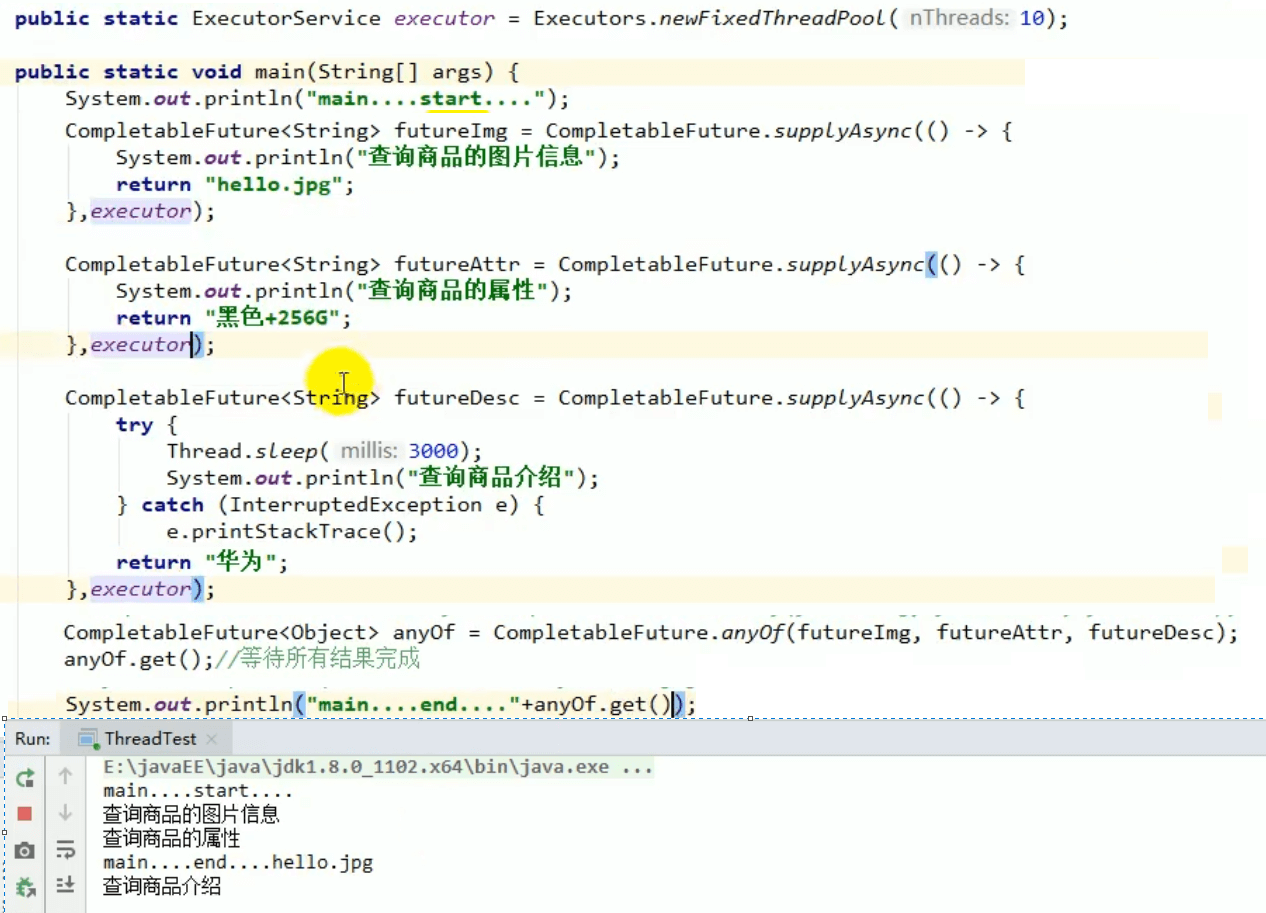
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Object>() {@Overridepublic Object get() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t completableFuture");int i = 10 / 0;return 1024;}}).whenComplete(new BiConsumer<Object, Throwable>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Object o, Throwable throwable) {System.out.println("-------o=" + o.toString());System.out.println("-------throwable=" + throwable);}}).exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, Object>() {@Overridepublic Object apply(Throwable throwable) {System.out.println("throwable=" + throwable);return 6666;}});System.out.println(future.get());}}
3、handle方法

和 complete 一样,可对结果做最后的处理(可处理异常),可改变返回值。
whenComplete:方法执行完成后的感知,但不处理
handle:方法执行完成后的处理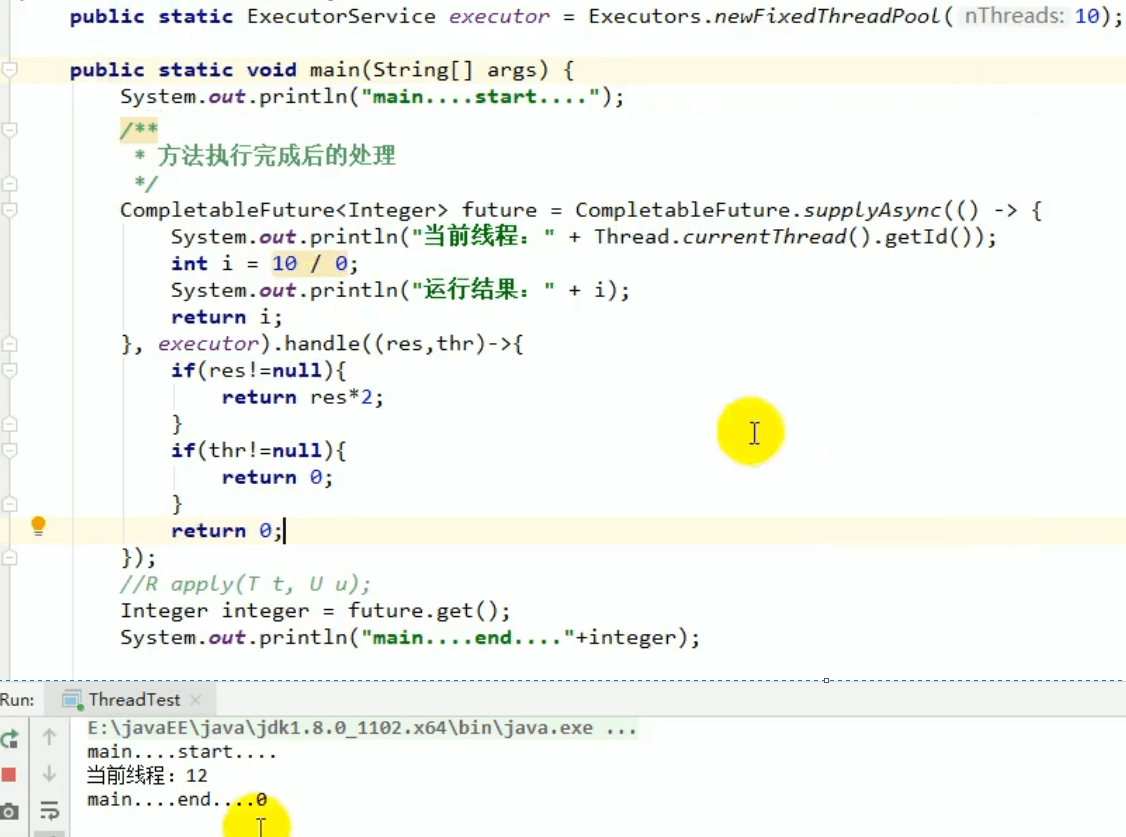
4、线程串行化方法
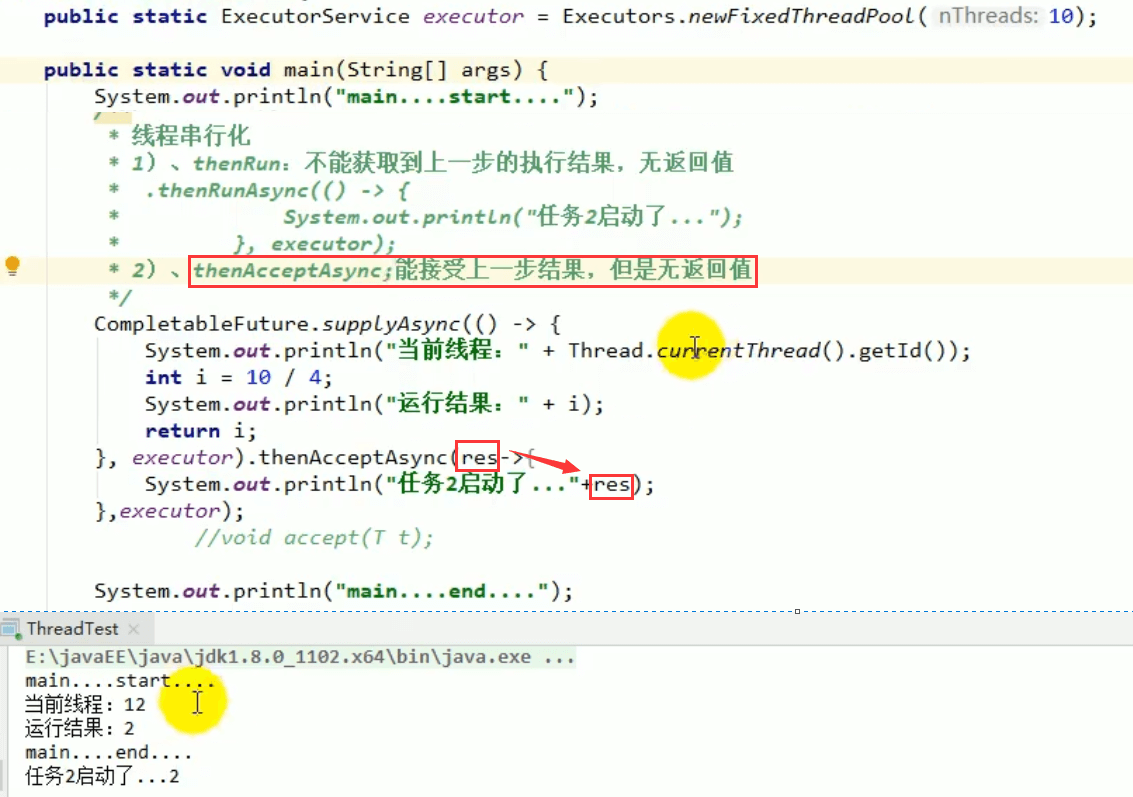
4.1 thenRun方法
只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行thenRun ,只是处理完任务后,执行 thenRun 的后续操作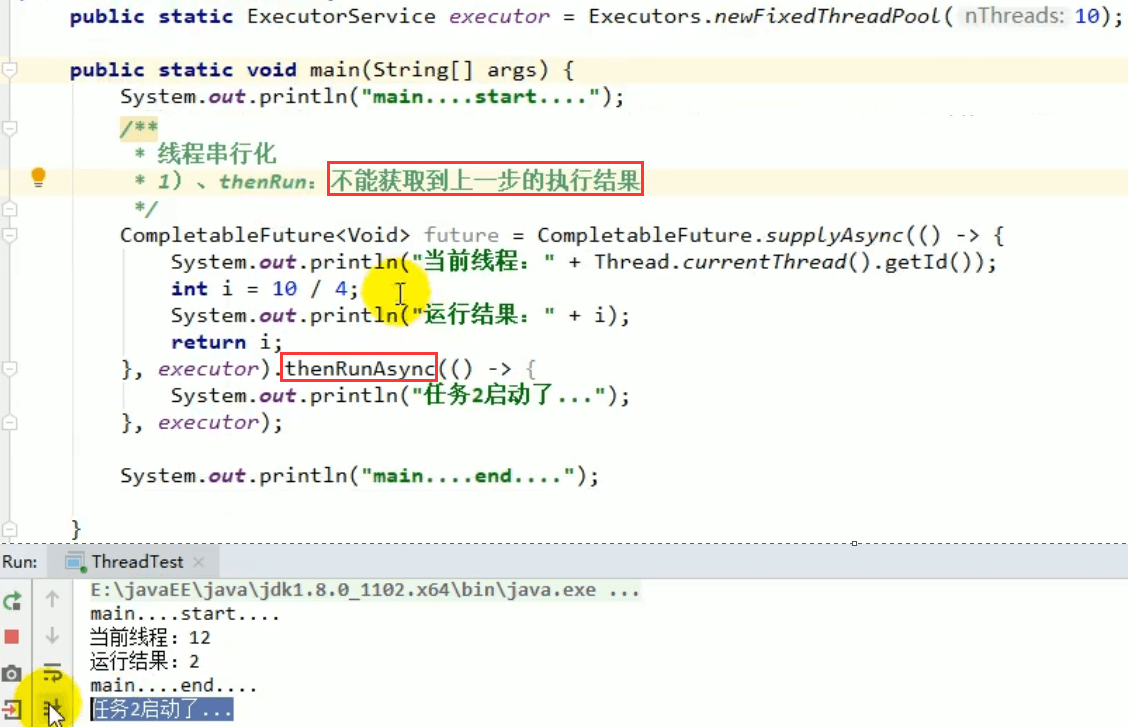
4.2 thenAccept方法
4.3 thenApply方法
当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前任务的返回值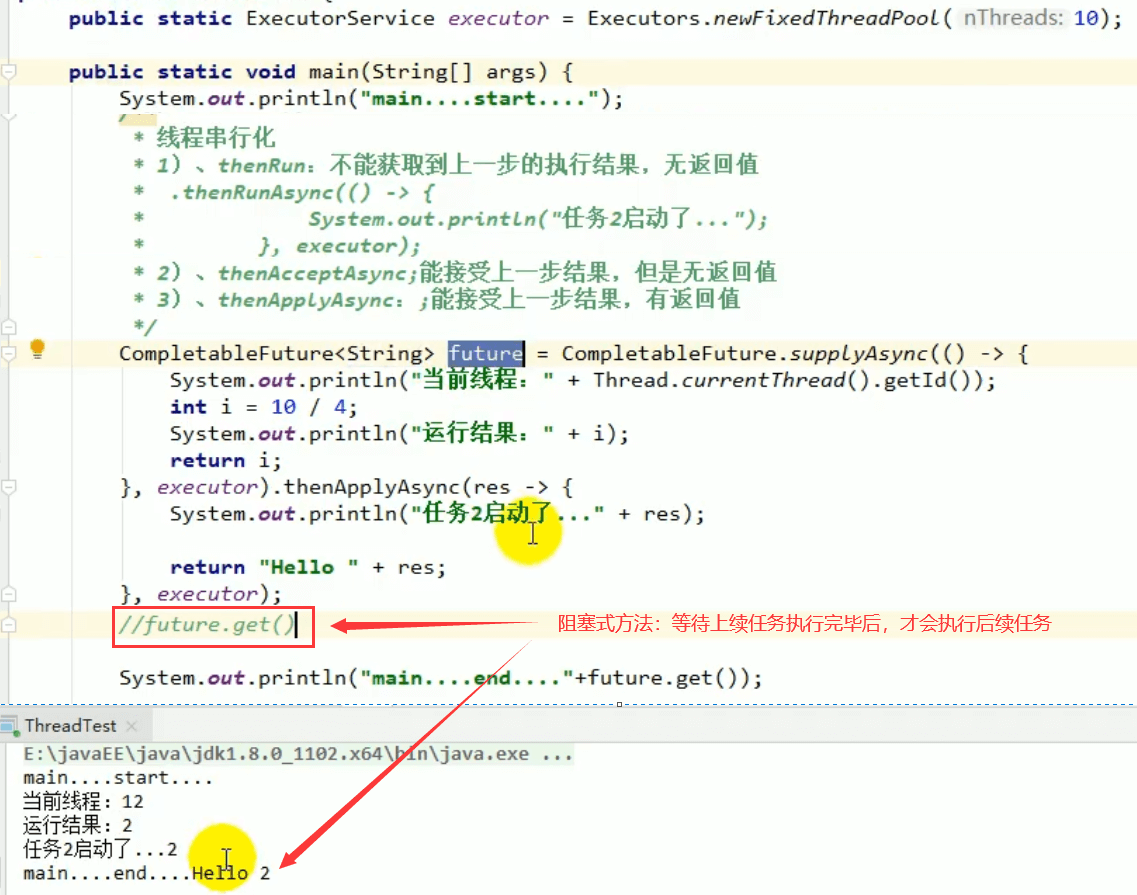
带有 Async 默认是异步执行的。同之前。
以上都要前置任务成功完成。
Function<? super T,? extends U>T:上一个任务返回结果的类型U:当前任务的返回值类型
5、两任务组合 - 都要完成
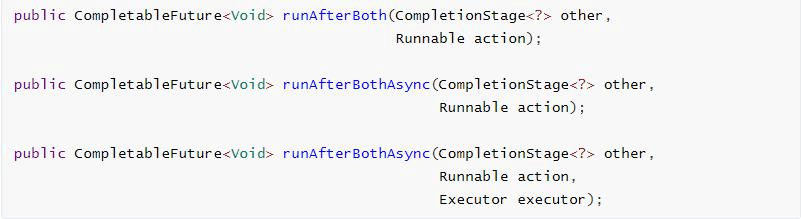
5.1 runAfterBoth
组合两个future ,不需要获取 future 的结果,只需两个 future 处理完任务后, 处理该任务
5.2 thenAcceptBoth
组合两个 future ,获取两个 future 任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有 返回值。
5.3 thenCombine
组合两个 future,获取两个 future 的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值 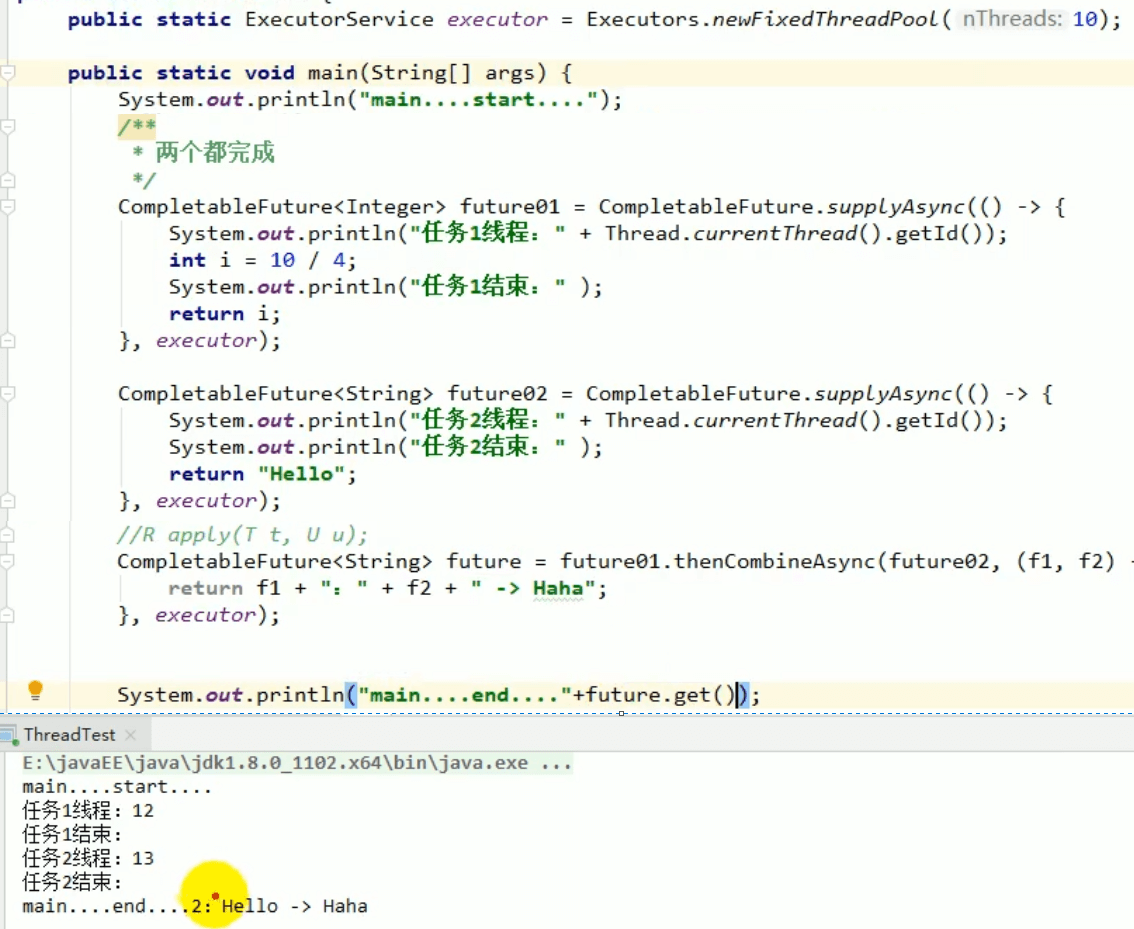
6、两任务组合 - 一个完成

当两个任务中,任意一个 future 任务完成的时候,执行任务。
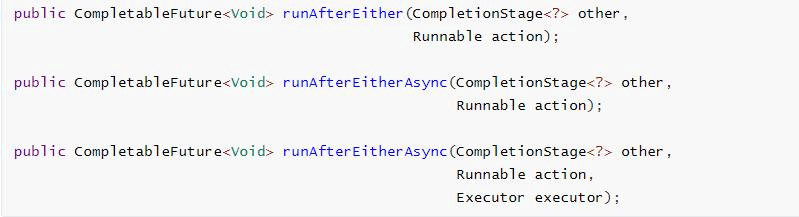
6.1 runAfterEither
两个任务有一个执行完成,不需要获取future的结果,处理任务,也没有返回值。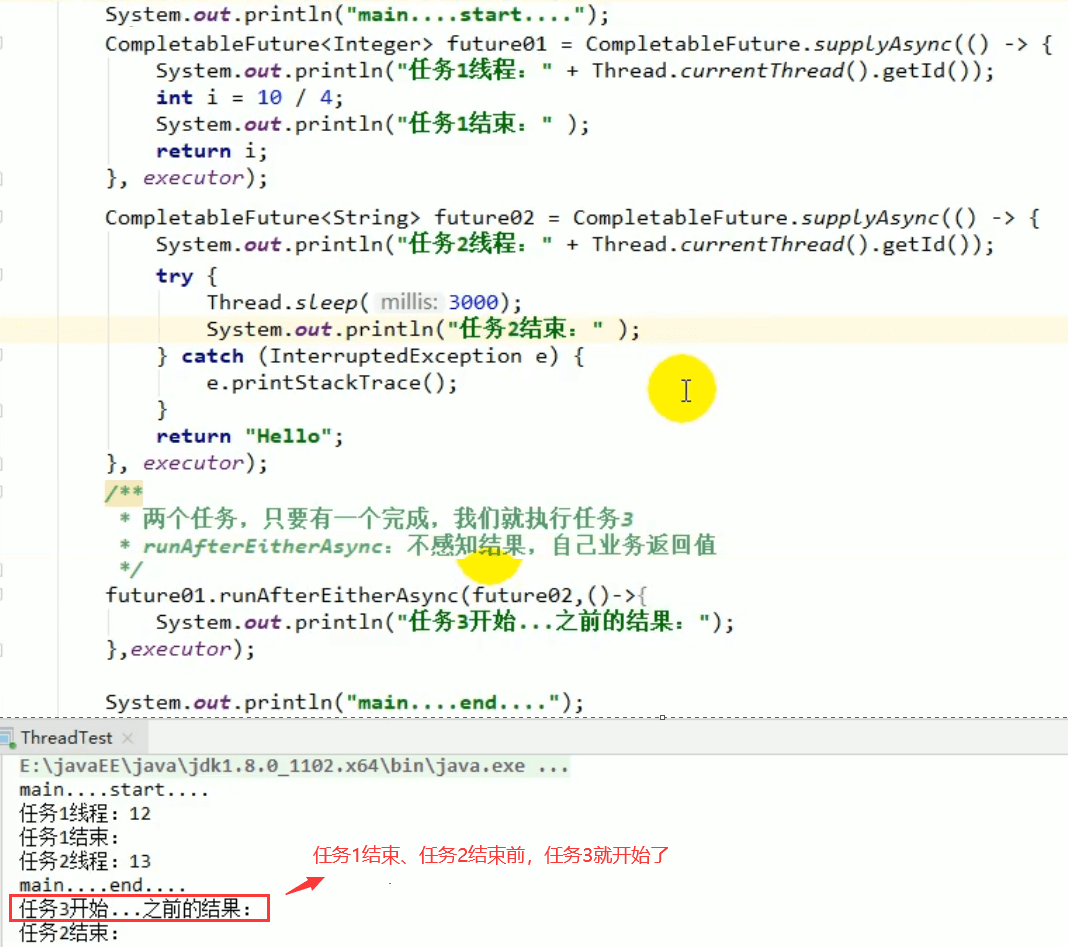
6.2 acceptEither
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务,没有新的返回值。 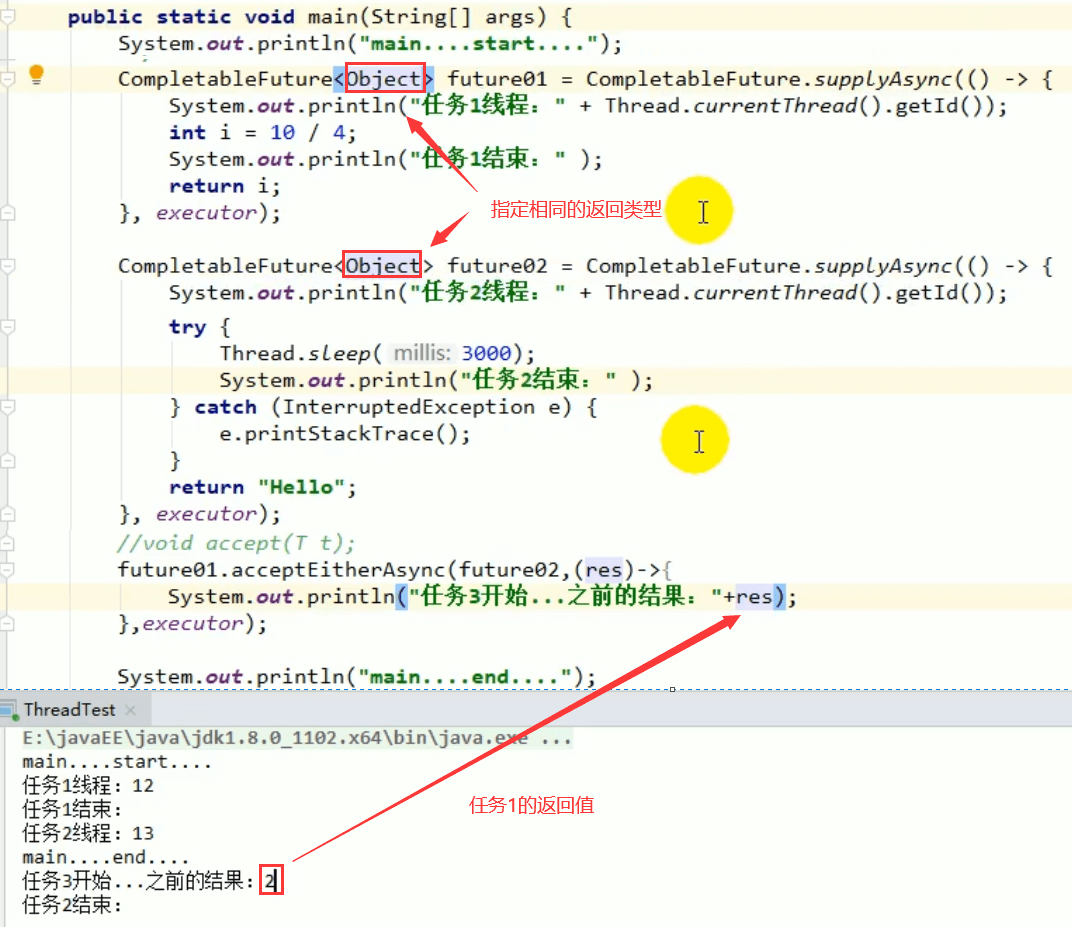
6.3 applyToEither
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务并有新的返回值。 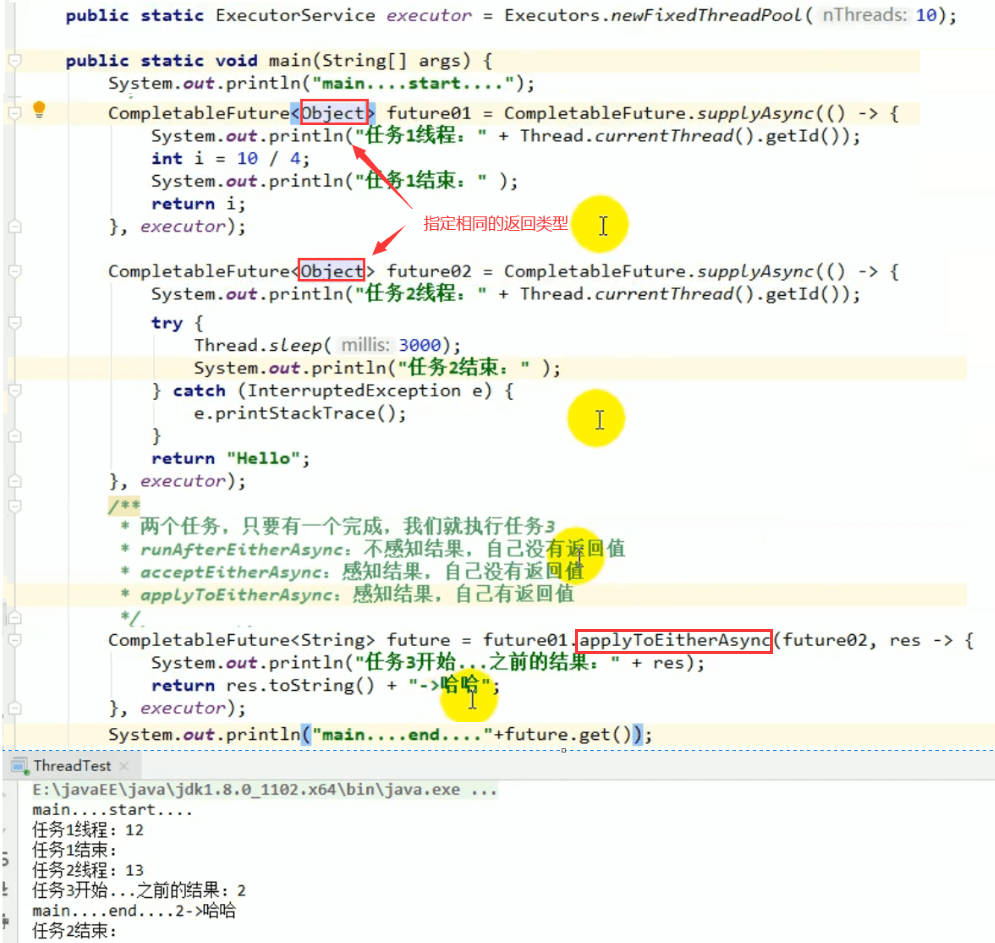
7、多任务组合
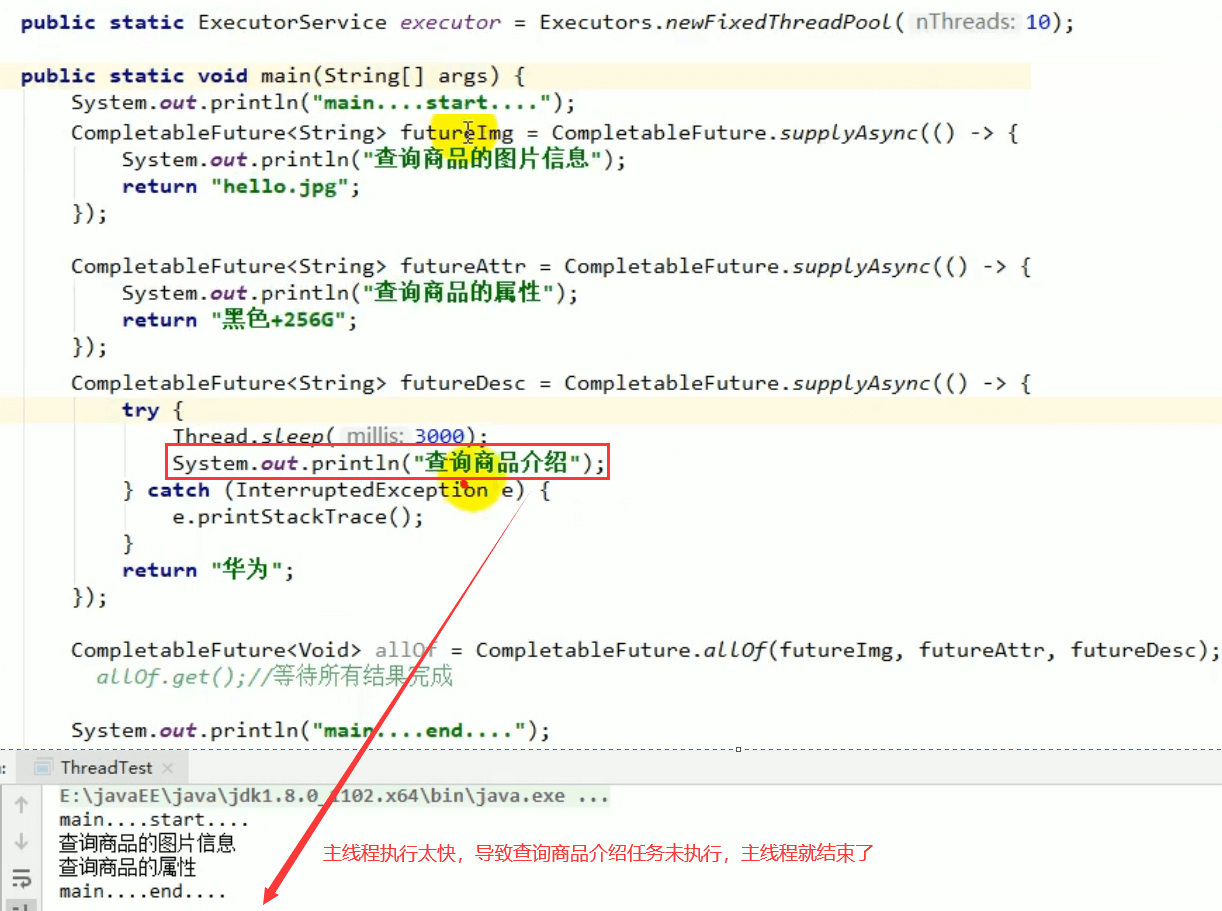
7.1 allOf
7.2 anyOf
三、商城业务-商品详情
1、前置步骤
1)设置域名跳转:
添加hosts内容 192.168.56.10 item.gulimall.com。访问item.gulimall.com即可跳转到商品详情页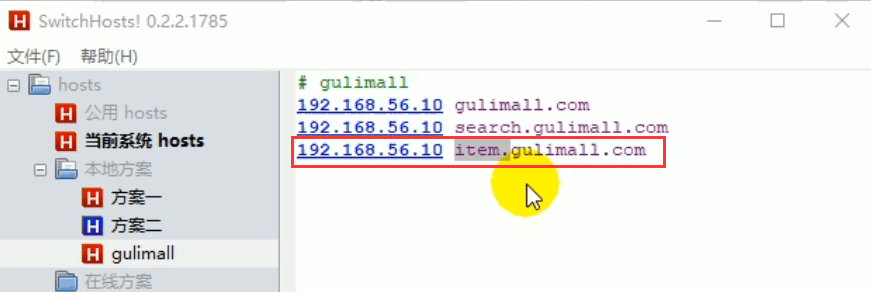
2)nginx内的域名配置
在gulimall.conf文件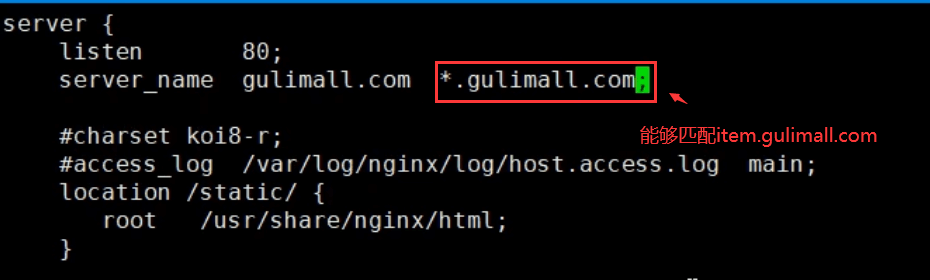
请求item.gulimall.com先转到nginx,nginx带上域名后转给网关,然后网关再交给微服务
3)修改网关,使item路由到product
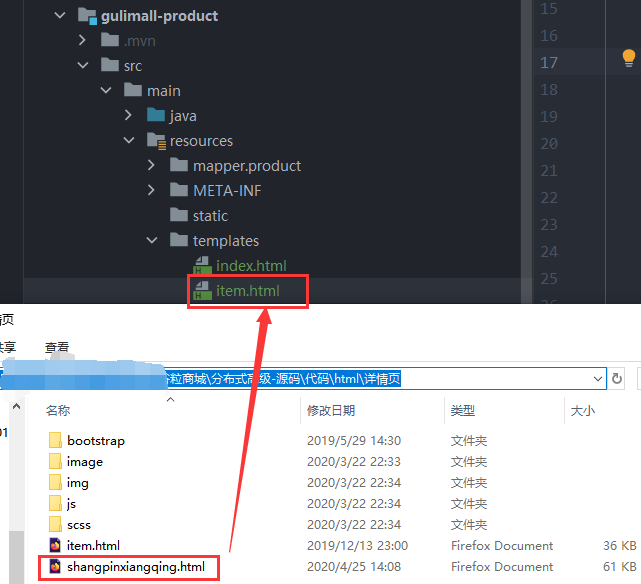
4)复制详情页的html到product,静态文件放到nginx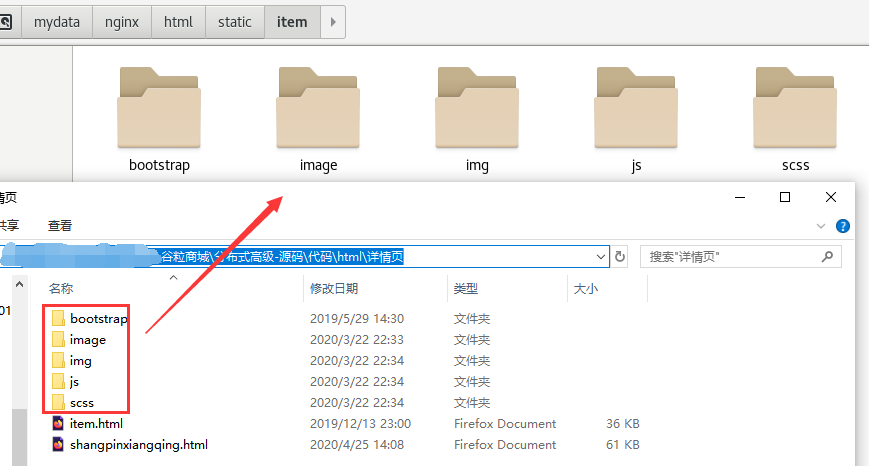
2、商品详情Vo
package com.atguigu.gulimall.product.vo.skuItemvo;@Datapublic class SkuItemVo {//1.sku基本信息获取 pms_sku_infoSkuInfoEntity info;// 是否有货boolean hasStock = true;//2.sku图片信息 pms_sku_imagesList<SkuImagesEntity> imagesEntites;//3.spu的销售属性组合List<SkuItemSaleAttrsVo> saleAttr;//4.spu的详细介绍SpuInfoDescEntity desp;//5.规格参数List<SpuItemAttrGroupVo> groupAttrs;//6.当前商品的秒杀优惠信息SeckillInfoVo seckillInfo;}
3、ItemController
package com.atguigu.gulimall.product.web;@Controllerpublic class ItemController {@Autowiredprivate SkuInfoService skuInfoService;/*** 查看商品详情* @param skuId* @param model* @return* @throws ExecutionException* @throws InterruptedException*/@GetMapping("/{skuId}.html")public String skuItem(@PathVariable("skuId") Long skuId, Model model) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {SkuItemVo vo = skuInfoService.item(skuId);model.addAttribute("item",vo);return "item";}}
4、SkuInfoServiceImpl
package com.atguigu.gulimall.product.service.impl;@Service("skuInfoService")public class SkuInfoServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<SkuInfoDao, SkuInfoEntity>implements SkuInfoService {@AutowiredSkuImagesService imagesService;@AutowiredSpuInfoDescService spuInfoDescService;@AutowiredAttrGroupService attrGroupService;@AutowiredSkuSaleAttrValueService skuSaleAttrValueService;// @Autowired// SeckillFeginService seckillFeginService;@AutowiredThreadPoolExecutor executor;/*** 查看商品详情* 异步执行* @param skuId* @return* @throws ExecutionException* @throws InterruptedException*/@Overridepublic SkuItemVo item(Long skuId) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {SkuItemVo skuItemVo = new SkuItemVo();// 1、sku基本信息获取 pms_sku_infoCompletableFuture<SkuInfoEntity> infoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {SkuInfoEntity info = getById(skuId);skuItemVo.setInfo(info);return info;}, executor);// 2、获取spu的销售属性组合CompletableFuture<Void> saleFuture = infoFuture.thenAcceptAsync((res) -> {List<SkuItemSaleAttrsVo> saleAttrsVos = skuSaleAttrValueService.getSaleAttrsBySpuId(res.getSpuId());skuItemVo.setSaleAttr(saleAttrsVos);}, executor);// 3、获取spu的详细介绍,pms_spu_info_descCompletableFuture<Void> descFuture = infoFuture.thenAcceptAsync((res) -> {SpuInfoDescEntity spuInfoDescEntity = spuInfoDescService.getById(res.getSpuId());skuItemVo.setDesp(spuInfoDescEntity);}, executor);// 4、获取spu的规格参数信息CompletableFuture<Void> baseFuture = infoFuture.thenAcceptAsync((res) -> {List<SpuItemAttrGroupVo> attrGroupVos = attrGroupService.getAttrGroupWithAttrsBySpuId(res.getSpuId(), res.getCatalogId());skuItemVo.setGroupAttrs(attrGroupVos);}, executor);// 5、获取sku图片信息 pms_sku_imagesCompletableFuture<Void> imgFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {List<SkuImagesEntity> images = imagesService.getImagesBySkuId(skuId);skuItemVo.setImagesEntites(images);}, executor);// 6、查询当前商品是否是秒杀商品CompletableFuture<Void> seckillFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {R seckillInfo = seckillFeginService.getSkuSeckillInfo(skuId);if (seckillInfo.getCode() == 0) {SeckillInfoVo seckillInfoVo = seckillInfo.getData(new TypeReference<SeckillInfoVo>() {});skuItemVo.setSeckillInfo(seckillInfoVo);}},executor);//等待所有任务都完成CompletableFuture.allOf(saleFuture,descFuture,baseFuture,imgFuture,seckillFuture).get();return skuItemVo;}}
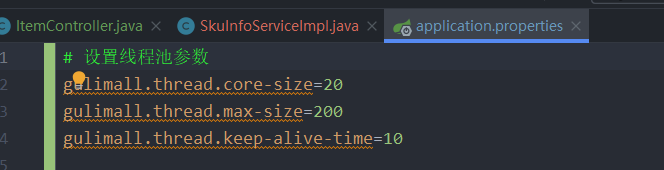
5、自定义线程池
package com.atguigu.gulimall.product.config;@Configuration//@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThreadPoolConfigProperties.class) // 开启指定属性配置,与@Component功能相同public class MyThreadConfig {@Beanpublic ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor(com.atguigu.gulimall.product.config.ThreadPoolConfigProperties pool) {ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(pool.getCoreSize(),pool.getMaxSize(),pool.getKeepAliveTime(),TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100000), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());return executor;}}
package com.atguigu.gulimall.product.config;import lombok.Data;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "gulimall.thread")@Component // 加入容器中@Datapublic class ThreadPoolConfigProperties {private Integer coreSize;private Integer maxSize;private Integer keepAliveTime;}