1598.文件夹操作日志搜集器——easy
每当用户执行变更文件夹操作时,LeetCode 文件系统都会保存一条日志记录。
下面给出对变更操作的说明:
“../“ :移动到当前文件夹的父文件夹。如果已经在主文件夹下,则 继续停留在当前文件夹 。
“./“ :继续停留在当前文件夹。
“x/“ :移动到名为 x 的子文件夹中。题目数据 保证总是存在文件夹 x 。
给你一个字符串列表 logs ,其中 logs[i] 是用户在 i 步执行的操作。
文件系统启动时位于主文件夹,然后执行 logs 中的操作。
执行完所有变更文件夹操作后,请你找出 返回主文件夹所需的最小步数 。
示例 1: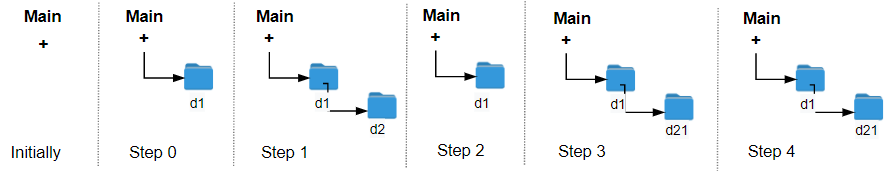
输入:logs = [“d1/“,”d2/“,”../“,”d21/“,”./“]
输出:2
解释:执行 “../“ 操作变更文件夹 2 次,即可回到主文件夹
示例 2: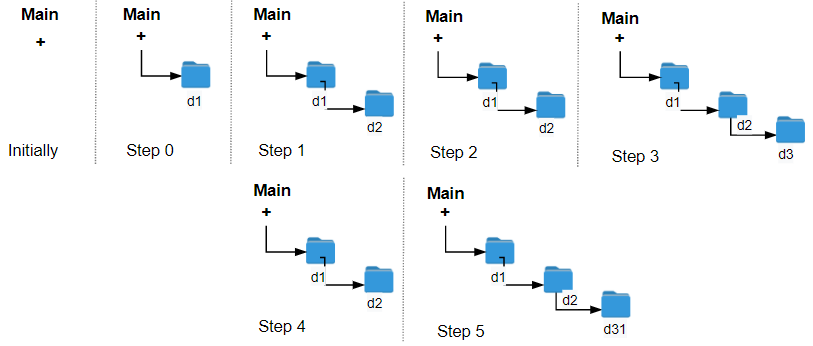
输入:logs = [“d1/“,”d2/“,”./“,”d3/“,”../“,”d31/“]
输出:3
**
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/crawler-log-folder
提示:
- 1 <= logs.length <= 103
- 2 <= logs[i].length <= 10
- logs[i] 包含小写英文字母,数字,’.’ 和 ‘/‘
- logs[i] 符合语句中描述的格式
- 文件夹名称由小写英文字母和数字组成
思路:
模拟即可
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
/*** @param {string[]} logs* @return {number}*/var minOperations = function(logs) {let n = logs.length;let ans = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n ; i++ ){if(logs[i] === '../'){ans = ans ? ans - 1 : ans;}else if(logs[i] === './'){}else{ans = ans+1;}}return ans;};
1599.经营摩天轮的最大利润——medium
你正在经营一座摩天轮,该摩天轮共有 4 个座舱 ,每个座舱 最多可以容纳 4 位游客 。你可以 逆时针 轮转座舱,但每次轮转都需要支付一定的运行成本 runningCost 。摩天轮每次轮转都恰好转动 1 / 4 周。
给你一个长度为 n 的数组 customers , customers[i] 是在第 i 次轮转(下标从 0 开始)之前到达的新游客的数量。这也意味着你必须在新游客到来前轮转 i 次。每位游客在登上离地面最近的座舱前都会支付登舱成本 boardingCost ,一旦该座舱再次抵达地面,他们就会离开座舱结束游玩。
你可以随时停下摩天轮,即便是 在服务所有游客之前 。如果你决定停止运营摩天轮,为了保证所有游客安全着陆,将免费进行所有后续轮转 。注意,如果有超过 4 位游客在等摩天轮,那么只有 4 位游客可以登上摩天轮,其余的需要等待 下一次轮转 。
返回最大化利润所需执行的 最小轮转次数 。 如果不存在利润为正的方案,则返回 -1 。
示例 1: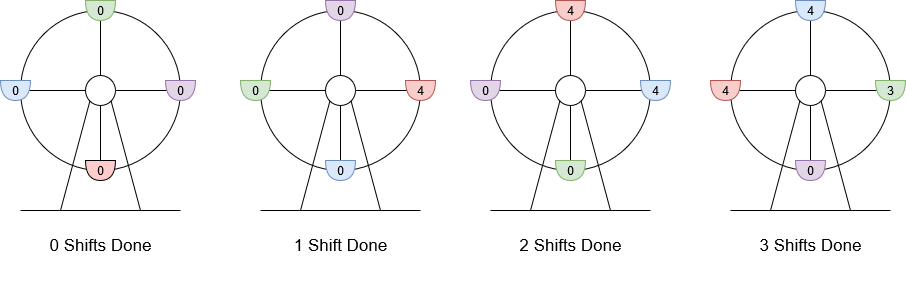
输入:customers = [8,3], boardingCost = 5, runningCost = 6
输出:3
解释:座舱上标注的数字是该座舱的当前游客数。
1. 8 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,4 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 $5 - 1 $6 = $14 。
2. 3 位游客抵达,4 位在等待的游客登舱,其他 3 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 $5 - 2 $6 = $28 。
3. 最后 3 位游客登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 11 $5 - 3 $6 = $37 。
轮转 3 次得到最大利润,最大利润为 $37 。
示例 2:
**
输入:customers = [10,9,6], boardingCost = 6, runningCost = 4
输出:7
解释:
1. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,6 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 $6 - 1 $4 = $20 。
2. 9 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,11 位等待(2 位是先前就在等待的,9 位新加入等待的),摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 $6 - 2 $4 = $40 。
3. 最后 6 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,13 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 $6 - 3 $4 = $60 。
4. 4 位登舱,9 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 $6 - 4 $4 = $80 。
5. 4 位登舱,5 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 20 $6 - 5 $4 = $100 。
6. 4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 24 $6 - 6 $4 = $120 。
7. 1 位登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 25 $6 - 7 $4 = $122 。
轮转 7 次得到最大利润,最大利润为$122 。
示例 3:
**
输入:customers = [3,4,0,5,1], boardingCost = 1, runningCost = 92
输出:-1
解释:
1. 3 位游客抵达,3 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 3 $1 - 1 $92 = -$89 。
2. 4 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 is 7 $1 - 2 $92 = -$177 。
3. 0 位游客抵达,0 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 7 $1 - 3 $92 = -$269 。
4. 5 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 $1 - 4 $92 = -$356 。
5. 1 位游客抵达,2 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 13 $1 - 5 $92 = -$447 。
利润永不为正,所以返回 -1 。
示例 4:
**
输入:customers = [10,10,6,4,7], boardingCost = 3, runningCost = 8
输出:9
解释:
1. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,6 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 $3 - 1 $8 = $4 。
2. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,12 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 $3 - 2 $8 = $8 。
3. 6 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,14 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 $3 - 3 $8 = $12 。
4. 4 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,14 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 16 $3 - 4 $8 = $16 。
5. 7 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,17 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 20 $3 - 5 $8 = $20 。
6. 4 位登舱,13 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 24 $3 - 6 $8 = $24 。
7. 4 位登舱,9 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 28 $3 - 7 $8 = $28 。
8. 4 位登舱,5 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 32 $3 - 8 $8 = $32 。
9. 4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 36 $3 - 9 $8 = $36 。
10. 1 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 37 $3 - 10 $8 = $31 。
轮转 9 次得到最大利润,最大利润为 $36 。
提示:
- n == customers.length
- 1 <= n <= 105
- 0 <= customers[i] <= 50
- 1 <= boardingCost, runningCost <= 100
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-profit-of-operating-a-centennial-wheel
思路:
模拟即可,注意更新最大收益轮数,以及清空剩余人数,和更新最大收益轮数。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
/*** @param {number[]} customers* @param {number} boardingCost* @param {number} runningCost* @return {number}*/var minOperationsMaxProfit = function(customers, boardingCost, runningCost) {let times = 0;let n = customers.length;let wait = 0;let bc = 0;let rc = 0;let profit = 0;let ans = -1;for(let i = 0;i < n;i++){times += 1;wait += customers[i];let inboard = Math.min(4,wait);bc += boardingCost * inboard;rc += runningCost;wait -= inboard;// 更新最大利润的最小轮数if(profit < bc - rc){profit = bc-rc;ans = times;}}//清空队列while(wait > 0 ){times += 1;let inboard = Math.min(4,wait);bc += boardingCost * inboard;rc += runningCost;wait -= inboard;// 更新最大利润的最小轮数if(profit < bc - rc){profit = bc-rc;ans = times;}}return ans;};
1600.皇位继承顺序——medium
一个王国里住着国王、他的孩子们、他的孙子们等等。每一个时间点,这个家庭里有人出生也有人死亡。
这个王国有一个明确规定的皇位继承顺序,第一继承人总是国王自己。我们定义递归函数 Successor(x, curOrder) ,给定一个人 x 和当前的继承顺序,该函数返回 x 的下一继承人。
Successor(x, curOrder):
如果 x 没有孩子或者所有 x 的孩子都在 curOrder 中:
如果 x 是国王,那么返回 null
否则,返回 Successor(x 的父亲, curOrder)
否则,返回 x 不在 curOrder 中最年长的孩子
比方说,假设王国由国王,他的孩子 Alice 和 Bob (Alice 比 Bob 年长)和 Alice 的孩子 Jack 组成。
- 一开始, curOrder 为 [“king”].
- 调用 Successor(king, curOrder) ,返回 Alice ,所以我们将 Alice 放入 curOrder 中,得到 [“king”, “Alice”] 。
- 调用 Successor(Alice, curOrder) ,返回 Jack ,所以我们将 Jack 放入 curOrder 中,得到 [“king”, “Alice”, “Jack”] 。
- 调用 Successor(Jack, curOrder) ,返回 Bob ,所以我们将 Bob 放入 curOrder 中,得到 [“king”, “Alice”, “Jack”, “Bob”] 。
- 调用 Successor(Bob, curOrder) ,返回 null 。最终得到继承顺序为 [“king”, “Alice”, “Jack”, “Bob”] 。
- 通过以上的函数,我们总是能得到一个唯一的继承顺序。
请你实现 ThroneInheritance 类:
ThroneInheritance(string kingName) 初始化一个 ThroneInheritance 类的对象。国王的名字作为构造函数的参数传入。
void birth(string parentName, string childName) 表示 parentName 新拥有了一个名为 childName 的孩子。
void death(string name) 表示名为 name 的人死亡。一个人的死亡不会影响 Successor 函数,也不会影响当前的继承顺序。你可以只将这个人标记为死亡状态。
string[] getInheritanceOrder() 返回 除去 死亡人员的当前继承顺序列表。
示例:
输入:
[“ThroneInheritance”, “birth”, “birth”, “birth”, “birth”, “birth”, “birth”, “getInheritanceOrder”, “death”, “getInheritanceOrder”]
[[“king”], [“king”, “andy”], [“king”, “bob”], [“king”, “catherine”], [“andy”, “matthew”], [“bob”, “alex”], [“bob”, “asha”], [null], [“bob”], [null]]
输出:
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, [“king”, “andy”, “matthew”, “bob”, “alex”, “asha”, “catherine”], null, [“king”, “andy”, “matthew”, “alex”, “asha”, “catherine”]]
解释:
ThroneInheritance t= new ThroneInheritance(“king”); // 继承顺序:king
t.birth(“king”, “andy”); // 继承顺序:king > andy
t.birth(“king”, “bob”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > bob
t.birth(“king”, “catherine”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > bob > catherine
t.birth(“andy”, “matthew”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > catherine
t.birth(“bob”, “alex”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > alex > catherine
t.birth(“bob”, “asha”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > alex > asha > catherine
t.getInheritanceOrder(); // 返回 [“king”, “andy”, “matthew”, “bob”, “alex”, “asha”, “catherine”]
t.death(“bob”); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob(已经去世)> alex > asha > catherine
t.getInheritanceOrder(); // 返回 [“king”, “andy”, “matthew”, “alex”, “asha”, “catherine”]
提示:
- 1 <= kingName.length, parentName.length, childName.length, name.length <= 15
- kingName,parentName, childName 和 name 仅包含小写英文字母。
- 所有的参数 childName 和 kingName 互不相同。
- 所有 death 函数中的死亡名字 name 要么是国王,要么是已经出生了的人员名字。
- 每次调用 birth(parentName, childName) 时,测试用例都保证 parentName 对应的人员是活着的。
- 最多调用 10 次birth 和 death 。
- 最多调用 10 次 getInheritanceOrder 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/throne-inheritance
思路:
主要问题在于找继承序列,通过读题可知:国王的大儿子优先继承,而大儿子的儿子优先于他的兄弟和叔叔们。则我们可以通过dfs的方式找到未死亡的所有人,并按照继承顺序加入答案中。见代码
复杂度分析:**
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(n)
var ThroneInheritance = function(kingName) {this.name = kingNamethis.children = {}this.deathList = {}}ThroneInheritance.prototype.birth = function(parentName, childName) {this.children[parentName] = this.children[parentName] ? [...this.children[parentName], childName] : [childName]}ThroneInheritance.prototype.death = function(name) {this.deathList[name] = true}ThroneInheritance.prototype.getInheritanceOrder = function() {const allOrder = []const dfs = name => {if (!this.deathList[name]) allOrder.push(name)if (this.children[name]) {for (let i = 0; i < this.children[name].length; i++) dfs(this.children[name][i])}}dfs(this.name)return allOrder}
1601.最多可达成的换楼请求数目——hard
我们有 n 栋楼,编号从 0 到 n - 1 。每栋楼有若干员工。由于现在是换楼的季节,部分员工想要换一栋楼居住。
给你一个数组 requests ,其中 requests[i] = [fromi, toi] ,表示一个员工请求从编号为 fromi 的楼搬到编号为 toi 的楼。
一开始 所有楼都是满的,所以从请求列表中选出的若干个请求是可行的需要满足 每栋楼员工净变化为 0 。意思是每栋楼 离开 的员工数目 等于 该楼 搬入 的员工数数目。比方说 n = 3 且两个员工要离开楼 0 ,一个员工要离开楼 1 ,一个员工要离开楼 2 ,如果该请求列表可行,应该要有两个员工搬入楼 0 ,一个员工搬入楼 1 ,一个员工搬入楼 2 。
请你从原请求列表中选出若干个请求,使得它们是一个可行的请求列表,并返回所有可行列表中最大请求数目。
示例 1:
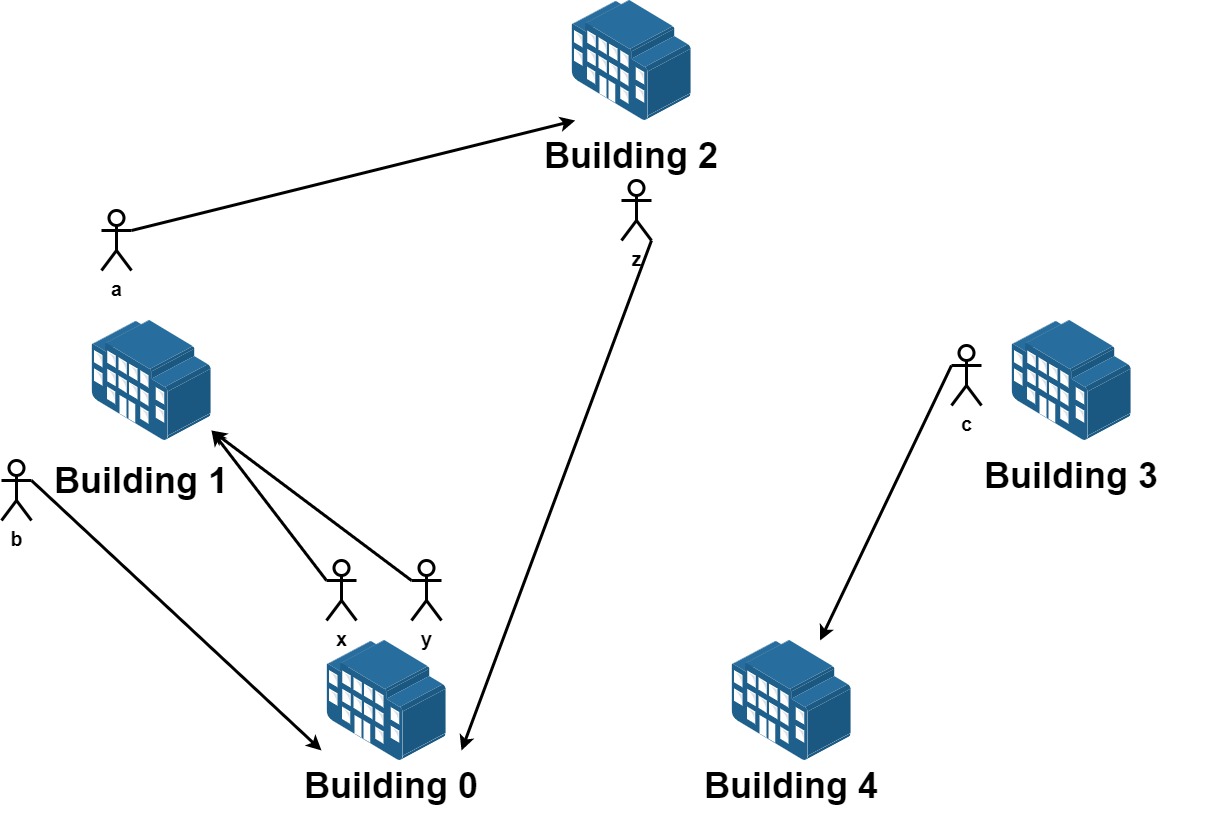
输入:n = 5, requests = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4]]
输出:5
解释:请求列表如下:
从楼 0 离开的员工为 x 和 y ,且他们都想要搬到楼 1 。
从楼 1 离开的员工为 a 和 b ,且他们分别想要搬到楼 2 和 0 。
从楼 2 离开的员工为 z ,且他想要搬到楼 0 。
从楼 3 离开的员工为 c ,且他想要搬到楼 4 。
没有员工从楼 4 离开。
我们可以让 x 和 b 交换他们的楼,以满足他们的请求。
我们可以让 y,a 和 z 三人在三栋楼间交换位置,满足他们的要求。
所以最多可以满足 5 个请求。
示例 2:
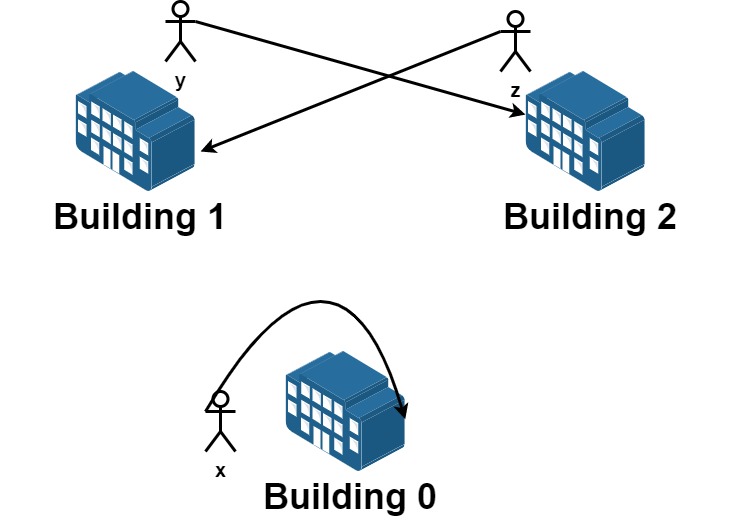
输入:n = 3, requests = [[0,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
输出:3
解释:请求列表如下:
从楼 0 离开的员工为 x ,且他想要回到原来的楼 0 。
从楼 1 离开的员工为 y ,且他想要搬到楼 2 。
从楼 2 离开的员工为 z ,且他想要搬到楼 1 。
我们可以满足所有的请求。
示例 3:
输入:n = 4, requests = [[0,3],[3,1],[1,2],[2,0]]
输出:4
提示:
- 1 <= n <= 20
- 1 <= requests.length <= 16
- requests[i].length == 2
- 0 <= fromi, toi < n
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-number-of-achievable-transfer-requests
思路:
最多只有16个请求,共有2种可能,可以二进制枚举满足的请求的状态,然后验证是否满足要求。
看别人题解说可以用最小费用最大流来做,但是数据量太小完全可以暴力做。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度O(2n) (m为request长度
空间复杂度O(n)
var maximumRequests = function (n, requests) {let length = requests.length;let ans = 0;for (let i = 1; i <= (1 << length); i++) {let count = 0;let build = new Array(n).fill(0);for (let j = 0; j < length; j++) {if ((1 << j) & i) {let [f, t] = [...requests[j]];build[f]--;build[t]++;count++;}}let isValid = true;build.forEach(item => {if (item !== 0) {isValid = false;}});if (isValid) {ans = Math.max(count, ans);}}return ans;};

