- 驱动程序中调用的内核函数,在 4.x 版本的内核里都是一样的
- LED驱动编写详细步骤如下:
① 看原理图确定引脚,确定引脚输出什么电平才能点亮/熄灭 LED
② 看主芯片手册,确定寄存器操作方法:哪些寄存器?哪些位?地址是?
③ 编写驱动:先写框架,再写硬件操作的代码
- 需要注意的是:
- 在芯片手册中确定的寄存器地址被称为物理地址,在 Linux 内核中无法直接使用。
- 需要使用内核提供的 ioremap 把物理地址映射为虚拟地址,使用虚拟地址。


实际上,它是按页(4096 字节)进行映射的,是整页整页地映射的。
假设 phys_addr = 0x10002,size=4,ioremap 的内部实现是:
a. phys_addr 按页取整,得到地址 0x10000
b. size 按页取整,得到 4096
c. 把起始地址 0x10000,大小为 4096 的这一块物理地址空间,映射到虚拟地址空间,
假设得到的虚拟空间起始地址为 0xf0010000
d. 那么 phys_addr = 0x10002 对应的 virt_addr = 0xf0010002
- 即使传入的是4byte大小也将会映射成4096一页的大小
- 不再使用该段虚拟地址时,要 iounmap(virt_addr):

- 为什么需要ioremap?
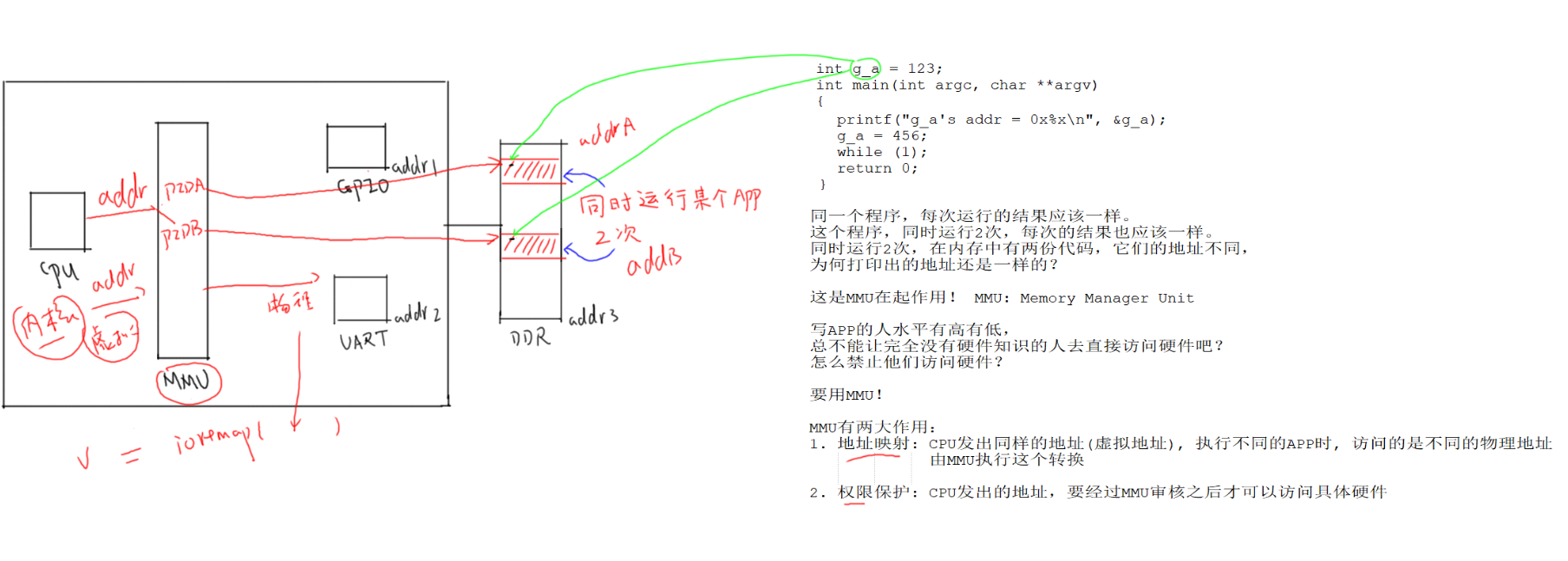
- 运行程序两次,那么在内存中必定会由两份代码
- 同一个程序,运行时打印的全局变量的地址应该是一样的才对;但是运行两次实际内存保存的是两份代码,即两者全局变量在内存中的物理地址是不同的;显然,程序中打印的不是物理地址,而是CPU看到的虚拟地址
- CPU使用同一个地址来访问同时运行的两个程序;根据不同的pid进程号进而访问不同的物理地址
- 使用MMU来实现虚拟地址到物理地址的转换
- 内核发出一个地址,能不能访问到硬件也是由MMU来决定的;mmu需要把物理地址映射成虚拟地址,内核才能使用虚拟地址来访问硬件
- volatile的使用
- 为了避免编译器自动优化,需要加上 volatile,告诉它“这是容易出错的,别乱优化”
- volatile int *p = ioremap(xxxx, 4); // GPIO 寄存器的地址
- 每个单板所使用的Linux内核、头文件可能不一样,在编写makefile时需指定对应board内核的目录,在对应的内核中编译
- 修改board结构体
struct led_operations {int num; /* LED灯的数量 */int (*init) (int which); /* 初始化LED, which-哪个LED */int (*ctl) (int which, char status); /* 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 */int (*exit) (int which); /* 退出LED */};
include “led_opr.h”
static volatile unsigned int CCM_CCGR1 ; static volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3; static volatile unsigned int GPIO5_GDIR ; static volatile unsigned int GPIO5_DR ;
static int board_demo_led_init (int which) / 初始化LED, which-哪个LED /
{
unsigned int val;
//printk("%s %s line %d, led %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, which);if (which == 0){if (!CCM_CCGR1){CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(0x20C406C, 4);IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = ioremap(0x2290014, 4);GPIO5_GDIR = ioremap(0x020AC000 + 0x4, 4);GPIO5_DR = ioremap(0x020AC000 + 0, 4);}/* GPIO5_IO03 *//* a. 使能GPIO5* set CCM to enable GPIO5* CCM_CCGR1[CG15] 0x20C406C* bit[31:30] = 0b11*/*CCM_CCGR1 |= (3<<30);/* b. 设置GPIO5_IO03用于GPIO* set IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3* to configure GPIO5_IO03 as GPIO* IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 0x2290014* bit[3:0] = 0b0101 alt5*/val = *IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3;val &= ~(0xf);val |= (5);*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = val;/* b. 设置GPIO5_IO03作为output引脚* set GPIO5_GDIR to configure GPIO5_IO03 as output* GPIO5_GDIR 0x020AC000 + 0x4* bit[3] = 0b1*/*GPIO5_GDIR |= (1<<3);}return 0;
}
static int boarddemoledctl (int which, char status) / 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 / { //printk(“%s %s line %d, led %d, %s\n”, FILE, _FUNCTION, __LINE, which, status ? “on” : “off”); if (which == 0) { if (status) / on: output 0/ { /* d. 设置GPIO5_DR输出低电平
* set GPIO5_DR to configure GPIO5_IO03 output 0* GPIO5_DR 0x020AC000 + 0* bit[3] = 0b0*/*GPIO5_DR &= ~(1<<3);}else /* off: output 1*/{/* e. 设置GPIO5_IO3输出高电平* set GPIO5_DR to configure GPIO5_IO03 output 1* GPIO5_DR 0x020AC000 + 0* bit[3] = 0b1*/*GPIO5_DR |= (1<<3);}}return 0;
}
/ 自己添加的 / static int board_demo_led_exit(int which) { if (which == 0) { board_demo_led_ctl(which, 0); / 将相关寄存器的值恢复为默认 / //不去设置 b[31:30],GPIO5 也是默认使能的
/* 取消映射 */iounmap( CCM_CCGR1 );iounmap( IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 );iounmap( GPIO5_GDIR );iounmap( GPIO5_DR );}return 0;
} static struct led_operations board_demo_led_opr = { .num = 1, .init = board_demo_led_init, .ctl = board_demo_led_ctl, .exit = board_demo_led_exit, };
struct led_operations *get_board_led_opr(void) { return &board_demo_led_opr; }
- 在leddrv.c的open函数中调用led_operations的init,close函数中调用led_operations的exit```cstatic int led_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file){int minor = iminor(node);printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);/* 根据次设备号初始化LED */p_led_opr->init(minor);return 0;}static int led_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file){int minor = iminor(node);printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);p_led_opr->exit(minor);return 0;}
- 使用 QEMU 模拟的硬件,它的硬件资源可以随意扩展。
- IMX6ULL-QEMU代码 ```c struct iomux { volatile unsigned int unnames[23]; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO00; / offset 0x5c/ volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO01; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO02; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO03; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO04; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO05; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO06; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO07; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO08; volatile unsigned int IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO09; };
struct imx6ull_gpio { volatile unsigned int dr; volatile unsigned int gdir; volatile unsigned int psr; volatile unsigned int icr1; volatile unsigned int icr2; volatile unsigned int imr; volatile unsigned int isr; volatile unsigned int edge_sel; };
/ enable GPIO1,GPIO5 / static volatile unsigned int *CCM_CCGR1;
/ set GPIO5_IO03 as GPIO / static volatile unsigned int *IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3;
static struct iomux *iomux;
static struct imx6ull_gpio gpio1; static struct imx6ull_gpio gpio5;
static int board_demo_led_init (int which) / 初始化LED, which-哪个LED /
{
if (!CCM_CCGR1)
{
CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(0x20C406C, 4);
IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = ioremap(0x2290014, 4);
iomux = ioremap(0x20e0000, sizeof(struct iomux));gpio1 = ioremap(0x209C000, sizeof(struct imx6ull_gpio));gpio5 = ioremap(0x20AC000, sizeof(struct imx6ull_gpio));}if (which == 0){/* 1. enable GPIO5* CG15, b[31:30] = 0b11*/*CCM_CCGR1 |= (3<<30);/* 2. set GPIO5_IO03 as GPIO* MUX_MODE, b[3:0] = 0b101*/*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = 5;/* 3. set GPIO5_IO03 as output* GPIO5 GDIR, b[3] = 0b1*/gpio5->gdir |= (1<<3);}else if(which == 1){/* 1. enable GPIO1* CG13, b[27:26] = 0b11*/*CCM_CCGR1 |= (3<<26);/* 2. set GPIO1_IO03 as GPIO* MUX_MODE, b[3:0] = 0b101*/iomux->IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = 5;/* 3. set GPIO1_IO03 as output* GPIO1 GDIR, b[3] = 0b1*/gpio1->gdir |= (1<<3);}else if(which == 2){/* 1. enable GPIO1* CG13, b[27:26] = 0b11*/*CCM_CCGR1 |= (3<<26);/* 2. set GPIO1_IO05 as GPIO* MUX_MODE, b[3:0] = 0b101*/iomux->IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO05 = 5;/* 3. set GPIO1_IO05 as output* GPIO1 GDIR, b[5] = 0b1*/gpio1->gdir |= (1<<5);}else if(which == 3){/* 1. enable GPIO1* CG13, b[27:26] = 0b11*/*CCM_CCGR1 |= (3<<26);/* 2. set GPIO1_IO06 as GPIO* MUX_MODE, b[3:0] = 0b101*/iomux->IOMUXC_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_GPIO1_IO06 = 5;/* 3. set GPIO1_IO06 as output* GPIO1 GDIR, b[6] = 0b1*/gpio1->gdir |= (1<<6);}//printk("%s %s line %d, led %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, which);return 0;
}
static int boarddemoledctl (int which, char status) / 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 / { //printk(“%s %s line %d, led %d, %s\n”, FILE, _FUNCTION, __LINE, which, status ? “on” : “off”); if (which == 0) { if (status) / on : output 0 / gpio5->dr &= ~(1<<3); else /* on : output 1 */ gpio5->dr |= (1<<3); } else if (which == 1) { if (status) /* on : output 0 */ gpio1->dr &= ~(1<<3); else /* on : output 1 */ gpio1->dr |= (1<<3); } else if (which == 2) { if (status) /* on : output 0 */ gpio1->dr &= ~(1<<5); else /* on : output 1 */ gpio1->dr |= (1<<5); } else if (which == 3) { if (status) /* on : output 0 */ gpio1->dr &= ~(1<<6); else /* on : output 1 */ gpio1->dr |= (1<<6); } return 0; }
static struct led_operations board_demo_led_opr = { .num = 4, .init = board_demo_led_init, .ctl = board_demo_led_ctl, };
struct led_operations *get_board_led_opr(void) { return &board_demo_led_opr; } ```

