通常,我们会为每个 Mapper.xml 配置文件创建一个对应的 Mapper 接口,并且无须提供这个接口的实现,在执行 SQL 语句时直接调用这个 Mapper 对象的方法执行即可。那 MyBatis 是如何通过这个 Mapper 接口来执行相应的 SQL 语句的呢?实际上,在 MyBatis 中,实现 Mapper 接口与 Mapper.xml 配置文件映射功能的是 binding 模块,其涉及的核心类如下图所示:
MapperRegistry
MapperRegistry 是 MyBatis 初始化过程中构造的一个对象,主要作用就是统一维护 Mapper 接口以及这些 Mapper 的代理对象工厂。在 MyBatis 初始化时,所有配置信息会被解析成相应的对象记录到 Configuration 对象中。其中,Configuration 的 mapperRegistry 属性就记录了当前使用的 MapperRegistry 对象。
下面我们先来看 MapperRegistry 中的核心字段:
// 指向MyBatis全局唯一的Configuration对象,其中维护了解析之后的全部MyBatis配置信息private final Configuration config;// 维护了所有解析的Mapper接口以及MapperProxyFactory工厂对象之间的映射关系private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
在 MyBatis 初始化时,会读取全部 Mapper.xml 配置文件,还会扫描全部 Mapper 接口中的注解信息,之后会调用 MapperRegistry 的 addMapper() 方法填充 knownMappers 集合。在填充 knownMappers 集合之前,MapperRegistry 会先保证传入的 type 参数是一个接口且是 knownMappers 集合没有加载过 type 类型,然后才会创建相应的 MapperProxyFactory 工厂并记录到 knownMappers 集合中。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {// 是否是接口if (type.isInterface()) {// 是否已经存在if (hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {// 添加到knownMappers集合中knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));// Mapper对应的XML解析和注解处理MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);parser.parse();loadCompleted = true;} finally {if (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}}
MapperProxyFactory
在需要执行某 SQL 语句时,会先调用 MapperRegistry 的 getMapper() 方法获取实现了 Mapper 接口的代理对象,然后通过代理对象执行具体的操作。这里会先拿到之前创建的 MapperProxyFactory 工厂对象,并调用其 newInstance() 方法创建 Mapper 接口的代理对象。底层是通过 JDK 动态代理的方式生成代理对象的,如下代码所示,这里使用的 InvocationHandler 实现是 MapperProxy。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}}
MapperProxy
通过分析 MapperProxyFactory 这个工厂类,我们可以清晰地看到 MapperProxy 是生成 Mapper 接口代理对象的关键,它实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,是执行 SQL 的关键。来看下 MapperProxy 中的核心字段:
// 记录了当前MapperProxy关联的SqlSession对象, 用于访问数据库private final SqlSession sqlSession;// Mapper接口类型,也是当前MapperProxy关联的代理对象实现的接口类型private final Class<T> mapperInterface;// key是Mapper接口中的方法对应的Method对象,value是该方法对应的MapperMethod对象// MapperMethod对象会完成参数转换以及SQL语句的执行功能private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
MapperProxy 中的 invoke() 方法是代理对象执行的主要逻辑,其实现如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {// 如果是Object中定义的方法,则直接调用,无需代理if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {// 针对Java7以上版本对动态类型语言的支持return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}// 从缓冲中获取MapperMethod对象,如果缓冲中没有,则创建新的MapperMethod对象并添加到缓存中final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);// 执行SQL语句return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
MapperMethod
MapperMethod 中封装了 Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应 SQL 语句的信息。我们可以将 MapperMethod 看作是连接 Mapper 接口与 Mapper.xml 配置文件中定义的 SQL 语句的桥梁。其核心字段如下代码所示:
// 记录了SQL语句的名称和类型private final SqlCommand command;// Mapper接口中对应方法的相关信息private final MethodSignature method;
1. SqlCommand
SqlCommand 是 MapperMethod 中定义的内部类,它使用 name 字段记录了 SQL 语句的名称,使用 type 字段(SqlCommandType 枚举类型)记录了 SQL 语句的类型。SqlCommand 的构造方法会初始化 name 字段和 type 字段,代码如下:
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {// 获取Mapper接口中对应的方法名称final String methodName = method.getName();// 获取Mapper接口的类型final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();// 将Mapper接口名称和方法名称拼接起来作为SQL语句唯一标识,到Configuration这个全局配置对象中查找SQL语句// MappedStatement对象就是Mapper.xml配置文件中一条SQL语句解析之后得到的对象MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,configuration);if (ms == null) {// 针对@Flush注解的处理if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {name = null;type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;} else {throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);}} else {// 记录SQL语句唯一标识name = ms.getId();// 记录SQL语句的操作类型type = ms.getSqlCommandType();if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);}}}
这里调用的 resolveMappedStatement() 方法不仅会尝试根据 SQL 语句的唯一标识从 Configuration 全局配置对象中查找关联的 MappedStatement 对象,还会尝试顺着 Mapper 接口的继承树进行查找,直至找到为止。
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {// 将Mapper接口名称和方法名称拼接起来作为SQL语句唯一标识String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;// 检测Configuration中是否包含相应的MappedStatement对象if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {// 如果方法就定义在当前接口中,则证明没有对应的SQL语句,返回nullreturn null;}// 如果当前检查的Mapper接口(mapperInterface)中不是定义该方法的接口(declaringClass),则会从mapperInterface开始,沿着继承关系向上查找递归每个接口,// 查找该方法对应的MappedStatement对象for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,declaringClass, configuration);if (ms != null) {return ms;}}}return null;}
2. MethodSignature
MethodSignature 也是 MapperMethod 中定义的内部类,其维护了 Mapper 接口中方法的相关信息。
// 表示方法返回值是否为Collection集合或数组private final boolean returnsMany;// 表示方法返回值是否为Map集合private final boolean returnsMap;// 表示方法返回值是否为voidprivate final boolean returnsVoid;// 表示方法返回值是否为Cursorprivate final boolean returnsCursor;// 方法返回值的具体类型private final Class<?> returnType;// 如果方法的返回值为Map集合,则通过mapKey字段记录了作为key的列名。mapKey字段的值是通过解析方法上的@MapKey注解得到的private final String mapKey;// 记录了Mapper接口方法的参数列表中ResultHandler类型参数的位置private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;// 记录了Mapper接口方法的参数列表中RowBounds类型参数的位置private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;// 用来解析方法参数列表的工具类private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
在上述字段中,需要着重讲解的是 ParamNameResolver 这个解析方法参数列表的工具类。在 ParamNameResolver 中有一个 names 字段(SortedMap
另外,names 集合会跳过 RowBounds 类型以及 ResultHandler 类型的参数,如果使用下标索引作为参数名称,在 names 集合中就会出现 KV 不一致的场景。例如下图就很好地说明了这种不一致的场景,其中 saveCustomer(long id, String name, RowBounds bounds, String address) 方法对应的 names 集合为 {{0, “0”}, {1, “1”}, {2, “3”}}。由于 RowBounds 参数的存在,第四个参数在 names 集合中的 KV 出现了不一致,即 key = 2 与 value = “3” 不一致。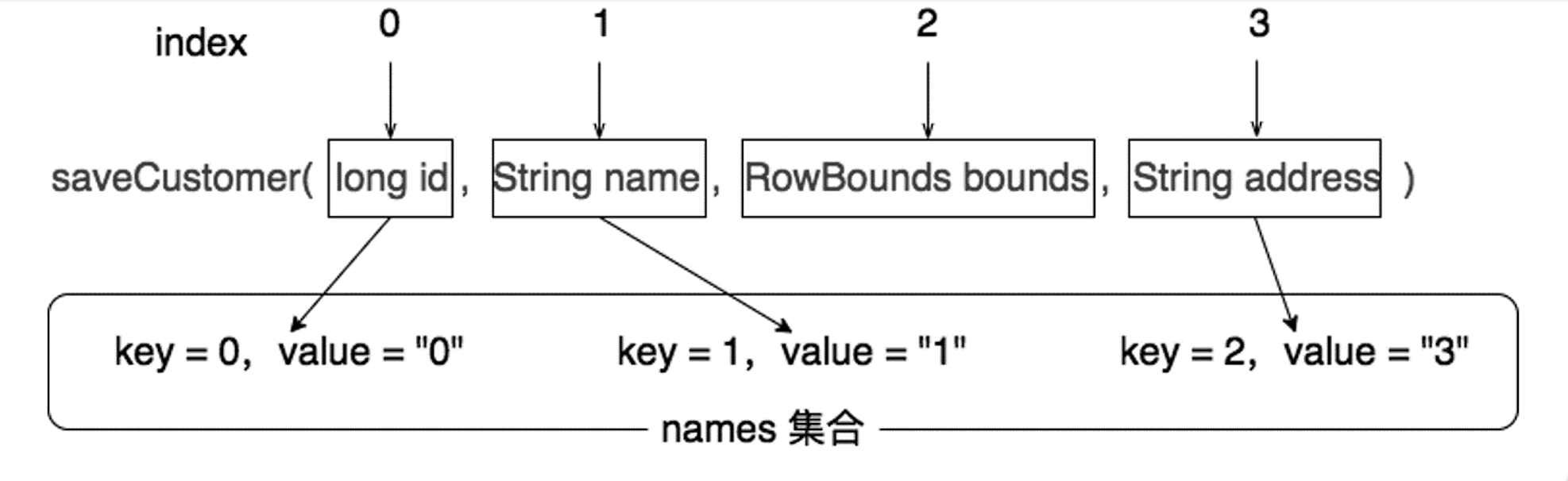
在 ParamNameResolver 的构造方法中,会通过反射的方式读取 Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,并初始化 names 集合,具体实现代码如下:
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {// 获取参数列表中每个参数的类型final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();// 获取参数列表上的注解final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();// 该集合用于记录参数索引与参数名称的对应关系final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {// 如果参数是RowBounds或ResultHandler类型,则跳过该参数if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {continue;}String name = null;// 遍历该参数对应的注解集合for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {if (annotation instanceof Param) {hasParamAnnotation = true;// 获取@Param注解指定的参数名称name = ((Param) annotation).value();break;}}if (name == null) {// 获取原始参数名称,Configuration中的useActualParamName默认为trueif (config.isUseActualParamName()) {name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);}if (name == null) {// 获取参数下标索引作为参数名称name = String.valueOf(map.size());}}map.put(paramIndex, name);}// 保存到names集合中names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);}
names 集合主要在 ParamNameResolver 的 getNamedParams() 方法中使用,该方法接收的参数是用户传入的实参列表,并将实参与其对应名称进行关联。
了解了 ParamNameResolver 的核心功能后,我们回到 MethodSignature 继续分析,在构造 MethodSignature 时会解析方法中的返回值、参数列表等信息,并会初始化上面介绍的几个核心字段。
3. 方法执行
介绍完 MapperMethod 中定义的内部类,我们回到 MapperMethod 继续分析。MapperMethod 中最核心的方法是 execute() 方法,它会根据 SQL 语句的类型调用 SqISession 对应的方法完成数据库操作。SqlSession 是 MyBatis 的核心组件之一,其具体实现我们后面会详细介绍。MapperMethod.execute() 方法的具体实现如下:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;// 根据SQL语句的类型调用SqlSession对应的方法switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {// 使用ParamNameResolver处理args[]数组(用户传入的实参列表),将用户传入的实参与指定参数名称关联起来Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 调用SqlSession的insert方法,rowCountResult方法会根据method字段中记录的方法的返回值类型对结果进行转换result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}// UPDATE和DELETE类型的SQL语句的处理与INSERT类型的SQL语句相似case UPDATE:case DELETE:......case SELECT:// 处理返回值为void且ResultSet通过ResultHandler处理的方法if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) {// 处理返回值为集合或数组的方法result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) {// 处理返回值为Map的方法result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {// 处理返回值为Cursor的方法result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {// 处理返回值为单一对象的方法Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);}break;......}return result;}
在 execute() 方法中,当执行 INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 这三种类型的 SQL 语句时,其执行结果都需要经过 rowCountResult() 方法处理。比如:SqISession 中的 insert() 方法返回的是 int 值,rowCountResult() 方法会将该 int 值转换成 Mapper 接口中对应方法的返回值。多数场景中这个 int 值代表了 SQL 语句影响的数据行数,但这个返回值的具体含义会根据 MySQL 的配置有所变化。

