1、包装类概述
基本类型的包装类主要提供了更多的实用操作,这样更容易处理基本类型。所有的包装类都是final的,所以不能创建其子类,包装类都是不可变对象
| 基本类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| char | Character |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
2、类层次结构
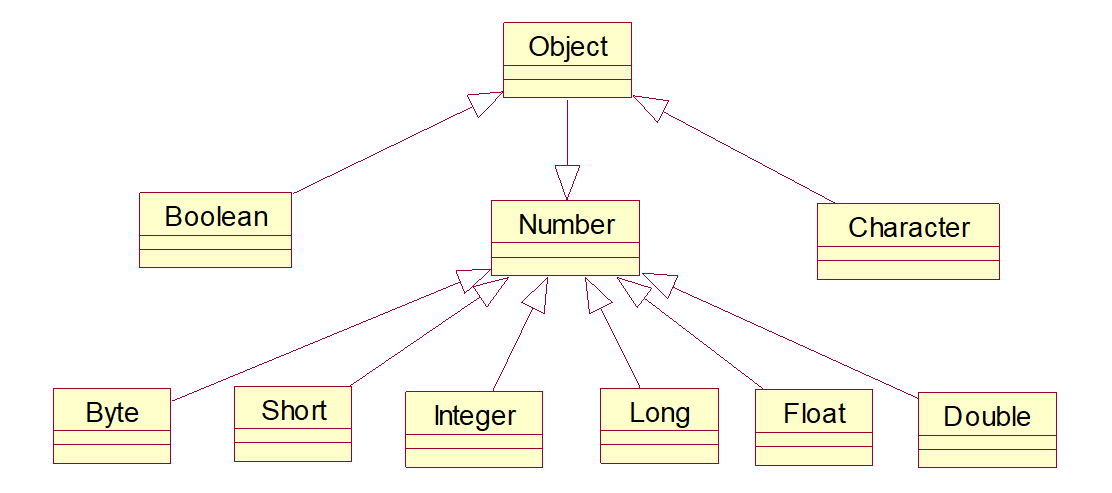
除了boolean和Character外,其它的包装类都有valueOf()和parseXXX方法,并且还具有byteVaue(),shortVaue(),intValue(),longValue(),floatValue()和doubleValue()方法,这些方法是最常用的方法
public class IntegerTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i1 = 100;Integer i2 = new Integer(i1);double i3 = i2.doubleValue();String s = "123";int i4 = Integer.parseInt(s);Integer i5 = new Integer(s);Integer i6 = Integer.valueOf(s);}}
3、JDK5.0的新特性
在JDK5.0以前,包装类和基本类型做运算时,必须将包装类转换成基本类型才可以,而JDK5.0提供Auto-boxing/unboxing(自动装箱和拆箱)
- 自动将基础类型转换为对象
自动将对象转换为基础类型
public class IntegerTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//jdk1.5以前版本,必须按如下方式赋值Integer i1 = new Integer(100);//jdk1.5及以后版本支持//自动装箱Integer i2 = 100;//jdk1.5及以后版本支持//自动拆箱int i3 = i2;//jdk1.5以前版本,必须按如下方式赋值int i4 = i2.intValue();}}
4、常用方法
```java int i = Integer.parseInt(“223”); String s = Integer.toBinaryString(125); String d = Integer.toHexString(125); String s1 = Integer.toOctalString(125); Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(“100”);
```

