具体分类position
position
1.relative—-相对定位
2.absolute—绝对定位
3.static—无定位
4.fixed—固定定位
相对定位
1.相对定位的偏移参数元素是元素本身,不会是元素脱离文档流,元素的初始位置占据的控件会被保留
2.position:relative
3.相对定位的偏移是自己之前的位置作为参照进行的一个偏移
4.相对定位不作为元素单独显示出来,卫视作为父容器去包含其他元素使用
5.子绝父相—子元素设置绝对定位,父元素设置相对定位
绝对定位
1.绝对定位对于一定为的最近的祖先元素,如果没有一定位的最近的祖先元素,那么她的位置就相对于最初的包含快(body)
2.position:absolute
相对定位和绝对定位的区别
作为父容器存在的时候,使用相对定位还是绝对定位
总结
绝对定位和浮动
相对定位和浮动
z-index的使用
1、层叠模式
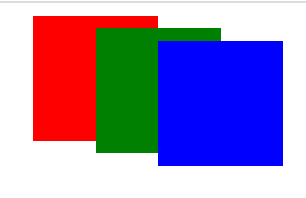
2、案例代码演示
原始图片位置: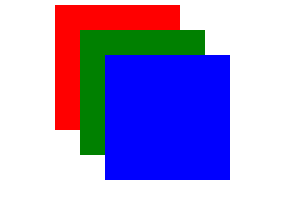
z-index后的效果图:
3、总结:
- 决定谁在前面,谁在后面,数字大小上不封顶
- 数值不适宜设置的过大,没意义。但是也适宜设置的过小,因为以后的页面的div很多,可以让他们一起重叠显示
固定定位
1、相对于浏览器窗口进行定位
2、position:fixed
3、案例代码演示
综合案例 — 购物车
1、效果图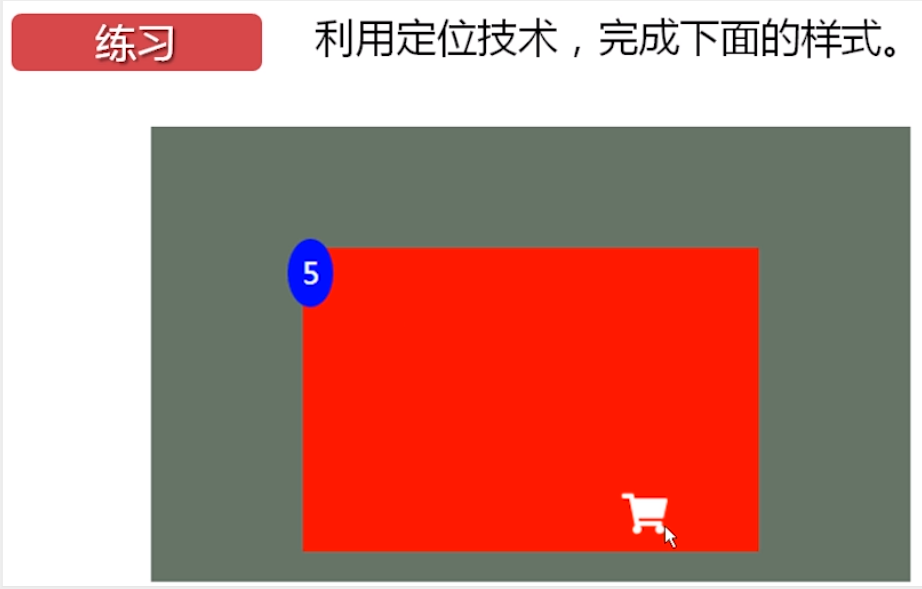
购物车代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>购物车</title><style type="text/css">.div0{background: rgba(0,0,0,0.5);width: 800px;height: 600px;position: relative;/*设置定位*/top: 40px;left: 80px;}.div1{background: red;width: 600px;height: 400px;position: absolute;top: 171px;left: 100px;}.div2{background: blue;width: 50px;height: 90px;border-radius: 50%;font-size: 40px;text-align: center;color: white;position: absolute;top: -10px;left: -20px;line-height: 89px;}img{width: 50px;height: 65px;position: absolute;/*子随父动*/bottom: 20px;right: 100px;}</style></head><body><div class="div0"><div class="div1"><div class="div2">5</div><div class="div3"><img src="cart.svg"></div></div></div></body></html>