一、前言
React 从 v16 开始,像是跨入了新的时代,性能和新的 API 都令人瞩目。重新认识 React,从重新认识生命周期开始。> 为了更好的支持异步渲染(Async Rendering),解决一些生命周期滥用可能导致的问题,React 从 V16.3
开始,对生命周期进行渐进式调整,同时在官方文档也提供了使用的最佳实践。 这里我们将简要对比 React 新旧生命周期,重新认识一下 React 生命周期。
React V16.3 新增的生命周期方法
getDerivedStateFromProps()getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
逐渐废弃的生命周期方法:
componentWillMount()componentWillReceiveProps()componentWillUpdate()
虽然废弃了这三个生命周期方法,但是为了向下兼容,将会做渐进式调整。(详情见#12028)
V16.3 并未删除这三个生命周期,同时还为它们新增以 UNSAFE_前缀为别名的三个函数 UNSAFE_componentWillMount()、UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()、UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate()。
在 16.4 版本给出警告将会弃用 componentWillMount()、componentWillReceiveProps()、componentWillUpdate() 三个函数
然后在 17 版本将会删除 componentWillMount()、componentWillReceiveProps()、componentWillUpdate() 这三个函数,会保留使用 UNSAFE_componentWillMount()、UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()、UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate()
二、react-v16.3之前版本的生命周期(老生命周期)

1.生命周期总览
react的生命周期大概分为
- 组件装载(Mount)组件第一次渲染到Dom树
- 组件更新(update)组件state,props变化引发的重新渲染
- 组件卸载(Unmount)组件从Dom树删除
2.组件装载过程
- constructor: 在此初始化state,绑定成员函数this环境,props本地化
- componentWillMount: 预装载函数,
不能进行修改state的操作,即使做了,也不会进行新数据状态的渲染。在该函数中做的操作,都可以提前到构造函数中。 - render:
渲染函数,唯一的一定不能省略的函数,必须有返回值,返回null或false表示不渲染任何DOM元素。它是一个仅仅用于渲染的纯函数,返回值完全取决于this.state和this.props,不能在函数中任何修改props、state、拉取数据等具有副作用的操作。render函数返回的是JSX的对象,该函数并不因为这渲染到DOM树,何时进行真正的渲染是有React库决定的。(setState是一个”异步函数”) - componentDidMount:
挂载成功函数。该函数不会再render函数调用完成之后立即调用,因为render函数仅仅是返回了JSX的对象,并没有立即挂载到DOM树上,而componentDidMount是在组件被渲染到DOM树之后被调用的。另外,componentDidMount函数在进行服务器端渲染时不会被调用。
3.组件更新过程
当组件挂载到DOM树上之后,props/state被修改会导致组件进行更新操作。更新过程会以此调用如下的生命周期函数:
- componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps): 该函数在组件进行更新以及父组件render函数(不管数据是否发生了改变)被调用后执行,this.props取得当前的props,nextProps传入的是要更新的props。通常是比较this.props和nextProps来重新setState。
- shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState): 返回bool值,true表示要更新,false表示不更新,使用得当将大大提高React组件的性能,避免不需要的渲染。
- componentWillUpdate: 预更新函数。
- render: 渲染函数。
- componentDidUpdate: 更新完成函数。 相比装载过程的生命周期函数,更新过程的生命周期函数使用的相对来说要少一些。常用的是componentWillReceiveProps、componentShouldUpdate,前者经常用于根据前后两个数据去设置组件的状态,而后者则是常用于优化,避免不必要的渲染。
4.组件卸载过程
卸载过程只涉及一个函数componentWillUnmount,当React组件要从DOM树上删除前,会调用一次这个函数。这个函数经常用于去除componentDidMount函数带来的副作用,例如清除计时器、删除componentDidMount中创造的非React元素。
5.注意事项
setState
要修改state,只能使用this.setState(),不能使用this.state.value=’myData’ 类似方式设置state,一是不会驱动重新渲染,二是很可能被后面的操作替换,造成无法预知的错误。此外,React利用``状态队列``来实现setState的异步更新,避免频繁地重复更新state。当同时做了很多setState操作的时候,react会智能的合并成一个setState,当需要确定的setState完成后的操作,可以使用
setState({}, () => {// 在这里进行state改变后的操作})
setState的调用是有风险的,在某些生命周期函数中调用可能会无用甚至早恒循环调用导致崩溃。state的初始化一般在构造函数中实现;setState可以在装载过程的componentWillMount、componentDidMount中调用;setState可以在更新过程中的componentWillReceiveProps、componentDidUpdate中调用
render
render是一个异步函数,render执行后并不会直接生成Dom,而是生成虚拟Dom节点(模拟HTML Dom节点的一个javaScript数据结构),何时生成真实的DOM树取决于react框架本身的计算
三、react-v16.3之后版本的生命周期(新生命周期)
1.新的生命周期
getDerivedStateFromProps
- 触发时间(v16.4修正):组件每次被render的时候,包括在组件构建之后(虚拟dom之后,实际dom挂载之前),每次获取新的props或state之后。在v16.3版本时,组件state的更新不会触发该生命周期。
- 每次接收新的props之后都会返回一个对象作为新的state,返回null则说明不需要更新state.
- 配合componentDidUpdate,可以覆盖componentWillReceiveProps的所有用法
- getDerivedStateFromProps是一个静态函数,所以函数体内不能访问this,输出完全由输入决定。
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {//根据nextProps和prevState计算出预期的状态改变,返回结果会被送给setState}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- 触发时间: update发生的时候,在render之后,在组件dom渲染之前。
- 返回一个值,作为componentDidUpdate的第三个参数。
- 配合componentDidUpdate, 可以覆盖componentWillUpdate的所有用法。
2.删除的生命周期
- componentWillReceiveProps
- componentWillMount
- componentWillUpdate
差异
所有被删除的生命周期函数,目前还凑合着用,但是只要用了,开发模式下会有红色警告,在下一个大版本(也就是React v17)更新时会彻底废弃。
3.生命周期功能替换一览
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {4. Updating state based on props7. Fetching external data when props change}constructor() {1. Initializing state}componentDidMount() {2. Fetching external data3. Adding event listeners (or subscriptions)}shouldComponentUpdate() {}render() {}getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {8. Reading DOM properties before an update}componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {5. Invoking external callbacks6. Side effects on props change}componentWillUnmount() {}
// before
**
componentWillMount() {// 1. Initializing state// 2. Fetching external data// 3. Adding event listeners (or subscriptions)}componentWillReceiveProps() {// 4. Updating state based on props// 6. Side effects on props change// 7. Fetching external data when props change}componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {// 5. Invoking external callbacks// 8. Reading DOM properties before an update}
四、react生命周期总结
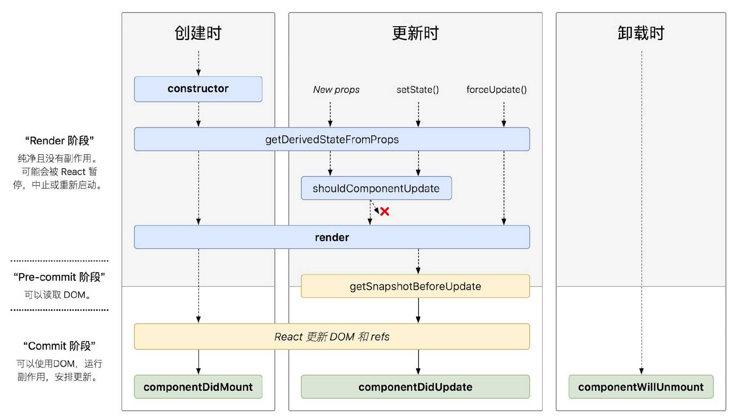
目前 react 16.8 +的生命周期分为三个阶段,分别是> 挂载阶段、> 更新阶段、> 卸载阶段
1.简介
挂载阶段:
**constructor(props): 实例化。static getDeriverdStateFromProps 从 props 中获取 state。render 渲染。componentDidMount: 完成挂载。
更新阶段:
**static getDeriverdStateFromProps 从 props 中获取 state。shouldComponentUpdate 判断是否需要重绘。render 渲染。getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 获取快照。componentDidUpdate 渲染完成后回调。
卸载阶段:
**componentWillUnmount 即将卸载。
错误处理:
**static getDerivedStateFromError 从错误中获取 state。componentDidCatch 捕获错误并进行处理。
2.创建阶段 Mounting
组件实例创建并插入 DOM 时,按顺序调用以下方法:
constructor()static getDerivedStateFromProps()
componentWillMount()/UNSAFE_componentWillMount()(being deprecated)render()componentDidMount()
有定义 getDerivedStateFromProps 时,会忽略 componentWillMount()/UNSAFE_componentWillMount()
(详情查看源码)
1)constructor()
**constructor(props)
构造函数通常用于:
- 使用 this.state 来初始化 state
- 给事件处理函数绑定 this
注意:ES6 子类的构造函数必须执行一次 super()。React 如果构造函数中要使用 this.props,必须先执行 super(props)。
2)static getDerivedStateFromProps()
**static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState)
当创建时、接收新的 props 时、setState 时、forceUpdate 时会执行这个方法。
注意:v16.3 setState 时、forceUpdate 时不会执行这个方法,v16.4 修复了这个问题。
这是一个静态方法,参数 nextProps 是新接收的 props,prevState 是当前的 state。返回值(对象)将用于更新 state,如果不需要更新则需要返回 null。
下面是官方文档给出的例子
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {// Initialize state in constructor,// Or with a property initializer.state = {isScrollingDown: false,lastRow: null,};static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {// 新的状态和老的状态if (props.currentRow !== state.lastRow) {return {isScrollingDown: props.currentRow > state.lastRow,lastRow: props.currentRow,};}// Return null to indicate no change to state.return null;}}
这个方法的常用作用也很明显了:父组件传入新的 props 时,用来和当前的 state 对比,判断是否需要更新 state。以前一般使用 componentWillReceiveProps 做这个操作。
这个方法在建议尽量少用,只在必要的场景中使用,一般使用场景如下:
无条件的根据 props 更新 state
当 props 和 state 的不匹配情况更新 state
详情可以参考官方文档的最佳实践 You Probably Don’t Need Derived State
3)componentWillMount()/UNSAFE_componentWillMount()(弃用)UNSAFE_componentWillMount()
这个方法已经不推荐使用。因为在未来异步渲染机制下,该方法可能会多次调用。它所行使的功能也可以由 componentDidMount() 和 constructor() 代替:
之前有些人会把异步请求放在这个生命周期,其实大部分情况下都推荐把异步数据请求放在 componentDidMount() 中。在服务端渲染时,通常使用 componentWillMount() 获取必要的同步数据,但是可以使用 constructor() 代替它。
可以使用 setState,不会触发 re-render
(4)renderrender()
每个类组件中,render() 唯一必须的方法。
render() 正如其名,作为渲染用,可以返回下面几种类型:
- React 元素(React elements)
- 数组(Arrays)
- 片段(fragments)
- 插槽(Portals)
- 字符串或数字(String and numbers)
- 布尔值或 null(Booleans or null)
注意:
Arrays 和 String 是 v16.0.0 新增。
fragments 是 v16.2.0 新增。
Portals 是 V16.0.0 新增。
里面不应该包含副作用,应该作为纯函数。
不能使用 setState。
(5)componentDidMount()**componentDidMount()组件完成装载(已经插入 DOM 树)时,触发该方法。这个阶段已经获取到真实的 DOM。
一般用于下面的场景:
- 异步请求 ajax
- 添加事件绑定(注意在 componentWillUnmount 中取消,以免造成内存泄漏)
- 可以使用 setState,触发re-render,影响性能。
3.更新阶段 Updating
componentWillReceiveProps()/UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()(being deprecated)static getDerivedStateFromProps()shouldComponentUpdate()
componentWillUpdate()/UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate()(being deprecated)render()getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()componentDidUpdate()
有 getDerivedStateFromProps 或者 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 时,componentWillReceiveProps()/UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps() 和 componentWillUpdate()/UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate() 不会执行 (详情查看源码)
1)componentWillReceiveProps()/UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()(弃用)UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
这个方法在接收新的 props 时触发,即使 props 没有变化也会触发。
一般用这个方法来判断 props 的前后变化来更新 state,如下面的例子:
class ExampleComponent extends React.Component {state = {isScrollingDown: false,};componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {if (this.props.currentRow !== nextProps.currentRow) {this.setState({isScrollingDown:nextProps.currentRow > this.props.currentRow,});}}}
这个方法将被弃用,推荐使用 getDerivedStateFromProps 代替。
可以使用 setState
(2)static getDerivedStateFromProps()
同 Mounting 时所述一致。
(3)shouldComponentUpdate()
在接收新的 props 或新的 state 时,在渲染前会触发该方法。
该方法通过返回 true 或者 false 来确定是否需要触发新的渲染。返回 false, 则不会触发后续的 UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate()、render() 和 componentDidUpdate()(但是 state 变化还是可能引起子组件重新渲染)。
所以通常通过这个方法对 props 和 state 做比较,从而避免一些不必要的渲染。
PureComponent 的原理就是对 props 和 state 进行浅对比(shallow comparison),来判断是否触发渲染。
(4)componentWillUpdate()/UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate() (弃用)UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
当接收到新的 props 或 state 时,在渲染前执行该方法。
在以后异步渲染时,可能会出现某些组件暂缓更新,导致 componentWillUpdate 和 componentDidUpdate 之间的时间变长,这个过程中可能发生一些变化,比如用户行为导致 DOM 发生了新的变化,这时在 componentWillUpdate 获取的信息可能就不可靠了。
不能使用 setState
(5)render()
同 Mounting 时所述一致。
(6)getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()getSnapShotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
这个方法在 render() 之后,componentDidUpdate() 之前调用。
两个参数 prevProps 表示更新前的 props,prevState 表示更新前的 state。
返回值称为一个快照(snapshot),如果不需要 snapshot,则必须显示的返回 null —— 因为返回值将作为 componentDidUpdate() 的第三个参数使用。所以这个函数必须要配合 componentDidUpdate() 一起使用。
**
这个函数的作用是在真实 DOM 更新(componentDidUpdate)前,获取一些需要的信息(类似快照功能),然后作为参数传给 componentDidUpdate。例如:在 getSnapShotBeforeUpdate 中获取滚动位置,然后作为参数传给 componentDidUpdate,就可以直接在渲染真实的 DOM 时就滚动到需要的位置。
下面是官方文档给出的例子:
class ScrollingList extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.listRef = React.createRef();}getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {// Are we adding new items to the list?// Capture the scroll position so we can adjust scroll later.if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {const list = this.listRef.current;return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;}return null;}componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {// If we have a snapshot value, we've just added new items.// Adjust scroll so these new items don't push the old ones out of view.// (snapshot here is the value returned from getSnapshotBeforeUpdate)if (snapshot !== null) {const list = this.listRef.current;list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;}}render() {return (<div ref={this.listRef}>{/* ...contents... */}</div>);}}
(7)componentDidUpdate()componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
这个方法是在更新完成之后调用,第三个参数 snapshot 就是 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 的返回值。
**
正如前面所说,有 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 时,必须要有 componentDidUpdate。所以这个方法的一个应用场景就是上面看到的例子,配合 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 使用。
可以使用 setState,会触发 re-render,所以要注意判断,避免导致死循环。
4.卸载阶段 Unmounting
(1)componentWillUnmount()componentWillUnmount()
在组件卸载或者销毁前调用。这个方法主要用来做一些清理工作,例如:
- 取消定时器
- 取消事件绑定
- 取消网络请求
5.错误处理 Error Handling
componentDidCatch()componentDidCatch(err, info)
任何子组件在渲染期间,生命周期方法中或者构造函数 constructor 发生错误时调用。
错误边界不会捕获下面的错误:
- 事件处理 (Event handlers) (因为事件处理不发生在 React 渲染时,报错不影响渲染)
- 异步代码 (Asynchronous code) (e.g. setTimeout or requestAnimationFrame callbacks)
- 服务端渲染 (Server side rendering)
- 错误边界本身(而不是子组件)抛出的错误
总结
React 生命周期可以查看 生命周期图
虽然 React 有做向下兼容,但是推荐尽量避免使用废弃的生命周期,而是拥抱未来,用新的生命周期替换它们。
如果你不想升级 React,但是想用新的生命周期方法,也是可以的。使用 react-lifecycles-compat polyfill,可以为低版本的 React(0.14.9+)提供新的生命周期方法。