我们可以看看对应的二维中图形的平移,其实就可以理解为对应的点的移动,我们来看看顶点着色器中的核心代码
一. 核心代码
<canvas id="canvas"></canvas><div id="uiContainer"><div id="ui"><div id="x"></div><div id="y"></div></div></div><!-- vertex shader --><script id="vertex-shader-2d" type="x-shader/x-vertex">attribute vec2 a_position;uniform vec2 u_resolution;void main() {// 将矩形点从像素转换为 0.0 到 1.0vec2 zeroToOne = a_position / u_resolution;// 从 0->1 转换为 0->2vec2 zeroToTwo = zeroToOne * 2.0;// 从 0->2 转换为 -1 -> 1vec2 clipSpace = zeroToTwo - 1.0;gl_Position = vec4(clipSpace * vec2(1, -1), 0, 1);}</script><!-- fragment shader --><script id="fragment-shader-2d" type="x-shader/x-fragment">precision mediump float;uniform vec4 u_color;void main() {gl_FragColor = u_color;}</script>
二. 逻辑流程
首先我们来定义一些变量存储矩形的平移,宽,高和颜色。
var translation = [0, 0];var width = 100;var height = 30;var color = [Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1];
然后定义一个方法重绘所有东西,我们可以在更新变换之后调用这个方法。
// 绘制场景function drawScene() {webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas);// 告诉WebGL如何从裁剪空间对应到像素gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);// 清空画布gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);// 使用我们的程序gl.useProgram(program);// 启用属性gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionLocation);// 绑定位置缓冲gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// 设置矩形参数setRectangle(gl, translation[0], translation[1], width, height);// 告诉属性怎么从positionBuffer中读取数据 (ARRAY_BUFFER)var size = 2; // 每次迭代运行提取两个单位数据var type = gl.FLOAT; // 每个单位的数据类型是32位浮点型var normalize = false; // 不需要归一化数据var stride = 0; // 0 = 移动单位数量 * 每个单位占用内存(sizeof(type))var offset = 0; // 从缓冲起始位置开始读取gl.vertexAttribPointer(positionLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset)// 设置分辨率gl.uniform2f(resolutionLocation, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);// 设置颜色gl.uniform4fv(colorLocation, color);// 绘制矩形var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 6;gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);}
但是想象一下如果对一个更复杂的图形做类似操作怎么办。
假设我们想绘制一个由六个三角形组成的 ‘F’ ,像这样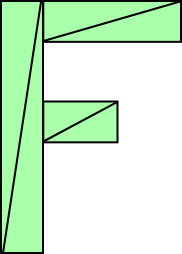
接着当前的代码我们需要修改setRectangle,像这样
// 在缓冲存储构成 'F' 的值function setGeometry(gl, x, y) {var width = 100;var height = 150;var thickness = 30;gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,new Float32Array([// 左竖x, y,x + thickness, y,x, y + height,x, y + height,x + thickness, y,x + thickness, y + height,// 上横x + thickness, y,x + width, y,x + thickness, y + thickness,x + thickness, y + thickness,x + width, y,x + width, y + thickness,// 中横x + thickness, y + thickness * 2,x + width * 2 / 3, y + thickness * 2,x + thickness, y + thickness * 3,x + thickness, y + thickness * 3,x + width * 2 / 3, y + thickness * 2,x + width * 2 / 3, y + thickness * 3,]),gl.STATIC_DRAW);}// 在缓冲存储构成 'F' 的值,这样就不需要很多点一起集合function setGeometry(gl) {gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,new Float32Array([// 左竖0, 0,30, 0,0, 150,0, 150,30, 0,30, 150,// 上横30, 0,100, 0,30, 30,30, 30,100, 0,100, 30,// 中横30, 60,67, 60,30, 90,30, 90,67, 60,67, 90,]),gl.STATIC_DRAW);}// 通过定点着色器同步移动var translationLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_translation");...// 创建一个存放位置信息的缓冲var positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();// 绑定到 ARRAY_BUFFER (简单的理解为 ARRAY_BUFFER = positionBuffer)gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// 将几何数据存到缓冲setGeometry(gl);...// 绘制场景function drawScene() {...// 设置平移gl.uniform2fv(translationLocation, translation);// 绘制矩形var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 18;gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);}
注意到setGeometry只调用了一次,它不在drawScene内部了。
三. 全部代码
"use strict";function main() {// Get A WebGL context/** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */var canvas = document.querySelector("#canvas");var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl");if (!gl) {return;}// setup GLSL programvar program = webglUtils.createProgramFromScripts(gl, ["vertex-shader-2d", "fragment-shader-2d"]);gl.useProgram(program);// look up where the vertex data needs to go.var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position");// lookup uniformsvar resolutionLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_resolution");var colorLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_color");var translationLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_translation");// Create a buffer to put positions invar positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();// Bind it to ARRAY_BUFFER (think of it as ARRAY_BUFFER = positionBuffer)gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// Put geometry data into buffersetGeometry(gl);var translation = [0, 0];var color = [Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1];drawScene();// Setup a ui.webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#x", {slide: updatePosition(0), max: gl.canvas.width });webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#y", {slide: updatePosition(1), max: gl.canvas.height});function updatePosition(index) {return function(event, ui) {translation[index] = ui.value;drawScene();};}// Draw the scene.function drawScene() {webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas);// Tell WebGL how to convert from clip space to pixelsgl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);// Clear the canvas.gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);// Tell it to use our program (pair of shaders)gl.useProgram(program);// Turn on the attributegl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionLocation);// Bind the position buffer.gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// Tell the attribute how to get data out of positionBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER)var size = 2; // 2 components per iterationvar type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floatsvar normalize = false; // don't normalize the datavar stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next positionvar offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffergl.vertexAttribPointer(positionLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset);// set the resolutiongl.uniform2f(resolutionLocation, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);// set the colorgl.uniform4fv(colorLocation, color);// Set the translation.gl.uniform2fv(translationLocation, translation);// Draw the geometry.var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 18; // 6 triangles in the 'F', 3 points per trianglegl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);}}// Fill the buffer with the values that define a letter 'F'.function setGeometry(gl) {gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,new Float32Array([// left column0, 0,30, 0,0, 150,0, 150,30, 0,30, 150,// top rung30, 0,100, 0,30, 30,30, 30,100, 0,100, 30,// middle rung30, 60,67, 60,30, 90,30, 90,67, 60,67, 90,]),gl.STATIC_DRAW);}main();// html代码<canvas id="canvas"></canvas><div id="uiContainer"><div id="ui"><div id="x"></div><div id="y"></div></div></div><!-- vertex shader --><script id="vertex-shader-2d" type="x-shader/x-vertex">attribute vec2 a_position;uniform vec2 u_resolution;uniform vec2 u_translation;void main() {// Add in the translation.vec2 position = a_position + u_translation;// convert the position from pixels to 0.0 to 1.0vec2 zeroToOne = position / u_resolution;// convert from 0->1 to 0->2vec2 zeroToTwo = zeroToOne * 2.0;// convert from 0->2 to -1->+1 (clipspace)vec2 clipSpace = zeroToTwo - 1.0;gl_Position = vec4(clipSpace * vec2(1, -1), 0, 1);}</script><!-- fragment shader --><script id="fragment-shader-2d" type="x-shader/x-fragment">precision mediump float;uniform vec4 u_color;void main() {gl_FragColor = u_color;}</script><script src="https://webglfundamentals.org/webgl/resources/webgl-utils.js"></script><script src="https://webglfundamentals.org/webgl/resources/webgl-lessons-ui.js"></script>

