在我们的日常的生活的中看到的物体在视觉上并不是前后大小一样;至少他应该是前大后小的模式;也就是我们之前的所看到的正视投影应该不符合肉眼的观察习惯的;
想要实现近大远小的效果, 简单的做法就是将裁减空间中的 X 和 Y 值除以 Z 值。
你可以这么想:如果一个线段是 (10, 15) 到 (20,15), 它长度为十个单位,在当前的代码中它就是 10 个像素长, 但是如果我们将它除以 Z ,且 Z 值 为 1
10 / 1 = 10 20 / 1 = 20 abs(10-20) = 10 它将是 10 个像素长
10 / 2 = 5 20 / 2 = 10 abs(5-10) = 5 它将是 5 个像素长
10 / 3 = 3.333 20 / 3 = 6.666 abs(3.333 - 6.666) = 3.333 它将是 3.333 个像素长
一. fudgeFactor
你可以看出随着 Z 变大距离就变远了,画的也会小一点。 如果我们除以裁剪空间中的 Z ,值可能会变大,因为 Z 是一个较小的值(-1 到 +1)。但是我们可以提供一个 fudgeFactor 因子和 Z 相乘,这样就可以调整缩放的程度。
让我们来试试,首先修改顶点着色器,除以 Z 再乘以我们的 “fudgeFactor” 因子。
<script id="vertex-shader-3d" type="x-shader/x-vertex">...uniform float u_fudgeFactor;...void main() {// 将位置和矩阵相乘vec4 position = u_matrix * a_position;// 调整除数float zToDivideBy = 1.0 + position.z * u_fudgeFactor;// x 和 y 除以调整后的除数gl_Position = vec4(position.xy / zToDivideBy, position.zw);}</script>
注意,由于裁减空间中的 Z 值是 -1 到 +1 的,所以 +1 是为了让 zToDivideBy 变成 0 到 +2 * fudgeFactor
还需要更新代码以设置 fudgeFactor。
...var fudgeLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_fudgeFactor");...var fudgeFactor = 1;...function drawScene() {...// 设置 fudgeFactorgl.uniform1f(fudgeLocation, fudgeFactor);// 绘制几何体var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 16 * 6;gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);

事实上WebGL会将我们提供给 gl_Position 的 x,y,z,w 值自动除以 w 。
我们可以通过修改着色器来证明,用 zToDivideBy 代替 gl_Position.w
...var fudgeLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_fudgeFactor");...var fudgeFactor = 1;...function drawScene() {...// 设置 fudgeFactorgl.uniform1f(fudgeLocation, fudgeFactor);// 绘制几何体var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 16 * 6;gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);
二. 矩阵隐藏着线性代数
为什么WebGL会自动除以 W ?
因为使用矩阵的魔力,可以用把值从 z 传值到 w 。
一个这样的矩阵
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0,
将会把 z 的值复制给 w , 你可以把每列看作
x_out = x_in 1 + y_in 0 + z_in 0 + w_in 0 ;
y_out = x_in 0 + y_in 1 + z_in 0 + w_in 0 ;
z_out = x_in 0 + y_in 0 + z_in 1 + w_in 0 ;
w_out = x_in 0 + y_in 0 + z_in 1 + w_in 0 ;
简化后得到
x_out = x_in;
y_out = y_in;
z_out = z_in;
w_out = z_in;
如果 w 原来就是 1.0 就会加 1
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0, 1,
他会将 W 的运算变为
w_out = x_in 0 + y_in 0 + z_in 1 + w_in 1 ;
因为 w_in = 1.0 是已知的
w_out = z_in + 1;
最后可以将 fudgeFactor 像这样放入矩阵中
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, fudgeFactor,
0, 0, 0, 1,
相当于
w_out = x_in 0 +y_in 0 +z_in fudgeFactor + w_in 1 ;
简化后为
w_out = z_in * fudgeFactor + 1;
我们来修改代码,使用这个矩阵。
首先将顶点着色器还原,又变成简单的样子
<script id="vertex-shader-2d" type="x-shader/x-vertex">uniform mat4 u_matrix;void main() {// 位置和矩阵相乘gl_Position = u_matrix * a_position;...}</script>//function makeZToWMatrix(fudgeFactor) {return [1, 0, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, fudgeFactor,0, 0, 0, 1,];}...// 计算矩阵var matrix = makeZToWMatrix(fudgeFactor);matrix = m4.multiply(matrix, m4.projection(gl.canvas.clientWidth, gl.canvas.clientHeight, 400));matrix = m4.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1], translation[2]);matrix = m4.xRotate(matrix, rotation[0]);matrix = m4.yRotate(matrix, rotation[1]);matrix = m4.zRotate(matrix, rotation[2]);matrix = m4.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1], scale[2]);...
这只是展示了除以 Z 值获可以实现透视投影,以及在WebGL中简单实现。
三. Z轴的空间的裁剪
但还有一些问题需要解决,比如将 Z 值设置为 -100 左右的时候会遇到下面的情形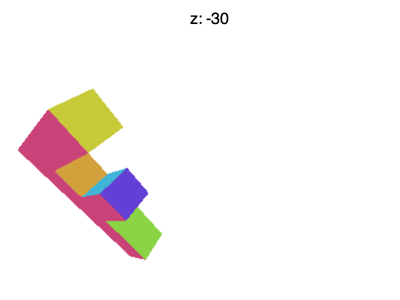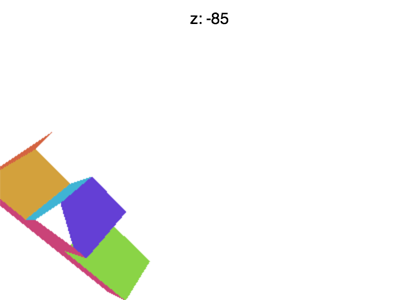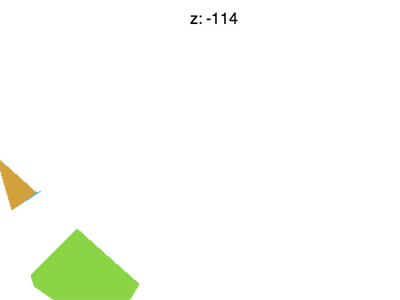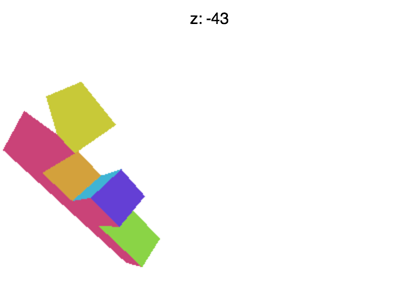
为什么会这样?为什么 F 提前消失了?WebGL裁剪空间中的 X 和 Y 会被 +1 和 -1 裁剪, Z也一样。我们看到的是 Z < -1 的情况。
我可以从数学方法深入探讨并寻找解决办法,但是你可以 联想 二维中的的解决方法。我们需要获取 Z 值,然后加上一些量, 缩放一些量,就可以将任意范围映射到 -1 到 +1 的范围内。
最有意思的是这件事可以在一个矩阵中完成,更方便的是, 我们可以定义一个 fieldOfView 代替 fudgeFactor , 计算出更合适的值。
这是创建矩阵的方法。
var m4 = {perspective: function(fieldOfViewInRadians, aspect, near, far) {var f = Math.tan(Math.PI * 0.5 - 0.5 * fieldOfViewInRadians);var rangeInv = 1.0 / (near - far);return [f / aspect, 0, 0, 0,0, f, 0, 0,0, 0, (near + far) * rangeInv, -1,0, 0, near * far * rangeInv * 2, 0];},...
这个矩阵会为我们完成所有转换。它可以调整单位以适应裁剪空间, 它可以自定义视场角,选择 Z-裁剪面。假设有一个眼睛或者摄像机 在原点(0, 0, 0),根据 zNear 和 fieldOfView 可以将 zNear 对应到 Z = -1 ,在 zNear 平面上一半的 fieldOfView 长度 对应画布中心到 Y = -1 或 Y = 1 的距离,X 的值通过乘以 aspect 获取,最后通过设置 zFar 对应 Z = 1 ,控制缩放的程度。
操作实景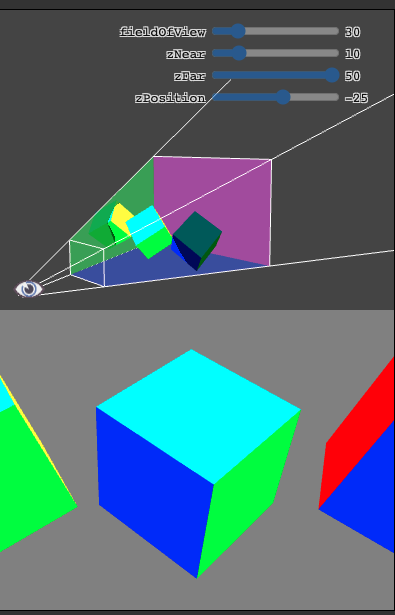
正方体所在的有四个侧面的椎体叫做“视锥”,矩阵将视锥中的空间转换到裁剪空间中, zNear 决定了被正面切割的位置,zFar 决定被背面切割的位置。 将 zNear 设置为 23 就会看到正方体正面被切割, 将 zFar 设置为 24 就会看到正方体背面被切割。
还有一个问题,矩阵假定观察位置为 0,0,0 并且看向 Z 轴负方向, Y 轴为上方向。这和我们目前为止做法不同, 为了解决这个问题我们需要将物体放到视图范围内。
我们在 (45, 150, 0) 绘制的 F,可以将它移动到 (-150, 0, -360)
使用 m4.projection 方法代替之前的投影方法,可以调用 m4.perspective
var aspect = gl.canvas.clientWidth / gl.canvas.clientHeight;var zNear = 1;var zFar = 2000;var matrix = m4.perspective(fieldOfViewRadians, aspect, zNear, zFar);matrix = m4.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1], translation[2]);matrix = m4.xRotate(matrix, rotation[0]);matrix = m4.yRotate(matrix, rotation[1]);matrix = m4.zRotate(matrix, rotation[2]);matrix = m4.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1], scale[2]);
这一块的基本内容基本上以后webgl中关于3d都会涉及到;
四. 终极代码
"use strict";function main() {// Get A WebGL context/** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */var canvas = document.querySelector("#canvas");var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl");if (!gl) {return;}// setup GLSL programvar program = webglUtils.createProgramFromScripts(gl, ["vertex-shader-3d", "fragment-shader-3d"]);// look up where the vertex data needs to go.var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position");var colorLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_color");// lookup uniformsvar matrixLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_matrix");// Create a buffer to put positions invar positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();// Bind it to ARRAY_BUFFER (think of it as ARRAY_BUFFER = positionBuffer)gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// Put geometry data into buffersetGeometry(gl);// Create a buffer to put colors invar colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();// Bind it to ARRAY_BUFFER (think of it as ARRAY_BUFFER = colorBuffer)gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);// Put geometry data into buffersetColors(gl);function radToDeg(r) {return r * 180 / Math.PI;}function degToRad(d) {return d * Math.PI / 180;}var translation = [-150, 0, -360];var rotation = [degToRad(190), degToRad(40), degToRad(320)];var scale = [1, 1, 1];var fieldOfViewRadians = degToRad(60);drawScene();// Setup a ui.webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#fieldOfView", {value: radToDeg(fieldOfViewRadians), slide: updateFieldOfView, min: 1, max: 179});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#x", {value: translation[0], slide: updatePosition(0), min: -200, max: 200 });webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#y", {value: translation[1], slide: updatePosition(1), min: -200, max: 200});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#z", {value: translation[2], slide: updatePosition(2), min: -1000, max: 0});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angleX", {value: radToDeg(rotation[0]), slide: updateRotation(0), max: 360});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angleY", {value: radToDeg(rotation[1]), slide: updateRotation(1), max: 360});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angleZ", {value: radToDeg(rotation[2]), slide: updateRotation(2), max: 360});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleX", {value: scale[0], slide: updateScale(0), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleY", {value: scale[1], slide: updateScale(1), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2});webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleZ", {value: scale[2], slide: updateScale(2), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2});function updateFieldOfView(event, ui) {fieldOfViewRadians = degToRad(ui.value);drawScene();}function updatePosition(index) {return function(event, ui) {translation[index] = ui.value;drawScene();};}function updateRotation(index) {return function(event, ui) {var angleInDegrees = ui.value;var angleInRadians = angleInDegrees * Math.PI / 180;rotation[index] = angleInRadians;drawScene();};}function updateScale(index) {return function(event, ui) {scale[index] = ui.value;drawScene();};}// Draw the scene.function drawScene() {webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas);// Tell WebGL how to convert from clip space to pixelsgl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);// Clear the canvas AND the depth buffer.gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);// Turn on culling. By default backfacing triangles// will be culled.gl.enable(gl.CULL_FACE);// Enable the depth buffergl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);// Tell it to use our program (pair of shaders)gl.useProgram(program);// Turn on the position attributegl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionLocation);// Bind the position buffer.gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);// Tell the position attribute how to get data out of positionBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER)var size = 3; // 3 components per iterationvar type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floatsvar normalize = false; // don't normalize the datavar stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next positionvar offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffergl.vertexAttribPointer(positionLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset);// Turn on the color attributegl.enableVertexAttribArray(colorLocation);// Bind the color buffer.gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);// Tell the attribute how to get data out of colorBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER)var size = 3; // 3 components per iterationvar type = gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE; // the data is 8bit unsigned valuesvar normalize = true; // normalize the data (convert from 0-255 to 0-1)var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next positionvar offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffergl.vertexAttribPointer(colorLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset);// Compute the matrixvar aspect = gl.canvas.clientWidth / gl.canvas.clientHeight;var zNear = 1;var zFar = 2000;var matrix = m4.perspective(fieldOfViewRadians, aspect, zNear, zFar);matrix = m4.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1], translation[2]);matrix = m4.xRotate(matrix, rotation[0]);matrix = m4.yRotate(matrix, rotation[1]);matrix = m4.zRotate(matrix, rotation[2]);matrix = m4.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1], scale[2]);// Set the matrix.gl.uniformMatrix4fv(matrixLocation, false, matrix);// Draw the geometry.var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES;var offset = 0;var count = 16 * 6;gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);}}var m4 = {perspective: function(fieldOfViewInRadians, aspect, near, far) {var f = Math.tan(Math.PI * 0.5 - 0.5 * fieldOfViewInRadians);var rangeInv = 1.0 / (near - far);return [f / aspect, 0, 0, 0,0, f, 0, 0,0, 0, (near + far) * rangeInv, -1,0, 0, near * far * rangeInv * 2, 0];},projection: function(width, height, depth) {// Note: This matrix flips the Y axis so 0 is at the top.return [2 / width, 0, 0, 0,0, -2 / height, 0, 0,0, 0, 2 / depth, 0,-1, 1, 0, 1,];},multiply: function(a, b) {var a00 = a[0 * 4 + 0];var a01 = a[0 * 4 + 1];var a02 = a[0 * 4 + 2];var a03 = a[0 * 4 + 3];var a10 = a[1 * 4 + 0];var a11 = a[1 * 4 + 1];var a12 = a[1 * 4 + 2];var a13 = a[1 * 4 + 3];var a20 = a[2 * 4 + 0];var a21 = a[2 * 4 + 1];var a22 = a[2 * 4 + 2];var a23 = a[2 * 4 + 3];var a30 = a[3 * 4 + 0];var a31 = a[3 * 4 + 1];var a32 = a[3 * 4 + 2];var a33 = a[3 * 4 + 3];var b00 = b[0 * 4 + 0];var b01 = b[0 * 4 + 1];var b02 = b[0 * 4 + 2];var b03 = b[0 * 4 + 3];var b10 = b[1 * 4 + 0];var b11 = b[1 * 4 + 1];var b12 = b[1 * 4 + 2];var b13 = b[1 * 4 + 3];var b20 = b[2 * 4 + 0];var b21 = b[2 * 4 + 1];var b22 = b[2 * 4 + 2];var b23 = b[2 * 4 + 3];var b30 = b[3 * 4 + 0];var b31 = b[3 * 4 + 1];var b32 = b[3 * 4 + 2];var b33 = b[3 * 4 + 3];return [b00 * a00 + b01 * a10 + b02 * a20 + b03 * a30,b00 * a01 + b01 * a11 + b02 * a21 + b03 * a31,b00 * a02 + b01 * a12 + b02 * a22 + b03 * a32,b00 * a03 + b01 * a13 + b02 * a23 + b03 * a33,b10 * a00 + b11 * a10 + b12 * a20 + b13 * a30,b10 * a01 + b11 * a11 + b12 * a21 + b13 * a31,b10 * a02 + b11 * a12 + b12 * a22 + b13 * a32,b10 * a03 + b11 * a13 + b12 * a23 + b13 * a33,b20 * a00 + b21 * a10 + b22 * a20 + b23 * a30,b20 * a01 + b21 * a11 + b22 * a21 + b23 * a31,b20 * a02 + b21 * a12 + b22 * a22 + b23 * a32,b20 * a03 + b21 * a13 + b22 * a23 + b23 * a33,b30 * a00 + b31 * a10 + b32 * a20 + b33 * a30,b30 * a01 + b31 * a11 + b32 * a21 + b33 * a31,b30 * a02 + b31 * a12 + b32 * a22 + b33 * a32,b30 * a03 + b31 * a13 + b32 * a23 + b33 * a33,];},translation: function(tx, ty, tz) {return [1, 0, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, 0,tx, ty, tz, 1,];},xRotation: function(angleInRadians) {var c = Math.cos(angleInRadians);var s = Math.sin(angleInRadians);return [1, 0, 0, 0,0, c, s, 0,0, -s, c, 0,0, 0, 0, 1,];},yRotation: function(angleInRadians) {var c = Math.cos(angleInRadians);var s = Math.sin(angleInRadians);return [c, 0, -s, 0,0, 1, 0, 0,s, 0, c, 0,0, 0, 0, 1,];},zRotation: function(angleInRadians) {var c = Math.cos(angleInRadians);var s = Math.sin(angleInRadians);return [c, s, 0, 0,-s, c, 0, 0,0, 0, 1, 0,0, 0, 0, 1,];},scaling: function(sx, sy, sz) {return [sx, 0, 0, 0,0, sy, 0, 0,0, 0, sz, 0,0, 0, 0, 1,];},translate: function(m, tx, ty, tz) {return m4.multiply(m, m4.translation(tx, ty, tz));},xRotate: function(m, angleInRadians) {return m4.multiply(m, m4.xRotation(angleInRadians));},yRotate: function(m, angleInRadians) {return m4.multiply(m, m4.yRotation(angleInRadians));},zRotate: function(m, angleInRadians) {return m4.multiply(m, m4.zRotation(angleInRadians));},scale: function(m, sx, sy, sz) {return m4.multiply(m, m4.scaling(sx, sy, sz));},};// Fill the buffer with the values that define a letter 'F'.function setGeometry(gl) {gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,new Float32Array([// left column front0, 0, 0,0, 150, 0,30, 0, 0,0, 150, 0,30, 150, 0,30, 0, 0,// top rung front30, 0, 0,30, 30, 0,100, 0, 0,30, 30, 0,100, 30, 0,100, 0, 0,// middle rung front30, 60, 0,30, 90, 0,67, 60, 0,30, 90, 0,67, 90, 0,67, 60, 0,// left column back0, 0, 30,30, 0, 30,0, 150, 30,0, 150, 30,30, 0, 30,30, 150, 30,// top rung back30, 0, 30,100, 0, 30,30, 30, 30,30, 30, 30,100, 0, 30,100, 30, 30,// middle rung back30, 60, 30,67, 60, 30,30, 90, 30,30, 90, 30,67, 60, 30,67, 90, 30,// top0, 0, 0,100, 0, 0,100, 0, 30,0, 0, 0,100, 0, 30,0, 0, 30,// top rung right100, 0, 0,100, 30, 0,100, 30, 30,100, 0, 0,100, 30, 30,100, 0, 30,// under top rung30, 30, 0,30, 30, 30,100, 30, 30,30, 30, 0,100, 30, 30,100, 30, 0,// between top rung and middle30, 30, 0,30, 60, 30,30, 30, 30,30, 30, 0,30, 60, 0,30, 60, 30,// top of middle rung30, 60, 0,67, 60, 30,30, 60, 30,30, 60, 0,67, 60, 0,67, 60, 30,// right of middle rung67, 60, 0,67, 90, 30,67, 60, 30,67, 60, 0,67, 90, 0,67, 90, 30,// bottom of middle rung.30, 90, 0,30, 90, 30,67, 90, 30,30, 90, 0,67, 90, 30,67, 90, 0,// right of bottom30, 90, 0,30, 150, 30,30, 90, 30,30, 90, 0,30, 150, 0,30, 150, 30,// bottom0, 150, 0,0, 150, 30,30, 150, 30,0, 150, 0,30, 150, 30,30, 150, 0,// left side0, 0, 0,0, 0, 30,0, 150, 30,0, 0, 0,0, 150, 30,0, 150, 0]),gl.STATIC_DRAW);}// Fill the buffer with colors for the 'F'.function setColors(gl) {gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,new Uint8Array([// left column front200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,// top rung front200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,// middle rung front200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,200, 70, 120,// left column back80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,// top rung back80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,// middle rung back80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,80, 70, 200,// top70, 200, 210,70, 200, 210,70, 200, 210,70, 200, 210,70, 200, 210,70, 200, 210,// top rung right200, 200, 70,200, 200, 70,200, 200, 70,200, 200, 70,200, 200, 70,200, 200, 70,// under top rung210, 100, 70,210, 100, 70,210, 100, 70,210, 100, 70,210, 100, 70,210, 100, 70,// between top rung and middle210, 160, 70,210, 160, 70,210, 160, 70,210, 160, 70,210, 160, 70,210, 160, 70,// top of middle rung70, 180, 210,70, 180, 210,70, 180, 210,70, 180, 210,70, 180, 210,70, 180, 210,// right of middle rung100, 70, 210,100, 70, 210,100, 70, 210,100, 70, 210,100, 70, 210,100, 70, 210,// bottom of middle rung.76, 210, 100,76, 210, 100,76, 210, 100,76, 210, 100,76, 210, 100,76, 210, 100,// right of bottom140, 210, 80,140, 210, 80,140, 210, 80,140, 210, 80,140, 210, 80,140, 210, 80,// bottom90, 130, 110,90, 130, 110,90, 130, 110,90, 130, 110,90, 130, 110,90, 130, 110,// left side160, 160, 220,160, 160, 220,160, 160, 220,160, 160, 220,160, 160, 220,160, 160, 220]),gl.STATIC_DRAW);}main();
<canvas id="canvas"></canvas><div id="uiContainer"><div id="ui"><div id="fieldOfView"></div><div id="x"></div><div id="y"></div><div id="z"></div><div id="angleX"></div><div id="angleY"></div><div id="angleZ"></div></div></div><!-- vertex shader --><script id="vertex-shader-3d" type="x-shader/x-vertex">attribute vec4 a_position;attribute vec4 a_color;uniform mat4 u_matrix;varying vec4 v_color;void main() {// Multiply the position by the matrix.gl_Position = u_matrix * a_position;// Pass the color to the fragment shader.v_color = a_color;}</script><!-- fragment shader --><script id="fragment-shader-3d" type="x-shader/x-fragment">precision mediump float;// Passed in from the vertex shader.varying vec4 v_color;void main() {gl_FragColor = v_color;}</script><script src="https://webglfundamentals.org/webgl/resources/webgl-utils.js"></script><script src="https://webglfundamentals.org/webgl/resources/webgl-lessons-ui.js"></script>

