域自适应综述:
Li, W., Li, F., Luo, Y., & Wang, P. (2020). Deep Domain Adaptive Object Detection: a Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.06797.
Wang, Mei, and Weihong Deng. “Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey.“ Neurocomputing 312 (2018): 135-153.
Marco Toldo, Andrea Maracani, Umberto Michieli and Pietro Zanuttigh. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation: a Review
Resource:
https://github.com/zhaoxin94/awesome-domain-adaptation#survey
关键词: Deep domain adaptive object detection (DDAOD), few-shot, unsupervised, domain-invariant feature**
背景
Domain** shift是不可避免对于目标检测在真实场景的运用中。例如,在自动驾驶中,很多真实场景环境都不可能在训练集中被观察到、场景文本检测中很多街景,或者户外户内场景不会出现在训练集中,因此解决domain shift是十分有意义的。**
域自适应解决两个问题:
(1)目前DP依赖大量的labeled data的问题,现实工业运用不可能都有大量的labeled 数据。
(2)training数据和testing数据要求具有相同的分布。这是很难实现的,对于cnn及其依赖数据,换个场景performance可能就不太好。
针对上面两个问题,对于从source domain上训练好的模型迁移到target domain场景下是值得探究的,这个过程叫做domain adaptive。然后因为不同domain数据的分布不同,造成了在target domain上面的表现效果极差,这叫domain shift。
DDAOD(Deep domain adaptive object detection)
目前在目标检测方向主要有四种方式解决domain shift:
Discrepancy-based
主要使用fine-tune进行域迁移
**
- [10] ICCV2019”A Robust Learning Approach to Domain Adaptive Object Detection” 基于faster rcnn
使用model pretrained only在source domain产生a set of noisy bounding box作为noisy label对target domain进行监督学习。这篇文章其实很简单,主要有三个机制:1、模型先用labled source domain训练一下,然后在**target domain上产生noisy label(很多地方叫做pseudo-label)**2、训一个classifier对第一阶段产生的pseudo-label进行打分。 3、使用产生的noisy label对网络进行监督学习。
**
- [11] CVPR2019 “**Expl**oring object relation in mean teacher for cross-domain detection.”基于faster rcnn.
(这篇的related work可以作为参考写论文,因为都是从合成数据迁移到真实场景数据上的应用)
3D CAD —-> real data. ** 为了使得model能从合成数据集迁移到真实场景的数据集上,该论文中提出了一种 Mean Teacher with Object Relations (MTOR)的网络结构。idea来源于[12], 基于faster rcnn将object relations加入了consistency cost进行域的更好的迁移。具体实现是:使用source domain(labed)对网络进行训练,在处理target domain的时候,将target image转化成两种带有噪声的image(调整灰度,对比度等),然后分布对这两张图做预测,对预测后的结果做three consistency regularization:
1) Region-Level Consistency to align the region-level predictions between teacher and student; 直接对检测区域做比较的正则
2) Inter-Graph consistency for matching the graph structures between teacher and student 对object 的关系做比较的正则
3) Intra-Graph Consistency to enhance the similarity between regions of same class within the graph of student. 和student的同类的关系graph对其做相似性。
总结:该论文使用了mean teacher去解决domain gap,对object的context做consistency regularization。
- [13] **Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks**
提出了一个自动标注的网络结构,迭代的在visible和thermal形式上面进行标注,利用多光谱数据中的互补信息。这个自动标注流程主要分为三个阶段:
1、迭代标注 2、时间追踪 3、label fusion。
Adversarial-based
Adversarial-based方式主要利用domain classifier进行对抗训练,想得到一个domain confusion的结果,学习domain-invariant 的feature.
具体可以参考一篇比较早的论文 [8] ICML 2015的一篇论文提出Gradient Reversal Layer(GRL)去学习domain-invariant feature ——-Unsupervised Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation。
- **[14] Domain Adaptive Faster R-CNN for Object Detection in the Wild
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.03243
代码:https://github.com/krumo/Domain-Adaptive-Faster-RCNN-PyTorch
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: H-divergence , domain classifier , consistency regularization
这CVPR2018的一篇工作,为了解决domain shift这一个问题,论文中认为domain shift主要发生在 **image level和instance level层面上,因此提出了两个在image level和instance level的components的机制去最小化在两个domain之间的H- divergence。具体在每个component之中,主要训练一个domain classifier去学习一个domain-invariant features。
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> **https://www.yuque.com/weijiawu/research/mpsw2x
- [15] **Adapting object detectors via selective cross-domain alignment**
论文:链接
代码:https://github.com/xinge008/SCDA
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: “**where to look” , “how to align”** ,
论文中认为使用GRL直接对齐整个image是不合适的对于detection任务来说,object detection任务是focuses on local regions的,因此论文中提出了一种方式去解决哪里需要align和如何去align。
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> https://www.yuque.com/weijiawu/research/cgcd23
- [16] Few-shot Adaptive Faster R-CNN
关键词:image-level , instance level , feature pairing mechanism , strong regularization
这是一篇CVPR2019的工作,为了解决domain shift的问题,论文中提出了一种few-shot的处理方式,只需要少量的target domain数据和标注就能完成很好的域迁移工作**。 其主要包含两个level(又是image-level和instance-level呗):**(1)一个基于image-level的split pooling机制对齐local patch上的特征。(2)instance-level在语义上面对齐object feature,避免了类内confusion。最后还有一个a source model feature regularization (SMFR)去稳定域迁移。
- [17] Strong-Weak Distribution Alignment for Adaptive Object Detection
论文:链接
代码:https://github.com/VisionLearningGroup/DA_Detection
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: “weak global alignment” , “strong local alignment” ,
主要提出了一个strong local alignment和一个weak global alignment的概念去更好的实现域迁移工作。
作者认为在object detection中,不同的domain有不同的场景层次分布,所以使用GRL进行域迁移时候应该有侧重点,对于object区域(domain-invariant feature比较多的情况下)应该进行strong alignment,对于global应该进行weak alignment。
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> https://www.yuque.com/weijiawu/research/iun9eb
- [18] Multi-Adversarial Faster-RCNN for Unrestricted Object Detection
关键词:multi-adversarial , hierarchical domain feature alignment , aggregated proposal feature alignment
为了解决domain-shift,论文中提出了一个multi-adversarial Faster- RCNN (MAF) framework:(1).首先提出了一个多层次的domain feature对齐模块(a hierarchical domain feature alignment module)(2).一个information invariant scale reduction module (SRM)被提出去提高adversarial domain adaptation的效率。(3)为了提升模型的域迁移能力,提出了一个weighted gradient reversal layer (WGRL)去有差别的对待feature alignments,解决那些hard confused domain samples。
- [19] SCL: Towards Accurate Domain Adaptive Object Detection via Gradient Detach Based Stacked Complementary Losses
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.02559.pdf
代码:https://github.com/harsh-99/SCL
关键词:**gradient detach based **stacked complementary losses (SCL)
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
为了解决domain-shift,论文中提出了一个a gradient detach based stacked complementary losses (SCL),在论文中作者认为[14]虽然用了更多不同level的loss function去学习discriminative representation, 但是忽略了不同loss的交互和兼容,因此论文提出了SCL(使用了multiple complementary losses)去更好的帮助网络优化学习更多的discriminative representation。
- [20] Synthetic-to-Real Domain Adaptation for Object Instance Segmentation
关键词:global- level , local-level , subtle-level mask
(也是从合成数据集到真实场景数据集的域迁移,可以借鉴)
论文中提出了一种从合成数据集迁移到真实场景数据集的域迁移方式,为了解决domain shift,提出了三种不同level的迁移机制:global level, local-level, 和 subtle - level mask层次的域自适应。
- [21] iFAN: Image- Instance Full Alignment Networks for Adaptive Object Detection
关键词:**image-level alignment , full alignment exploits**
为了能更好的进行域迁移,解决domain shift问题,论文中提出了下面两个alignments: (1)、image-level: 多种尺寸的features在对抗方式下进行对齐。 (2)、Full instance-level alignment: 充分利用了深层的语义信息和实例表示,可以在类别和域之间建立关系。
Reconstruction-based
通过reconstruction source domain或者target domain的方式去提升域迁移的效果,比如使用cycleGAN去产生一些数据用于训练。
- [22] Cross-Domain Car Detection Using Unsupervised Image-to- Image Translation: From Day to Night
论文:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8852008
代码:https://github.com/LCAD-UFES/publications-arruda-ijcnn-2019
关键词:CycleGAN , day-time domain to night-time domain.
论文中为了能试自动驾驶中白天的场景域迁移到晚上,使用了CycleGAN去产生一个合成数据集from day-time domain to night-time domain,最后检测模型训练在fake 数据集上。
- [23] Cross Domain Adaptation for on-Road Object Detection Using Multimodal Structure-Consistent Image-to-Image Translation
关键词:**multi-modal , diverse and structure-preserved translated images**
介绍了一种多模式结构一致的图像到图像转换模型,以实现领域自适应车辆检测。
Hybrid-based
关键词:**WST , BSR
CVPR2019oral基于SSD的域迁移目标检测,提出了WST和BSR进行解决domain shift———**
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> Self-Training and Adversarial Background Regularization for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive One-Stage Object Detection
UDASS(Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation)
在域迁移过程中按照source domain和target domain的类别不同可以分为以下几种情况:
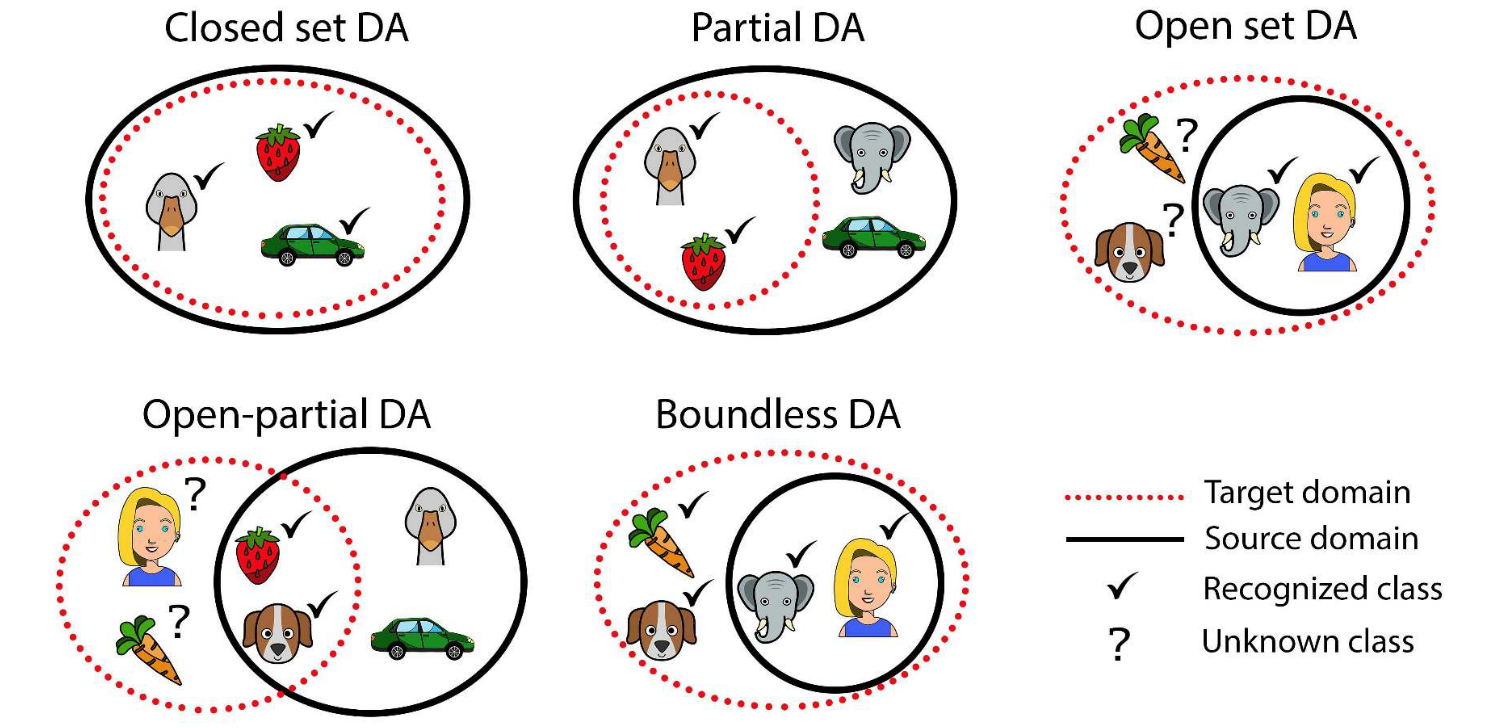
- Closed Set DA:source domain和target domain中的categories是相同的。
- Partial DA:target domain中的categories是source domian中的子集。
- Open Set DA:source domain 中的categories是target domain中的子集。
- Open-Partial DA:source 和target domain有交集的categories,但又有只属于自己的categories。
- Boundless DA:an Open Set DA where all the target domain categories are learned individually
Weakly- and Semi- Supervised Learning
Domain Adversarial Discriminative
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks 2016. 17, 2096–2030.
- Tzeng, E.; Hoffman, J.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. Proc. of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017, pp. 7167–7176.
- Hoffman, J.; Wang, D.; Yu, F.; Darrell, T. FCNs in the wild: Pixel-level adversarial and constraint-based adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.02649 2016
Chen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Huang, J.B. CrDoCo: Pixel-Level Domain Transfer With Cross-Domain Consistency. Proc. of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.
- [27] Pixel-Level Domain Transfer With Cross-Domain Consistency
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.03182
代码:https://github.com/YunChunChen/CrDoCo-pytorch
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: “image-to- image translation” , “**cross- domain consistency loss” ,
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> **
- [28] Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation with Maximum Squares Loss
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.13589.pdf
代码:https://github.com/ZJULearning/MaxSquareLoss
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: “**maximum squares loss**”
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> https://www.yuque.com/weijiawu/research/wx7qh1
- [29] Advent: Adversarial entropy minimization for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation.
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.12833.pdf
代码:https://github.com/valeoai/ADVENT
(有开源代码,好好读一读。。。)
关键词: “**entropy of the pixel-wise**” : 1. entropy loss 2.adversarial loss
为了解决domain gap,更好的实现domain之间的分割域迁移,论文中提出了一种the entropy ofthe pixel-wise predictions,主要有两部分1. entropy loss 2.adversarial loss可以帮助分割网络进行更好的域迁移
更详细可以参考我的另一篇笔记——> https://www.yuque.com/weijiawu/research/hkw6ru
**
Generative-Based Approaches
Classifier Discrepancy
Self-Training
Entropy Minimization
Curriculum Learning
Multi-Tasking
A Case Study: Synthetic to Real Adaptation for Semantic Understanding of Road Scenes
References
[1] Kim, S., Choi, J., Kim, T., & Kim, C. (2019). Self-training and adversarial background regularization for unsupervised domain adaptive one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 6092-6101).
[2] Saito, K., Yamamoto, S., Ushiku, Y., & Harada, T. (2018). Open set domain adaptation by backpropagation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 153-168).
[3] Li, Wanyi, Fuyu Li, Yongkang Luo, and Peng Wang. “Deep Domain Adaptive Object Detection: a Survey.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.06797 (2020).
[4] Özgen, Azmi Can, Mandana Fasounaki, and Hazim Kemal Ekenel. “Text detection in natural and computer-generated images.” In 2018 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2018.
[5] Chen, Ting, Simon Kornblith, Mohammad Norouzi, and Geoffrey Hinton. “A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05709 (2020).
[6] Ma, Chixiang, Lei Sun, Zhuoyao Zhong, and Qiang Huo. “ReLaText: Exploiting Visual Relationships for Arbitrary-Shaped Scene Text Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks.“ arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.06999 (2020).
[7] He, Kaiming, Haoqi Fan, Yuxin Wu, Saining Xie, and Ross Girshick. “Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.05722 (2019).
[8] Ganin, Yaroslav, and Victor Lempitsky. “Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.7495 (2014).
[10] M. Khodabandeh, A. Vahdat, M. Ranjbar, and W. G. Macready, “A Robust Learning Approach to Domain Adaptive Object Detection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02361, 2019.
[11] Cai, Q., Pan, Y., Ngo, C. W., Tian, X., Duan, L., & Yao, T. (2019). Exploring object relation in mean teacher for cross-domain detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 11457-11466).
[12] Geoffrey French, Michal Mackiewicz, and Mark Fisher. Self-ensembling for domain adaptation. In ICLR, 2018.
[13] Y. Cao, D. Guan, W. Huang, J. Yang, Y. Cao, and Y. Qiao, “Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks,” information fusion, vol. 46, pp. 206-217, 3/1/2019 2019.
[14] Y. Chen, W. Li, C. Sakaridis, D. Dai, and L. Van Gool, “Domain Adaptive Faster R-CNN for Object Detection in the Wild,” computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3339-3348, 2018
[15] Zhu, Xinge, Jiangmiao Pang, Ceyuan Yang, Jianping Shi, and Dahua Lin. “Adapting object detectors via selective cross-domain alignment.“ In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 687-696. 2019.
[16] T. Wang, X. Zhang, L. Yuan, and J. Feng, “Few-shot Adaptive Faster R-CNN,“ in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 7173-7182.
[17] K. Saito, Y. Ushiku, T. Harada, and K. Saenko, “Strong-Weak Distribution Alignment for Adaptive Object Detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 6956-6965
[18] Z. He and L. Zhang, “Multi-Adversarial Faster-RCNN for Unrestricted Object Detection,” presented at the International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019.
[19] Z. Shen, H. Maheshwari, W. Yao, and M. Savvides, “SCL: Towards Accurate Domain Adaptive Object Detection via Gradient Detach Based Stacked Complementary Losses,” ed, 2019
[20] H. Zhang, Y. Tian, K. Wang, H. He, and F.-Y. Wang, “Synthetic-to-Real Domain Adaptation for Object Instance Segmentation,“ in 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2019, pp. 1- 7.
[21] C. Zhuang, X. Han, W. Huang, and M. R. Scott, “iFAN: Image- Instance Full Alignment Networks for Adaptive Object Detection,” in AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2020
[22] V. F. Arruda, T. M. Paixão, R. F. Berriel, A. F. D. Souza, C. Badue, N. Sebe, et al., “Cross-Domain Car Detection Using Unsupervised Image-to- Image Translation: From Day to Night,” in 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2019, pp. 1-8
[23] C. Lin, “Cross Domain Adaptation for on-Road Object Detection Using Multimodal Structure-Consistent Image-to-Image Translation,” in 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2019, pp. 3029-3030
[24] Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks 2016. 17, 2096–2030.
[25] Tzeng, E.; Hoffman, J.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. Proc. of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017, pp. 7167–7176.
[26] Hoffman, J.; Wang, D.; Yu, F.; Darrell, T. FCNs in the wild: Pixel-level adversarial and constraint-based adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.02649 2016
[27] Chen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Huang, J.B. CrDoCo: Pixel-Level Domain Transfer With Cross-Domain Consistency. Proc. of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019
[28] Chen, M.; Xue, H.; Cai, D. Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation With Maximum Squares Loss. Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019
[29] Vu, T.H.; Jain, H.; Bucher, M.; Cord, M.; Pérez, P. Advent: Adversarial entropy minimization for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation. Proc. of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019, pp. 2517–2526.


