背景
ICML 2015的一篇论文,主要提出了一种方式帮助模型迁移,从有labeled的源域迁移到 unlabled的目标域上,要求在目标域上面的表现也尽可能表现的好一点。解决了一些场景下label难以得到或者得到的代价成本很高的一个问题现象。
首先有两个数据分布源域source domain和target domain目标域
,这两个domain的distribution是不同的,这里叫做domain shift。我们的目标是使得在source domain(labeled)和target domain(unlabled)上训练出来的模型在target domain上表现的尽可能的好,如何表现的好呢?使模型学到类别的本质特征domain-invariant feature。
创新点
这篇文章的主要创新点是Gradient Reversal Layer(GRL),下面具体解释这个GRL如何使得域迁移具有较好的效果。
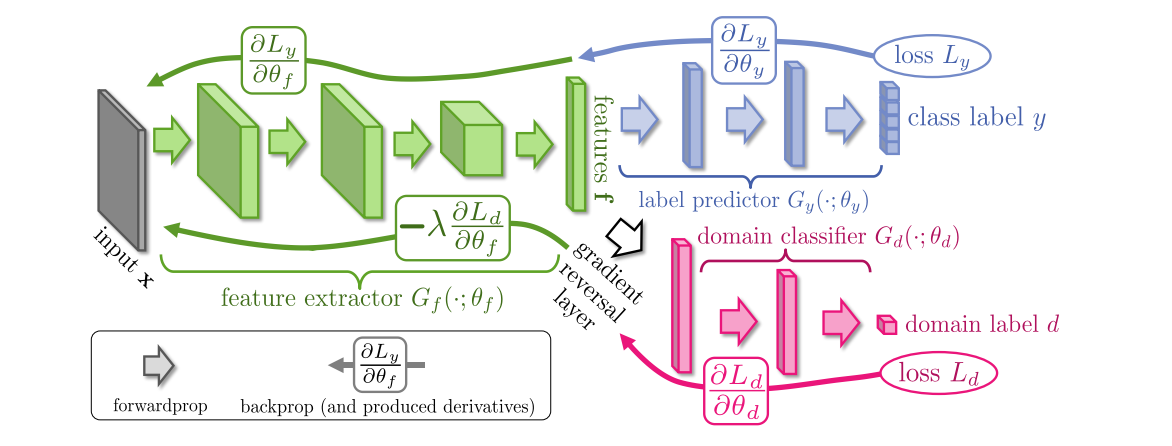
首先提出的框架包括三个部分:
绿色(后文用表示): Feature Extractor,提取到的feature是共享的
蓝色 (后文用表示): Label Predictor , 对源域进行训练,这部分这里是分类误差
紫色(后文用表示):Domain Classifier, 二分类器,标签是 源域 or 目标域
对于input ,首先经过一个
,提取特征到D-di mensional vector,在这个阶段所有的参数为
. 同理
和
的参数为
,
.
在训练阶段,对于source domain的数据,优化和
部分的参数,使得model在source上的表现尽可能的好。
为了学习到domian-invariant features, 在反传阶段,对于feature extractor 的参数,
domain classifier 的 loss(最大化
的目的是使得学到的feature分不开source和target(即学到了domian-invariant feature))。相反在domain classifier阶段,
这个
.使得classifier能够分类的更好。
为了实现上面这个目的学习到domain-invariant features,基于SGD优化器的参数更新应该是下面这个流程: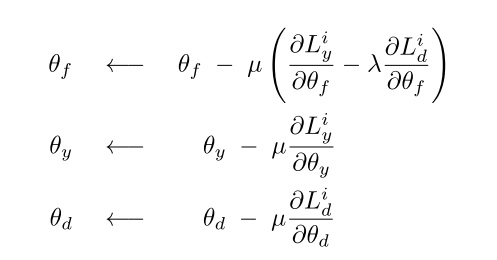
对于feature extractor的参数减去来自于label predictor的梯度加上来自于domain classifier回传的梯度。对于其他两部分(label predictor和domain classifier的话就正常的梯度下降就行)。为了实现这个过程引入了Gradient Reversal Layer(GRL)。
具体实现
GRL插入在feature extractor和domain classifier之间,很简单在backpropagation过程中,来自于GRL下游的梯度(即domain classifier的梯度)都乘以,因此被所代替。
代码实现
from torch.autograd import Function
class RevGrad(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
ctx.save_for_backward(input_)
output = input_
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output): # pragma: no cover
grad_input = None
if ctx.needs_input_grad[0]:
grad_input = -grad_output
return grad_input

