Reliable Weighted Optimal Transport for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Xu, Renjun, et al. “Reliable Weighted Optimal Transport for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation.“ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020.
Notes of Optimal Transport
Introduction
learn transferrable models for the unlabeled target domain
Optimal transport 是一个强有力的metric去对齐source 和target domain的representations.
问题:大多数based on optimal transport的方法都忽略了intra-domain structure,都进行简单粗暴的 coarse pair-wise matching。 然而在cluster过程中,距离对应的class center越远的点更容易被 misclassified by the decision boundary learned from the source domain .
论文中:论文中提出了 Reliable Weighted Optimal Transport (RWOT) for unsupervised domain adaptation
- Novel Shrinking Subspace Reliability (SSR)
Weighted optimal transport strategy
SSR:SSR 挖掘 spatial prototypical information 和 intra-domain structure去动态的衡量不同domain 的 sample-level domain discrepancy
Weighted optimal transport strategy:探索一种precise-pair-wise optimal transport procedure, reduces negative transfer brought by the samples near decision boundaries in the target domain.
Main Contributions :
- 评估 sample-level domain discrepancy 使用 spatial prototypical information 和 intra-domain structure dynamically.
- 提出了weighted optimal transport strategy,实现precise-pair-wise optimal transport,通过采样near decision boundaries去reduce negative transfer。
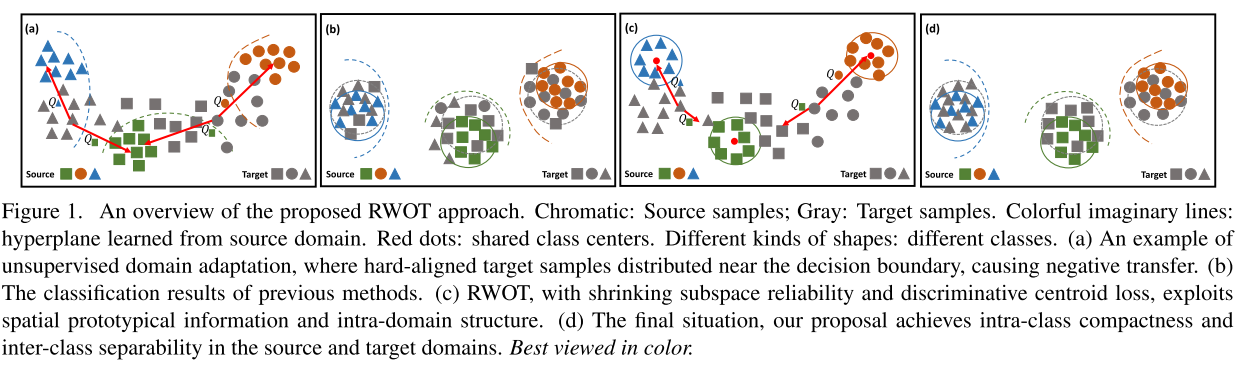
上图是RWOT整个框架,a -> b是经典的DA算法进行迁移,c->d是利用了centroid loss进行迁移。带颜色的是source domain,灰色的是target domain,红点是class center。
Reliable Weighted Optimal Transport
Settings
Source domain: 表示
个labeled samples
Target domain : 表示
个unlabeled samples
Source domain joint probability distributions:
Target domain joint probability distributions:
Shrinking Subspace Reliability
The spatial prototypical information: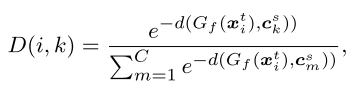
: Feature generator
: Adaptive classifier
:
-th source class center
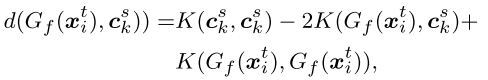
Gaussian process 的重要组成部分——关于那个被广泛应用的Kernel的林林总总
convex combination of PSD kernels
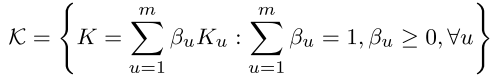
positive semi-definite(PSD) kernel(半正定):
半正定矩阵就是 对称矩阵并且特征值都>=0
Sharpen probability annotation matrix M:
Likelihood of intra-domain information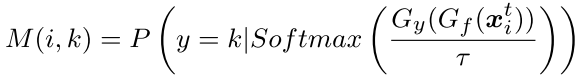
: The temperature hyper-parameter
SSR is defined by Q:
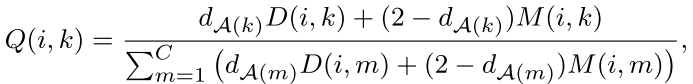
:评估 spatial prototypical information的相似性,用kernel算他们的距离
: intra-domain structure of target samples.
这两个指标都是评测likelihood of target sample having a label
。
在训练早期,是更可靠的相比
,在训练后期,则相反,所以用下面一个A-distance[9][10]去调节训练权重比例
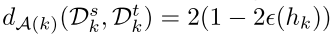
Weighted Optimal Transport
Reduce the wrong pair-wise transport
Weighted Kantorovich problem[11]: 可以从另一个角度来度量两个分布P,Q的距离,即将两个分布之间的距离定义为从分布P运输到分布Q所需要付出的最小代价。
Optimal Transport Divergence的定义如下:
约束条件为 和
为方便计算常用的
的平方来定义cost,即
。那么我们这是就可以得到2-Wasserstein Distance
更一般的情况,k-Wasserstein Distance则为:
论文里面Optimal Transport Divergence的定义如下: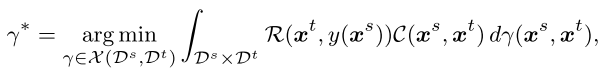
Optimal Transport minimizes a global transportation effort or cost:
[1] Nicolas Courty, R´emi Flamary, and Devis Tuia. Domain adaptation with regularized optimal transport. In Joint Euro- pean Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Dis- covery in Databases, pages 274–289. Springer, 2014.
[2] Filippo Santambrogio. Optimal transport for applied mathematicians. Birk¨auser, NY, 55:58–63, 2015
[3] Yuguang Yan, Wen Li, Hanrui Wu, Huaqing Min, and Mingkui Tan. Semi-supervised optimal transport for hetero- geneous domain adaptation. In Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence IJCAI-18, 2018
[4] C´edric Villani. Optimal transport: old and new, volume 338. Springer Science & Business Media, 2008.
Intra-domain structure
[5] Jindong Wang, Wenjie Feng, Yiqiang Chen, Han Yu, Meiyu Huang, and Philip S Yu. Visual domain adaptation with man -ifold embedded distribution alignment. In 2018 ACM Mul- timedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, pages 402– 410. ACM, 2018.
Prototypical networks
[6] Yingwei Pan, Ting Yao, Yehao Li, Yu Wang, Chong-Wah Ngo, and Tao Mei. Transferrable prototypical networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings ofthe IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2239–2247, 2019. 1,
two-stream siamese CNN architecture
[7] Chao Chen, Zhihong Chen, Boyuan Jiang, and Xinyu Jin. Joint domain alignment and discriminative feature learning for unsupervised deep domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 33, pages 3296–3303, 2019
[8] Bharath Bhushan Damodaran, Benjamin Kellenberger, R´emi Flamary, Devis Tuia, and Nicolas Courty. Deepjdot: Deep joint distribution optimal transport for unsupervised domain adaptation. In European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 467–483. Springer, 2018. 2,
A-distance(早期和后期的权重)
[9] Shai Ben-David, John Blitzer, Koby Crammer, and Fernando Pereira. Analysis of representations for domain adaptation. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pages 137–144, 2007
[10] Jindong Wang, Wenjie Feng, Yiqiang Chen, Han Yu, Meiyu Huang, and Philip S Yu. Visual domain adaptation with man- ifold embedded distribution alignment. In 2018 ACM Mul- timedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, pages 402– 410. ACM, 2018.
Weighted Kantorovich
[11] SigurdAngenent, Steven Haker, and Allen Tannenbaum. Minimizing flows for the monge–kantorovich problem. SIAM journal on mathematical analysis, 35(1):61–97, 2003.

