In Device mode, there’re five different block shapes: Hat, Stack, Boolean, Reporter and C.
- Hat Block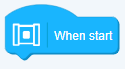
Hat blocks are the blocks that start every script. They are shaped with a rounded top and a bump at the bottom - this is so you can only place blocks below them. There’re 11 Hat blocks in device mode, ten of which are in the Events category, one in the Sensing category.
Hat Block is start each program code blocks. They have a rounded top and a raised bottom. So you can only be in placed under their pieces.
Heapable code block example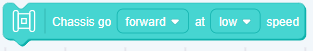
A heapable block is a block of code that executes the main command,
They have a notch shape at the top, in the bottom of a bump, this allows blocks of code to be placed above or below them.
- Boolean Block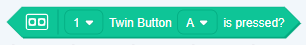
Boolean is a condition (true or false). It’s like asking your friend, “2 + 2 = 4?” “, they would tell You say “yes” or “no”. A Boolean block is a hexagon.
- Numerical block
Numeric blocks can hold Numbers and strings.
It’s like asking a friend, for example, what is the value of the 2 + 2?” “, he would answer “4”. However, it is more than just program, it can report variables, such as “how much is your age?” . He might answer, “15.” Their shape is round edge.
- C block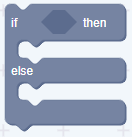
C block is made to look like a word “C” code block, also known as “change ⾏ piece”, these cycle C shape blocks of code in the activity or check whether the condition is true. There are five C blocks that can be found in the control category. The C block can be either code block or capped at the bottom.

