字节输出流FileOutputStream
创建输出流对象
OutputStream 流对象是一个抽象类,不能实例化。所以,我们要找一个具体的子类 :FileOutputStream。
查看FileOutputStream的构造方法:
FileOutputStream(File file)FileOutputStream(String name)
创建字节输出流对象了做了几件事情:
- 调用系统功能去创建文件
- 创建字节输出流对象
- 把该字节输出流对象引用指向这个文件
public class OutputStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("demo1.txt");/** 创建字节输出流对象了做了几件事情:* A:调用系统功能去创建文件* B:创建fos对象* C:把fos对象指向这个文件*///写数据fos.write("hello,IO".getBytes());fos.write("java".getBytes());//释放资源//关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。fos.close();/** 为什么一定要close()呢?* A:让流对象变成垃圾,这样就可以被垃圾回收器回收了* B:通知系统去释放跟该文件相关的资源*///java.io.IOException: Stream Closed//fos.write("java".getBytes());}}
- 为什么一定要close()呢?
- 让流对象变成垃圾,这样就可以被垃圾回收器回收了
- 通知系统去释放跟该文件相关的资源
写出数据
字节输出流操作步骤:
- 创建字节输出流对象
- 写数据
- 释放资源
FileOutputStream中的写出方法:
public void write(int b) //写一个字节public void write(byte[] b) //写一个字节数组public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) //写一个字节数组的一部分
public class OutputStreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("demo2.txt");// 调用write()方法fos.write(97); //97 -- 底层二进制数据 -- 通过记事本打开 -- 找97对应的字符值 -- a//public void write(byte[] b):写一个字节数组byte[] bys={98,99,100,101};fos.write(bys);//public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len):写一个字节数组的一部分fos.write(bys,1,3);//释放资源fos.close();}}
如何实现数据的换行?不同的系统针对不同的换行符号识别是不一样的?
windows:\r\nlinux:\nMac:\r
public class OutputStreamDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 创建一个向具有指定 name 的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。// 如果第二个参数为 true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("demo2.txt",true);// 写数据for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++) {fos.write(("hello" + x).getBytes());fos.write("\r\n".getBytes());}//释放资源fos.close();}}
加入异常处理的字节输出流操作
public class OutputStreamDemo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fos = new FileOutputStream("demo1.txt");fos.write("java".getBytes());} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 如果fos不是null,才需要close()if (fos != null) {// 为了保证close()一定会执行,就放到这里了try {fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
字节输入流FileInputStream
- 字节输入流操作步骤:
- 创建字节输入流对象
- 调用read()方法读取数据,并把数据显示在控制台
- 释放资源
- 读取数据的方式:
int read() //一次读取一个字节int read(byte[] b) //一次读取一个字节数组
- 一次读取一个字节
public class InputStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {InputStream fis=new FileInputStream("demo1.txt");int by = 0;// 读取,赋值,判断while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) by);}// 释放资源fis.close();}}
- 一次读取一个字节数组
public class InputStreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("demo1.txt");//数组的长度一般是1024或者1024的整数倍byte[] bys = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while ((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1) {System.out.print(new String(bys, 0, len));}// 释放资源fis.close();}}
带缓冲区的字节流BufferedOutputStream
public class BufferedOutputStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedOutputStream bos=newBufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("demo1.txt"));bos.write("hello".getBytes());bos.close();}}
带缓冲区的字节流BufferedInputStream
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bis=newBufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("demo1.txt"));int by=-1;while((by=bis.read())!=-1){System.out.print((char)by);}bis.close();}}
复制文件
public class CopyFile {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String strFile="国旗歌.mp4";String destFile="demo3.mp4";long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//copyFile(strFile,destFile); //共耗时:75309毫秒//copyFile2(strFile,destFile); //共耗时:153毫秒//copyFile3(strFile,destFile);//共耗时:282毫秒copyFile4(strFile,destFile);//共耗时:44毫秒long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("共耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");}/*** 基本字节流一次读写一个字节*/public static void copyFile(String srcFile,String destFile) throws IOException {FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(srcFile);FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(destFile);int by=0;while((by=fis.read())!=-1){fos.write(by);}fis.close();fos.close();}/*** 基本字节流一次读写一个字节数组*/public static void copyFile2(String srcFile,String destFile) throws IOException{FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(srcFile);FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(destFile);int len=0;byte[] bys=new byte[1024];while((len=fis.read(bys))!=-1){fos.write(bys,0,len);}fis.close();fos.close();}/*** 高效字节流一次读写一个字节*/public static void copyFile3(String srcFile,String destFile) throws IOException{BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));int by=0;while((by=bis.read())!=-1){bos.write(by);}bis.close();bos.close();}/*** 高效字节流一次读写一个字节数组*/public static void copyFile4(String srcFile,String destFile) throws IOException{BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));int len=0;byte[] bys=new byte[1024];while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){bos.write(bys,0,len);}bis.close();bos.close();}}
装饰者模式
Java I/O 使用了装饰者模式来实现。以 InputStream 为例,
- InputStream 是抽象组件;
- FileInputStream 是 InputStream 的子类,属于具体组件,提供了字节流的输入操作;
- FilterInputStream 属于抽象装饰者,装饰者用于装饰组件,为组件提供额外的功能。例如 BufferedInputStream 为 FileInputStream 提供缓存的功能。
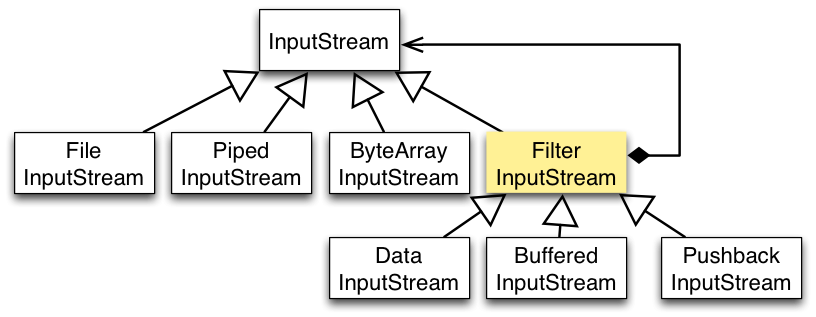
实例化一个具有缓存功能的字节流对象时,只需要在 FileInputStream 对象上再套一层 BufferedInputStream 对象即可。
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
DataInputStream 装饰者提供了对更多数据类型进行输入的操作,比如 int、double 等基本类型。

