参考来源:
Pytorch 使用 ReduceLROnPlateau 来更新学习率
解析说明
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer,mode='min',factor=0.1,patience=10,verbose=False,threshold=0.0001,threshold_mode='rel',cooldown=0,min_lr=0,eps=1e-08)
在发现 loss 不再降低或者 acc 不再提高之后,降低学习率。各参数意义如下:
**mode**:'min'模式检测metric是否不再减小,'max'模式检测metric是否不再增大;**factor**:触发条件后lr*=factor;**patience**:不再减小(或增大)的累计次数;**verbose**:触发条件后print;**threshold**:只关注超过阈值的显著变化;**threshold_mode**:有rel和abs两种阈值计算模式;**rel**规则:max模式下如果超过best(1+threshold)为显著,min模式下如果低于best(1-threshold)为显著;**abs**规则:max模式下如果超过best+threshold为显著,min模式下如果低于best-threshold为显著;
**cooldown**:触发一次条件后,等待一定epoch再进行检测,避免lr下降过速;**min_lr**:最小的允许lr;**eps**:如果新旧lr之间的差异小于1e-8,则忽略此次更新。
例子,如图所示的 y 轴为 lr,x 为调整的次序,初始的学习率为 0.0009575。则学习率的方程为:lr = 0.0009575 * (0.35)^x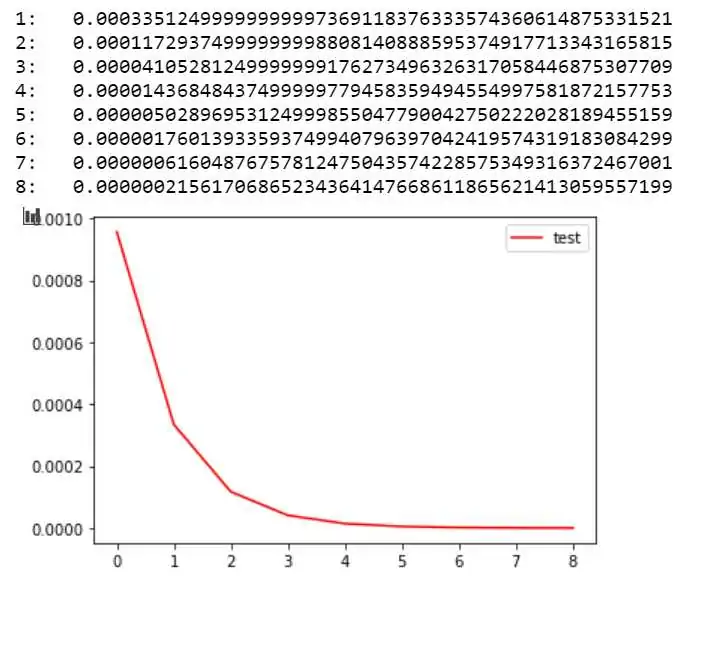
import mathimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt#%matplotlib inlinex = 0o = []p = []o.append(0)p.append(0.0009575)while(x < 8):x += 1y = 0.0009575 * math.pow(0.35,x)o.append(x)p.append(y)print('%d: %.50f' %(x,y))plt.plot(o,p,c='red',label='test') #分别为x,y轴对应数据,c:color,labelplt.legend(loc='best') # 显示label,loc为显示位置(best为系统认为最好的位置)plt.show()
难点
我感觉这里面最难的时这几个参数的选择,第一个是初始的学习率(我目前接触的 miniest 和下面的图像分类貌似都是 0.001,我这里训练调整时才发现自己设置的为 0.0009575,这个值是上一个实验忘更改了,但发现结果不错,第一次运行该代码接近到 0.001 这么小的损失值),这里面的乘积系数以及判断说多少次没有减少(增加)后决定变换学习率都是难以估计的。我自己的最好方法是先按默认不变的 0.001 来训练一下(结合 tensoarboard )观察从哪里开始出现问题就可以从这里来确定次数,而乘积系数,个人感觉还是用上面的代码来获取一个较为平滑且变化极小的数字来作为选择。建议在做这种测试时可以把模型先备份一下以免浪费过多的时间!
例子
该例子初始学习率为 0.0009575,乘积项系数为:0.35,在我的例子中 x 变化的条件是:累计 125 次没有减小则 x 加 1;自己训练在第一次 lr 变化后(从 0.0009575 变化到 0.00011729)损失值慢慢取向于 0.001(如第一张图所示),准确率达到 69%;
import torchimport torchvisionimport torchvision.transforms as transformsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fimport torch.optim as optimfrom datetime import datetimefrom torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriterfrom torch.optim import *PATH = './cifar_net_tensorboard_net_width_200_and_chang_lr_by_decrease_0_35^x.pth' # 保存模型地址transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True,download=True, transform=transform)trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=4,shuffle=True, num_workers=0)testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False,download=True, transform=transform)testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=4,shuffle=False, num_workers=0)classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat','deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")# Assuming that we are on a CUDA machine, this should print a CUDA device:print(device)print("获取一些随机训练数据")# get some random training imagesdataiter = iter(trainloader)images, labels = dataiter.next()# functions to show an imagedef imshow(img):img = img / 2 + 0.5 # unnormalizenpimg = img.numpy()plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0)))plt.show()# show imagesimshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images))# print labelsprint(' '.join('%5s' % classes[labels[j]] for j in range(4)))print("**********************")# 设置一个tensorborad# helper function to show an image# (used in the `plot_classes_preds` function below)def matplotlib_imshow(img, one_channel=False):if one_channel:img = img.mean(dim=0)img = img / 2 + 0.5 # unnormalizenpimg = img.cpu().numpy()if one_channel:plt.imshow(npimg, cmap="Greys")else:plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0)))# 设置tensorBoard# default `log_dir` is "runs" - we'll be more specific herewriter = SummaryWriter('runs/train')# get some random training imagesdataiter = iter(trainloader)images, labels = dataiter.next()# create grid of imagesimg_grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)# show images# matplotlib_imshow(img_grid, one_channel=True)imshow(img_grid)# write to tensorboard# writer.add_image('imag_classify', img_grid)# Tracking model training with TensorBoard# helper functionsdef images_to_probs(net, images):'''Generates predictions and corresponding probabilities from a trainednetwork and a list of images'''output = net(images)# convert output probabilities to predicted class_, preds_tensor = torch.max(output, 1)# preds = np.squeeze(preds_tensor.numpy())preds = np.squeeze(preds_tensor.cpu().numpy())return preds, [F.softmax(el, dim=0)[i].item() for i, el in zip(preds, output)]def plot_classes_preds(net, images, labels):preds, probs = images_to_probs(net, images)# plot the images in the batch, along with predicted and true labelsfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 48))for idx in np.arange(4):ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, idx+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])matplotlib_imshow(images[idx], one_channel=True)ax.set_title("{0}, {1:.1f}%\n(label: {2})".format(classes[preds[idx]],probs[idx] * 100.0,classes[labels[idx]]),color=("green" if preds[idx]==labels[idx].item() else "red"))return fig#class Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(Net, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 200, 5)self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(200, 16, 5)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)def forward(self, x):x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)return xnet = Net()# # 把net结构可视化出来writer.add_graph(net, images)net.to(device)try:net.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH))print("Modle file load successful !")except:print("no model file,it will creat a new file!")# 训练print("训练")criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()# optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)#在发现loss不再降低或者acc不再提高之后,降低学习率。optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.0009575, momentum=0.9)scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, 'min',factor=0.35,verbose=1,min_lr=0.0001,patience=125)startTime = datetime.now()for epoch in range(200): # loop over the dataset multiple timesrunning_loss = 0.0for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):# get the inputs; data is a list of [inputs, labels]# inputs, labels = datainputs, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device)# zero the parameter gradientsoptimizer.zero_grad() #将参数的grad值初始化为0# forward + backward + optimizeoutputs = net(inputs)loss = criterion(outputs, labels) #计算损失loss.backward() # 反向传播optimizer.step() # 反向传播求梯度# print statisticsrunning_loss += loss.item()if i % 2000 == 1999: # print every 2000 mini-batchesnow_loss = running_loss / 2000 # 2000mini-batches 的平均损失率print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' %(epoch + 1, i + 1, now_loss))# now_loss = running_loss / 2000scheduler.step(now_loss)# 把数据写入tensorflow# ...log the running losswriter.add_scalar('image training loss on net width 200 chang_lr_by_decrease',now_loss,epoch * len(trainloader) + i)writer.add_scalar('learning rate on net width 200 chang_lr_by_decrease',optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'],epoch * len(trainloader) + i)running_loss = 0.0torch.save(net.state_dict(), PATH)print('Finished Training')print("***************************")print("***************************")print("***************************")print("Time taken:", datetime.now() - startTime)print("***************************")print("***************************")print("***************************")#获取一些随机测试数据print("获取一些随机测试数据")dataiter = iter(testloader)images, labels = dataiter.next()# print imagesimshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images))print('GroundTruth: ', ' '.join('%5s' % classes[labels[j]] for j in range(4)))# 恢复模型并测试net = Net()net.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH))outputs = net(images)_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)print('Predicted: ', ' '.join('%5s' % classes[predicted[j]]for j in range(4)))print("**********************")print("输出训练得到的准确度")# 输出训练得到的准确度correct = 0total = 0with torch.no_grad():for data in testloader:images, labels = dataoutputs = net(images)_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)total += labels.size(0)correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % (100 * correct / total))class_correct = list(0. for i in range(10))class_total = list(0. for i in range(10))with torch.no_grad():for data in testloader:images, labels = dataoutputs = net(images)_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)c = (predicted == labels).squeeze()for i in range(4):label = labels[i]class_correct[label] += c[i].item()class_total[label] += 1for i in range(10):print('Accuracy of %5s : %2d %%' % (classes[i], 100 * class_correct[i] / class_total[i]))

