参考来源:
CSDN:GCN torchgeometric utils scatter方法源码解析及样例
源码及注释
源码位置:torch_geometric\utils\scatter.py
代码相当于在原有 torch_scatter 包的基础上进行二次开发,1.4.3 之后版本移除了,相当于只要理解 torch.scatter(…, reduce='add') 就好了。
下面是开发者说的原话:
“The scatter call got removed in one of the more recent versions, and you can now simply use torch.scatter(…, reduce=‘add’) for the same effect.”(scatter 调用在较新的版本之一中被删除,您现在可以简单地使用 torch.scatter(…, reduce=’add’) 来获得相同的效果。)
import torch_scatterdef scatter_(name, src, index, dim=0, dim_size=None):r"""Aggregates all values from the :attr:`src` tensor at the indicesspecified in the :attr:`index` tensor along the first dimension.If multiple indices reference the same location, their contributionsare aggregated according to :attr:`name` (either :obj:`"add"`,:obj:`"mean"` or :obj:`"max"`).Args:name (string): The aggregation to use (:obj:`"add"`, :obj:`"mean"`,:obj:`"min"`, :obj:`"max"`).src (Tensor): The source tensor.index (LongTensor): The indices of elements to scatter.dim (int, optional): The axis along which to index. (default: :obj:`0`)dim_size (int, optional): Automatically create output tensor with size:attr:`dim_size` in the first dimension. If set to :attr:`None`, aminimal sized output tensor is returned. (default: :obj:`None`):rtype: :class:`Tensor`"""# 例行断言assert name in ['add', 'mean', 'min', 'max']# 返回对象属性值op = getattr(torch_scatter, 'scatter_{}'.format(name))# 获取对象属性后返回值可直接使用,看具体案例out = op(src, index, dim, None, dim_size)out = out[0] if isinstance(out, tuple) else out# 限制取最值后数据约束if name == 'max':out[out < -10000] = 0elif name == 'min':out[out > 10000] = 0return out
torch_scatter 方法
结合官网和以下网址大家可以看得懂(看不懂没关系,多看几遍,我也是看了好几遍才懂的,不得不佩服其设计),这里不做过多解释。
语雀:torch.tensor.scatter() 和 torch.tensor.scatter_() 函数
Pytorch 文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Tensor.scatter_.html
scatter_ 方法解析
常规运行
在理解上述原有开发包的基础上,我们再来看一下此方法的作用。按传入方式聚合节点信息。其是用于创建消息传递层的基类。
为了便于理解,这里给出一个具体例子:
假设我们有一个图,图中有四个节点,节点特征维度为 3。
其关系如下图所示(为方便理解我画成了单向图):
import torchimport torch_scatterdef scatter_(name, src, index, dim=0, dim_size=None):r"""Aggregates all values from the :attr:`src` tensor at the indicesspecified in the :attr:`index` tensor along the first dimension.If multiple indices reference the same location, their contributionsare aggregated according to :attr:`name` (either :obj:`"add"`,:obj:`"mean"` or :obj:`"max"`).Args:name (string): The aggregation to use (:obj:`"add"`, :obj:`"mean"`,:obj:`"min"`, :obj:`"max"`).src (Tensor): The source tensor.index (LongTensor): The indices of elements to scatter.dim (int, optional): The axis along which to index. (default: :obj:`0`)dim_size (int, optional): Automatically create output tensor with size:attr:`dim_size` in the first dimension. If set to :attr:`None`, aminimal sized output tensor is returned. (default: :obj:`None`):rtype: :class:`Tensor`"""# 例行断言assert name in ['add', 'mean', 'min', 'max']# 返回对象属性值op = getattr(torch_scatter, 'scatter_{}'.format(name))# 获取对象属性后返回值可直接使用,看具体案例out = op(src, index, dim, None, dim_size)# out = src.clone()# out = op(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)out = out[0] if isinstance(out, tuple) else out# 限制取最值后数据约束if name == 'max':out[out < -10000] = 0elif name == 'min':out[out > 10000] = 0return out# src 节点特征a = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [2.0, 2.0, 2.0], [3.0, 3.0, 3.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]])# index 索引b = torch.tensor([2, 3, 0, 1])# dim 维度信息c = 1# dim_size 返回的维度e = 4print(scatter_('add', a, b, dim=0, dim_size=e))
结果:
tensor([[3., 3., 3.],[4., 4., 4.],[1., 1., 1.],[2., 2., 2.]])
可以看到他进行了一次消息传递,以节点 1 为例,他接收了来自节点 3 的消息,所以特征变为 [4., 4., 4.]。
节点特征维度
此样例说明节点信息聚合时,各个维度相互独立。
a = torch.tensor([[1.1, 1.2, 1.3], [2.1, 2.2, 2.3], [3.1, 3.2, 3.3], [4.1, 4.2, 4.3]])b = torch.tensor([2, 3, 0, 1])c = 1e = 4print(scatter_('add', a, b, dim=0, dim_size=e))"""output:tensor([[3.1000, 3.2000, 3.3000],[4.1000, 4.2000, 4.3000],[1.1000, 1.2000, 1.3000],[2.1000, 2.2000, 2.3000]])"""
dim_size(运算后返回的维度)参数
只修改 dim_size,可以看到返回维度增加。
a = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [2.0, 2.0, 2.0], [3.0, 3.0, 3.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]])b = torch.tensor([2, 3, 0, 1])c = 1e = 8print(scatter_('add', a, b, dim=0, dim_size=e))"""output:tensor([[3., 3., 3.],[4., 4., 4.],[1., 1., 1.],[2., 2., 2.],[0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.]])"""
index(索引)参数
这里相当于修改了节点的指向,修改后图: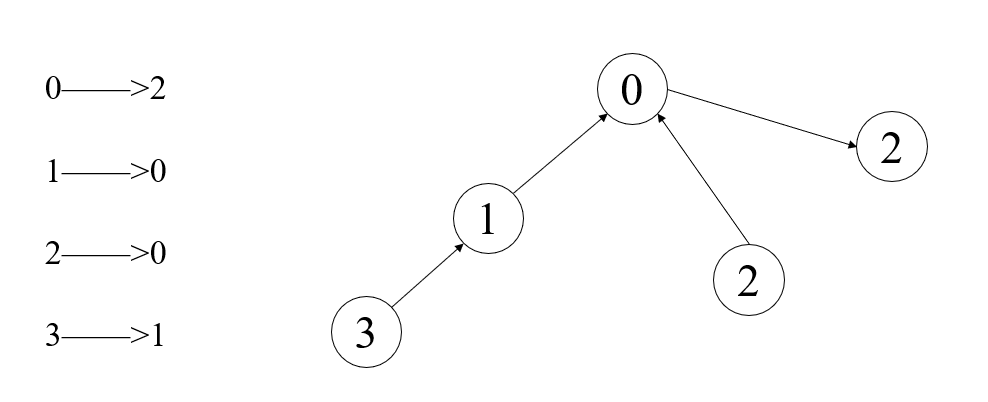
a = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [2.0, 2.0, 2.0], [3.0, 3.0, 3.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]])b = torch.tensor([2, 0, 0, 1])c = 1e = 4print(scatter_('add', a, b, dim=0, dim_size=e))"""output:tensor([[5., 5., 5.],[4., 4., 4.],[1., 1., 1.],[0., 0., 0.]])"""
因为这里使用的 'add' 方法,所以同时传递到一个节点的信息被累加。
name(聚合方式)
很显然,当我把聚合方式改为均值,除了节点1有两个值传入被平均,其他保持不变;同理最值一样道理。
a = torch.tensor([[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], [2.0, 2.0, 2.0], [3.0, 3.0, 3.0], [4.0, 4.0, 4.0]])b = torch.tensor([2, 0, 0, 1])c = 1e = 4print(scatter_('mean', a, b, dim=0, dim_size=e))"""output:tensor([[2.5000, 2.5000, 2.5000],[4.0000, 4.0000, 4.0000],[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000],[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]])"""
1.4.3 之后版本
源码位置:Lib\site-packages\torch_scatter\scatter.py
from typing import Optional, Tupleimport torchfrom .utils import broadcastdef scatter_sum(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> torch.Tensor:index = broadcast(index, src, dim)if out is None:size = list(src.size())if dim_size is not None:size[dim] = dim_sizeelif index.numel() == 0:size[dim] = 0else:size[dim] = int(index.max()) + 1out = torch.zeros(size, dtype=src.dtype, device=src.device)return out.scatter_add_(dim, index, src)else:return out.scatter_add_(dim, index, src)def scatter_add(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> torch.Tensor:return scatter_sum(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)def scatter_mul(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> torch.Tensor:return torch.ops.torch_scatter.scatter_mul(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)def scatter_mean(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> torch.Tensor:out = scatter_sum(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)dim_size = out.size(dim)index_dim = dimif index_dim < 0:index_dim = index_dim + src.dim()if index.dim() <= index_dim:index_dim = index.dim() - 1ones = torch.ones(index.size(), dtype=src.dtype, device=src.device)count = scatter_sum(ones, index, index_dim, None, dim_size)count[count < 1] = 1count = broadcast(count, out, dim)if out.is_floating_point():out.true_divide_(count)else:out.floor_divide_(count)return outdef scatter_min(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:return torch.ops.torch_scatter.scatter_min(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)def scatter_max(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:return torch.ops.torch_scatter.scatter_max(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)def scatter(src: torch.Tensor, index: torch.Tensor, dim: int = -1,out: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, dim_size: Optional[int] = None,reduce: str = "sum") -> torch.Tensor:r"""|.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rusty1s/pytorch_scatter/master/docs/source/_figures/add.svg?sanitize=true:align: center:width: 400px|Reduces all values from the :attr:`src` tensor into :attr:`out` at theindices specified in the :attr:`index` tensor along a given axis:attr:`dim`.For each value in :attr:`src`, its output index is specified by its indexin :attr:`src` for dimensions outside of :attr:`dim` and by thecorresponding value in :attr:`index` for dimension :attr:`dim`.The applied reduction is defined via the :attr:`reduce` argument.Formally, if :attr:`src` and :attr:`index` are :math:`n`-dimensionaltensors with size :math:`(x_0, ..., x_{i-1}, x_i, x_{i+1}, ..., x_{n-1})`and :attr:`dim` = `i`, then :attr:`out` must be an :math:`n`-dimensionaltensor with size :math:`(x_0, ..., x_{i-1}, y, x_{i+1}, ..., x_{n-1})`.Moreover, the values of :attr:`index` must be between :math:`0` and:math:`y - 1`, although no specific ordering of indices is required.The :attr:`index` tensor supports broadcasting in case its dimensions donot match with :attr:`src`.For one-dimensional tensors with :obj:`reduce="sum"`, the operationcomputes.. math::\mathrm{out}_i = \mathrm{out}_i + \sum_j~\mathrm{src}_jwhere :math:`\sum_j` is over :math:`j` such that:math:`\mathrm{index}_j = i`... note::This operation is implemented via atomic operations on the GPU and istherefore **non-deterministic** since the order of parallel operationsto the same value is undetermined.For floating-point variables, this results in a source of variance inthe result.:param src: The source tensor.:param index: The indices of elements to scatter.:param dim: The axis along which to index. (default: :obj:`-1`):param out: The destination tensor.:param dim_size: If :attr:`out` is not given, automatically create outputwith size :attr:`dim_size` at dimension :attr:`dim`.If :attr:`dim_size` is not given, a minimal sized output tensoraccording to :obj:`index.max() + 1` is returned.:param reduce: The reduce operation (:obj:`"sum"`, :obj:`"mul"`,:obj:`"mean"`, :obj:`"min"` or :obj:`"max"`). (default: :obj:`"sum"`):rtype: :class:`Tensor`.. code-block:: pythonfrom torch_scatter import scattersrc = torch.randn(10, 6, 64)index = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1])# Broadcasting in the first and last dim.out = scatter(src, index, dim=1, reduce="sum")print(out.size()).. code-block::torch.Size([10, 3, 64])"""if reduce == 'sum' or reduce == 'add':return scatter_sum(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)if reduce == 'mul':return scatter_mul(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)elif reduce == 'mean':return scatter_mean(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)elif reduce == 'min':return scatter_min(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)[0]elif reduce == 'max':return scatter_max(src, index, dim, out, dim_size)[0]else:raise ValueError

