参考来源:
知乎:一文学会 Pytorch 中的 einsum
实例代码:https://github.com/Ldpe2G/CodingForFun/tree/master/einsum_ex
爱因斯坦求和约定
爱因斯坦求和约定(einsum)提供了一套既简洁又优雅的规则,可实现包括但不限于:向量内积、向量外积、矩阵乘法、转置和张量收缩(tensor contraction)等张量操作,熟练运用 einsum 可以很方便的实现复杂的张量操作,而且不容易出错。
三条基本规则
首先看下 einsum 实现矩阵乘法的例子:
a = torch.rand(2,3)b = torch.rand(3,4)c = torch.einsum("ik,kj->ij", [a, b])# 等价操作 torch.mm(a, b)
其中需要重点关注的是 einsum 的第一个参数 "ik,kj->ij",该字符串(下文以 equation 表示)表示了输入和输出张量的维度。equation 中的箭头左边表示输入张量,以逗号分割每个输入张量,箭头右边则表示输出张量。表示维度的字符只能是 26 个英文字母 ‘a‘ - ‘z‘。
而 einsum 的第二个参数表示实际的输入张量列表,其数量要与 equation 中的输入数量对应。同时对应每个张量的子 equation 的字符个数要与张量的真实维度对应,比如 "ik,kj->ij" 表示输入和输出张量都是两维的。equation 中的字符也可以理解为索引,就是输出张量的某个位置的值,是怎么从输入张量中得到的,比如上面矩阵乘法的输出 c 的某个点 c[i, j] 的值是通过 a[i, k] 和b[i, k] 沿着 k 这个维度做内积得到的。
接着介绍两个基本概念,自由索引(**Free indices**)和求和索引(**Summation indices**):
- 自由索引:出现在箭头右边的索引,比如上面的例子就是
i和j; - 求和索引:只出现在箭头左边的索引,表示中间计算结果需要这个维度上求和之后才能得到输出,比如上面的例子就是
k;
接着是介绍三条基本规则:
- 规则一,
equation箭头左边,在不同输入之间重复出现的索引表示,把输入张量沿着该维度做乘法操作,比如还是以上面矩阵乘法为例,"ik,kj->ij",k在输入中重复出现,所以就是把a和b沿着 k 这个维度作相乘操作; - 规则二,只出现在
**equation**箭头左边的索引,表示中间计算结果需要在这个维度上求和,也就是上面提到的求和索引; - 规则三,
equation箭头右边的索引顺序可以是任意的,比如上面的"ik,kj->ij"如果写成"ik,kj->ji",那么就是返回输出结果的转置,用户只需要定义好索引的顺序,转置操作会在einsum内部完成。
特殊规则
特殊规则有两条:
equation可以不写包括箭头在内的右边部分,那么在这种情况下,输出张量的维度会根据默认规则推导。就是把输入中只出现一次的索引取出来,然后按字母表顺序排列,比如上面的矩阵乘法"ik,kj->ij"也可以简化为"ik,kj",根据默认规则,输出就是"ij"与原来一样;equation中支持"..."省略号,用于表示用户并不关心的索引,比如只对一个高维张量的最后两维做转置可以这么写:a = torch.randn(2,3,5,7,9)# i = 7, j = 9b = torch.einsum('...ij->...ji', [a])
实际例子解读
接下来将展示 13 个具体的例子,在这些例子中会将 Pytorch einsum 与对应的 Pytorch 张量接口和 python 简单的循环展开实现做对比,希望读者看完这些例子之后能轻松掌握 einsum 的基本用法。
实验代码 github 链接:https://github.com/Ldpe2G/CodingForFun/tree/master/einsum_ex
1. 提取矩阵对角线元素
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)# i = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ii->i', [a]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.diagonal(a, 0).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((3,), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环for i in range(0, 3):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子并没有求和索引,# 所以相当于是1sum_result = 0for inner in range(0, 1):sum_result += np_a[i, i]np_out[i] = sum_resultprint("input:\n", np_a)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印结果# input:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]# [6 7 8]]# torch ein out:# [0 4 8]# torch org out:# [0 4 8]# numpy out:# [0 4 8]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
2. 矩阵转置
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)# i = 2, j = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ij->ji', [a]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.transpose(a, 0, 1).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((3, 2), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环for j in range(0, 3):for i in range(0, 2):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子并没有求和索引# 所以相当于是1sum_result = 0for inner in range(0, 1):sum_result += np_a[i, j]np_out[j, i] = sum_resultprint("input:\n", np_a)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_org_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印结果# input:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# torch ein out:# [[0 3]# [1 4]# [2 5]]# torch org out:# [[0 3]# [1 4]# [2 5]]# numpy out:# [[0 3]# [1 4]# [2 5]]# is np_out == torch_org_out ? True# is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ? True
3. permute 高维张量转置
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.randn(2,3,5,7,9)# i = 7, j = 9torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('...ij->...ji', [a]).numpy()torch_org_out = a.permute(0, 1, 2, 4, 3).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2,3,5,9,7), dtype=np.float32)# 自由索引外循环for j in range(0, 9):for i in range(0, 7):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子没有求和索引sum_result = 0for inner in range(0, 1):sum_result += np_a[..., i, j]np_out[..., j, i] = sum_resultprint("is np_out == torch_org_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印结果# is np_out == torch_org_out ? True# is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ? True
4. reduce sum
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)# i = 2, j = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ij->', [a]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.sum(a).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((1, ), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子中没有自由索引# 相当于所有维度都加一起for o in range(0 ,1):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子中,i 和 j# 都是求和索引sum_result = 0for i in range(0, 2):for j in range(0, 3):sum_result += np_a[i, j]np_out[o] = sum_resultprint("input:\n", np_a)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印结果# input:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# torch ein out:# 15# torch org out:# 15# numpy out:# [15]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
5. 矩阵按列求和
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)# i = 2, j = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ij->j', [a]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.sum(a, dim=0).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((3, ), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子中是 jfor j in range(0, 3):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子中是 isum_result = 0for i in range(0, 2):sum_result += np_a[i, j]np_out[j] = sum_resultprint("input:\n", np_a)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, np_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# input:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# torch ein out:# [3 5 7]# torch org out:# [3 5 7]# numpy out:# [3 5 7]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
6. 矩阵向量乘法
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)b = torch.arange(3)# i = 2, k = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ik,k->i', [a, b]).numpy()# 等价形式,可以省略箭头和输出torch_ein_out2 = torch.einsum('ik,k', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.mv(a, b).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2, ), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子是 ifor i in range(0, 2):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子中是 ksum_result = 0for k in range(0, 3):sum_result += np_a[i, k] * np_b[k]np_out[i] = sum_resultprint("matrix a:\n", np_a)print("vector b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch ein out2: \n", torch_ein_out2)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out2, torch_ein_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# matrix a:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# vector b:# [0 1 2]# torch ein out:# [ 5 14]# torch ein out2:# [ 5 14]# torch org out:# [ 5 14]# numpy out:# [ 5 14]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
7. 矩阵乘法
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)b = torch.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)# i = 2, k = 3, j = 5torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ik,kj->ij', [a, b]).numpy()# 等价形式,可以省略箭头和输出torch_ein_out2 = torch.einsum('ik,kj', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.mm(a, b).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2, 5), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子是 i 和 jfor i in range(0, 2):for j in range(0, 5):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子是 ksum_result = 0for k in range(0, 3):sum_result += np_a[i, k] * np_b[k, j]np_out[i, j] = sum_resultprint("matrix a:\n", np_a)print("matrix b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch ein out2: \n", torch_ein_out2)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is numpy == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out2, torch_ein_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# matrix a:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# matrix b:# [[ 0 1 2 3 4]# [ 5 6 7 8 9]# [10 11 12 13 14]]# torch ein out:# [[ 25 28 31 34 37]# [ 70 82 94 106 118]]# torch ein out2:# [[ 25 28 31 34 37]# [ 70 82 94 106 118]]# torch org out:# [[ 25 28 31 34 37]# [ 70 82 94 106 118]]# numpy out:# [[ 25 28 31 34 37]# [ 70 82 94 106 118]]# is numpy == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
8. 向量内积
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(3)b = torch.arange(3, 6) # [3, 4, 5]# i = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('i,i->', [a, b]).numpy()# 等价形式,可以省略箭头和输出torch_ein_out2 = torch.einsum('i,i', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.dot(a, b).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((1, ), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子没有自由索引for o in range(0, 1):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子是 isum_result = 0for i in range(0, 3):sum_result += np_a[i] * np_b[i]np_out[o] = sum_resultprint("vector a:\n", np_a)print("vector b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch ein out2: \n", torch_ein_out2)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out2, torch_ein_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# vector a:# [0 1 2]# vector b:# [3 4 5]# torch ein out:# 14# torch ein out2:# 14# torch org out:# 14# numpy out:# [14]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
9. 矩阵元素对应相乘并求 reduce sum
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(6).reshape(2, 3)b = torch.arange(6,12).reshape(2, 3)# i = 2, j = 3torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ij,ij->', [a, b]).numpy()# 等价形式,可以省略箭头和输出torch_ein_out2 = torch.einsum('ij,ij', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = (a * b).sum().numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((1, ), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子没有自由索引for o in range(0, 1):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子是 i 和 jsum_result = 0for i in range(0, 2):for j in range(0, 3):sum_result += np_a[i,j] * np_b[i,j]np_out[o] = sum_resultprint("matrix a:\n", np_a)print("matrix b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch ein out2: \n", torch_ein_out2)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out2, torch_ein_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# matrix a:# [[0 1 2]# [3 4 5]]# matrix b:# [[ 6 7 8]# [ 9 10 11]]# torch ein out:# 145# torch ein out2:# 145# torch org out:# 145# numpy out:# [145]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
10. 向量外积
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.arange(3)b = torch.arange(3,7) # [3, 4, 5, 6]# i = 3, j = 4torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('i,j->ij', [a, b]).numpy()# 等价形式,可以省略箭头和输出torch_ein_out2 = torch.einsum('i,j', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.outer(a, b).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((3, 4), dtype=np.int32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子是 i 和 jfor i in range(0, 3):for j in range(0, 4):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子没有求和索引sum_result = 0for inner in range(0, 1):sum_result += np_a[i] * np_b[j]np_out[i, j] = sum_resultprint("vector a:\n", np_a)print("vector b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch ein out2: \n", torch_ein_out2)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out2, torch_ein_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_org_out, torch_ein_out))# 终端打印输出# vector a:# [0 1 2]# vector b:# [3 4 5 6]# torch ein out:# [[ 0 0 0 0]# [ 3 4 5 6]# [ 6 8 10 12]]# torch ein out2:# [[ 0 0 0 0]# [ 3 4 5 6]# [ 6 8 10 12]]# torch org out:# [[ 0 0 0 0]# [ 3 4 5 6]# [ 6 8 10 12]]# numpy out:# [[ 0 0 0 0]# [ 3 4 5 6]# [ 6 8 10 12]]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out2 == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
11. batch 矩阵乘法
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.randn(2,3,5)b = torch.randn(2,5,4)# i = 2, j = 3, k = 5, l = 4torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ijk,ikl->ijl', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.bmm(a, b).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2, 3, 4), dtype=np.float32)# 自由索引外循环# 这个例子是 i,j和lfor i in range(0, 2):for j in range(0, 3):for l in range(0, 4):# 求和索引内循环# 这个例子是 ksum_result = 0for k in range(0, 5):sum_result += np_a[i, j, k] * np_b[i, k, l]np_out[i, j, l] = sum_resultprint("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印输出# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
12. 张量收缩(tensor contraction)
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.randn(2,3,5,7)b = torch.randn(11,13,3,17,5)# p = 2, q = 3, r = 5, s = 7# t = 11, u = 13, v = 17, r = 5torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('pqrs,tuqvr->pstuv', [a, b]).numpy()torch_org_out = torch.tensordot(a, b, dims=([1, 2], [2, 4])).numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2, 7, 11, 13, 17), dtype=np.float32)# 自由索引外循环# 这里就是 p,s,t,u和vfor p in range(0, 2):for s in range(0, 7):for t in range(0, 11):for u in range(0, 13):for v in range(0, 17):# 求和索引内循环# 这里是 q和rsum_result = 0for q in range(0, 3):for r in range(0, 5):sum_result += np_a[p, q, r, s] * np_b[t, u, q, v, r]np_out[p, s, t, u, v] = sum_resultprint("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out, atol=1e-6))print("is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out, atol=1e-6))# 终端打印输出# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_ein_out == torch_org_out ? True
13. 二次变换(bilinear transformation)
import torchimport numpy as npa = torch.randn(2,3)b = torch.randn(5,3,7)c = torch.randn(2,7)# i = 2, k = 3, j = 5, l = 7torch_ein_out = torch.einsum('ik,jkl,il->ij', [a, b, c]).numpy()m = torch.nn.Bilinear(3, 7, 5, bias=False)m.weight.data = btorch_org_out = m(a, c).detach().numpy()np_a = a.numpy()np_b = b.numpy()np_c = c.numpy()# 循环展开实现np_out = np.empty((2, 5), dtype=np.float32)# 自由索引外循环# 这里是 i 和 jfor i in range(0, 2):for j in range(0, 5):# 求和索引内循环# 这里是 k 和 lsum_result = 0for k in range(0, 3):for l in range(0, 7):sum_result += np_a[i, k] * np_b[j, k, l] * np_c[i, l]np_out[i, j] = sum_result# print("matrix a:\n", np_a)# print("matrix b:\n", np_b)print("torch ein out: \n", torch_ein_out)print("torch org out: \n", torch_org_out)print("numpy out: \n", np_out)print("is np_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, np_out))print("is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ?", np.allclose(torch_ein_out, torch_org_out))# 终端打印输出# torch ein out:# [[-2.9185116 0.17024004 -0.43915534 1.5860008 10.016678 ]# [-0.48688257 -3.5114982 -0.7543343 -0.46790922 1.4816089 ]]# torch org out:# [[-2.9185116 0.17024004 -0.43915534 1.5860008 10.016678 ]# [-0.48688257 -3.5114982 -0.7543343 -0.46790922 1.4816089 ]]# numpy out:# [[-2.9185114 0.17023998 -0.4391551 1.5860008 10.016678 ]# [-0.4868826 -3.5114982 -0.7543342 -0.4679092 1.4816089 ]]# is np_out == torch_ein_out ? True# is torch_org_out == torch_ein_out ? True
从上面的13个例子可以看出,只要确定了自由索引和求和索引,einsum 的输出计算都可以用一套比较通用的多层循来实现,外层的循环对应自由索引,内层循环对应求和索引。
Pytorch einsum 实现简要解读
C++ 代码解读:
我只读懂了大概的实现思路,然后按照我自己的理解添加了注释(仅供参考):
// 为了方便理解,我简化了大部分代码,// 并把对于 "..." 省略号的处理去掉了/*** 代码实现主要分为3大步:* 1. 解析 equation,分别得到输入和输出对应的字符串* 2. 补全输出和输入张量的维度,通过 permute 操作对齐输入和输出的维度* 3. 将维度对齐之后的输入张量相乘,然后根据求和索引累加*/Tensor einsum(std::string equation, TensorList operands) {// ......// 把 equation 按照箭头分割// 得到箭头左边输入的部分const auto arrow_pos = equation.find("->");const auto lhs = equation.substr(0, arrow_pos);// 获取输入操作数个数const auto num_ops = operands.size();// 下面循环主要作用是解析 equation 左边输入部分,// 按 ',' 号分割得到每个输入张量对应的字符串,// 并把并把每个 char 字符转成 int, 范围 [0, 25]// 新建 vector 保存每个输入张量对应的字符数组std::vector<std::vector<int>> op_labels(num_ops);std::size_t curr_op = 0;for (auto i = decltype(lhs.length()){0}; i < lhs.length(); ++i) {switch (lhs[i]) {// ......case ',':// 遇到逗号,接下来解析下一个输入张量的字符串++curr_op;// ......break;default:// ......// 把 char 字符转成 intop_labels[curr_op].push_back(lhs[i] - 'a');}}// TOTAL_LABELS = 26constexpr int TOTAL_LABELS = 'z' - 'a' + 1;std::vector<int> label_count(TOTAL_LABELS, 0);// 遍历所有输入操作数// 统计 equation 中 'a' - 'z' 每个字符的出现次数for(const auto i : c10::irange(num_ops)) {const auto labels = op_labels[i];for (const auto& label : labels) {// ......++label_count[label];}// ......}// 创建一个 vector 用于保存 equation// 箭头右边输出的字符到索引的映射std::vector<int64_t> label_perm_index(TOTAL_LABELS, -1);int64_t perm_index = 0;// ......// 接下来解析输出字符串if (arrow_pos == std::string::npos) {// 处理用户省略了箭头的情况,// ......} else {// 一般情况// 得到箭头右边的输出const auto rhs = equation.substr(arrow_pos + 2);// 遍历输出字符串并解析for (auto i = decltype(rhs.length()){0}; i < rhs.length(); ++i) {switch (rhs[i]) {// ......default:// ......const auto label = rhs[i] - 'a';// ......// 建立字符到索引的映射,perm_index从0开始label_perm_index[label] = perm_index++;}}}// 保存原始的输出维度大小const int64_t out_size = perm_index;// 对齐输出张量的维度,使得对齐之后的维度等于// 自由索引加上求和索引的个数// 对输出补全省略掉的求和索引// 也就是在输入等式中出现,但是没有在输出等式中出现的字符for (const auto label : c10::irange(TOTAL_LABELS)) {if (label_count[label] > 0 && label_perm_index[label] == -1) {label_perm_index[label] = perm_index++;}}// 对所有输入张量,同样补齐维度至与输出维度大小相同// 最后对输入做 permute 操作,使得输入张量的每一维// 与输出张量的每一维能对上std::vector<Tensor> permuted_operands;for (const auto i: c10::irange(num_ops)) {// 保存输入张量最终做 permute 时候的维度映射std::vector<int64_t> perm_shape(perm_index, -1);Tensor operand = operands[i];// 取输入张量对应的 equationconst auto labels = op_labels[i];std::size_t j = 0;for (const auto& label : labels) {// ......// 建立当前遍历到的输入张量字符到// 输出张量的字符到的映射// label: 当前遍历到的字符// label_perm_index: 保存了输出字符对应的索引// 所以 perm_shape 就是建立了输入张量的每一维度// 与输出张量维度的对应关系perm_shape[label_perm_index[label]] = j++;}// 如果输入张量的维度小于补全后的输出// 那么 perm_shape 中一定存在值为 -1 的元素// 那么相当于需要扩充输入张量的维度// 扩充的维度添加在张量的尾部for (int64_t& index : perm_shape) {if (index == -1) {// 在张量尾部插入维度1operand = operand.unsqueeze(-1);// 修改了perm_shape中的index,// 因为是引用取值index = j++;}}// 把输入张量的维度按照输出张量的维度重排,采用 permute 操作permuted_operands.push_back(operand.permute(perm_shape));}// ......Tensor result = permuted_operands[0];// .....// 计算最终结果for (const auto i: c10::irange(1, num_ops)) {Tensor operand = permuted_operands[i];// 新建 vector 用于保存求和索引std::vector<int64_t> sum_dims;// ......// 详细的代码可以阅读 Pytorch 源码// 这里我还没有完全理解 sumproduct_pair 的实现,// 里面用的是 permute + bmm,// 不过我觉得可以简单理解为// 将张量做广播乘法,再根据求和索引做累加result = sumproduct_pair(result, operand, sum_dims, false);}return result;}
图解实现
下面还是用矩阵乘法来说明 C++ 的实现思路,下图展示的是矩阵乘法的通用实现: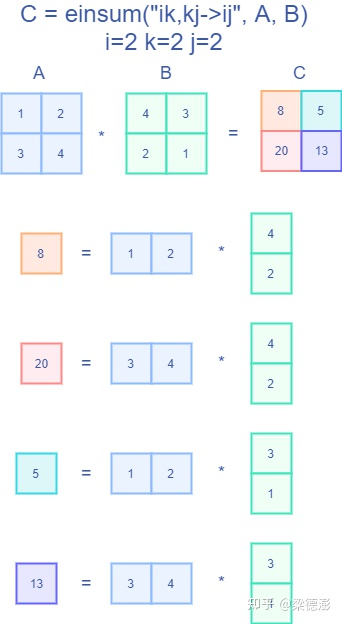
接下来展示 C++ 的实现思路: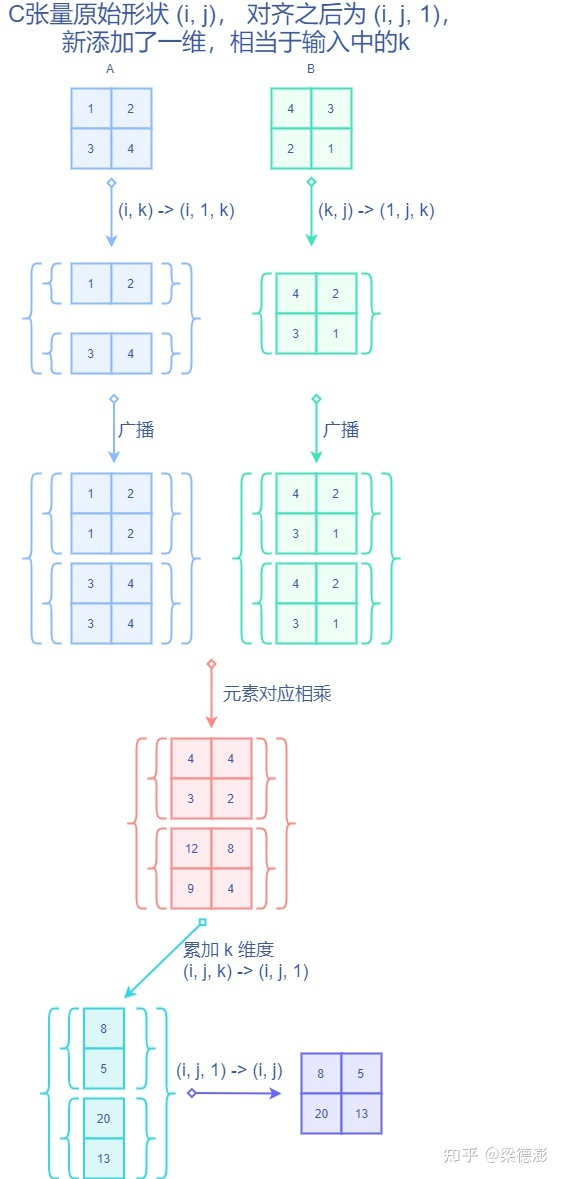
总结
通过上面的实际例子和代码解读,可以看到 einsum 非常灵活,可以方便的实现各种常用的张量操作。希望读者通过这篇文章也可以轻松掌握 einsum 的基本用法。文中对于 Pytorch C++实现代码的解析是基于我自己的理解,如果觉得有误或者不理解的地方欢迎讨论。
参考资料

