ZooKeeper 是一个典型的分布式数据一致性的解决方案,分布式应用程序可以基于它实现诸如数据发布订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调通知、集群管理、Master 选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。ZooKeeper 可以保证如下分布式一致性特性:
顺序一致性:从同一个客户端发起的事务请求会严格按照其发起顺序被应用到 ZooKeeper 中。
原子性:所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有机器上的应用情况是一致的,也就是说,要么整个集群所有机器都成功应用了某一事务,要么都没有应用,不会出现集群中部分机器应用了该事务,而另一部分没有应用的情况。
可靠性:一旦服务端成功的应用了一个事务,并完成对客户端的响应,那么该事务所引起的服务端状态变更会被一直保留下来,除非有另一个事务又对其进行了变更。
最终一致性:ZooKeeper 仅保证在一定时间内,客户端最终一定能从服务端上读取到最新的数据。
ZooKeeper 设计目标
ZooKeeper 致力于提供一个高性能、高可用且具有严格的顺序访问控制能力(主要是写操作的严格顺序性)的分布式协调服务。高性能使得 ZooKeeper 能够应用于那些对系统吞吐有明确要求的大型分布式系统中,高可用使得分布式单点问题得到了解决,而严格的顺序访问控制使得客户端能够基于 ZooKeeper 实现一些复杂的同步原语。下面我们来具体看一下 ZooKeeper 的四个设计目标。
1)简单的数据模型
ZooKeeper 使得分布式程序能够通过一个共享的、树型结构的名字空间来进行相互协调。这里的树型结构的名字空间,是指 ZooKeeper 服务器内存中的一个数据模型,其由一系列被称为 ZNode 的数据节点组成,总的来说,其数据模型类似于一个文件系统,而 ZNode 之间的层级关系就像文件系统的目录结构一样。
2)可以构建集群
一个 ZooKeeper 集群通常由一组机器组成,一般 3~5 台机器就可以组成一个可用的 ZooKeeper 集群了。组成 ZooKeeper 集群的每台机器都会在内存中维护当前的服务器状态,并且每台机器之间都互相保持通信。只要集群中存在超过一半的机器能够正常工作,那么整个集群就能够正常对外服务。
3)顺序访问
对于来自客户端的每个更新请求,ZooKeeper 都会分配一个全局唯一的递增编号,这个编号反映了所有事务操作的先后顺序,应用程序可以使用 ZooKeeper 的这个特性来实现更高层次的同步原语。
4)高性能
由于 ZooKeeper 将全量数据存储在内存中,并直接服务于客户端的所有非事务请求,因此它尤其适合用以读操作为主的使用场景。
ZooKeeper 部署使用
1. 配置文件
初次使用 ZooKeeper,需要将 %ZK_HOME%/conf 目录下的 zoo_sample.cfg 文件重命名为zoo.cfg。下面讲解以下几个常用的配置项含义:
tickTime=2000initLimit=10syncLimit=5dataDir=/tmp/zookeeperclientPort=2181dataLogDir=/tmp/zookeeper/log
- tickTime:该时间为 ZooKeeper 服务器之间或客户端与服务器之间维持心跳的时间间隔,也就是每过一个 tickTime 时间就会发送一个心跳;
- initLimit:该配置项用来配置 ZooKeeper 服务器集群中连接到 Leader 的 Follower 服务器在初始化连接时,ZooKeeper 最多能忍受多少个心跳时间间隔。当已经超过 5 个心跳的时间(也就是 tickTime)后,ZooKeeper 服务器还没有响应,那么表明 Follower 连接失败。
- syncLimit:该配置项用来设置 Leader 与 Follower 之间发送消息、请求和应答的时间长度,最长不能超过多少个 tickTime 时间。本配置中,总的时间长度不能超过 5 * 2000 = 10 秒;
- dataDir:快照日志的存储路径;
- dataLogDir:事物日志的存储路径,如果不配置该项,事物日志将默认存储到 dataDir 指定的目录中,这样当 ZooKeeper 吞吐量较大时,会产生很多事物日志、快照日志,会严重影响 ZooKeeper 的性能;
- clientPort:该端口为客户端连接 ZooKeeper 服务器的端口,ZooKeeper 会监听这个端口,接受客户端的访问请求。
此外,在集群模式下,集群中的每台机器都需要感知到整个集群是由哪几台机器组成的,因此,在配置文件中还需要按照如下格式配置集群节点信息,每一行都代表集群中的一个机器配置:
server.{id}={host}:{port}:{port}
- id:标识该机器在集群中的机器序号,这个序号需要写到 myid 文件中。
- port1:master 和 slave 之间的通信端口,默认是 2888。
- port2:leader 选举端口,默认是 3888。
此外,在每台 ZooKeeper 机器上,我们都需要在数据目录(即 dataDir 参数指定的那个目录)下创建一个 myid 文件,该文件的内容为当前机器的 Server ID 数字。注意,每个服务器的 myid 文件中的数字需不同,且要和自己所在机器的 zoo.cfg 中的 server.id=host:port:port 的 id 值一致。注意,id 范围是 1~255。
2. 服务端脚本
如果要启动服务器,可通过 %ZK_HOME%/bin 目录下的 zkServer.sh 脚本进行启动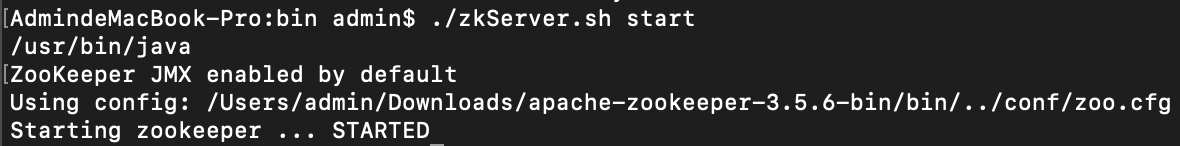
验证服务器状态(此处为单机模式)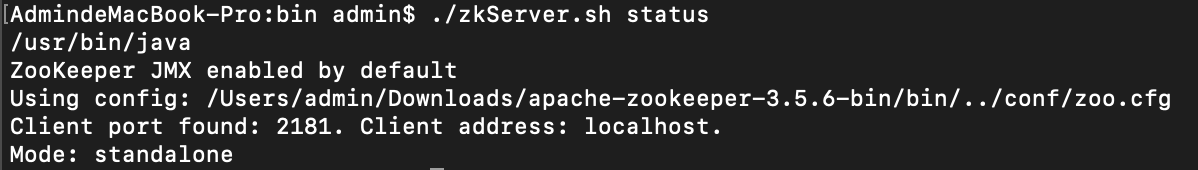
停止服务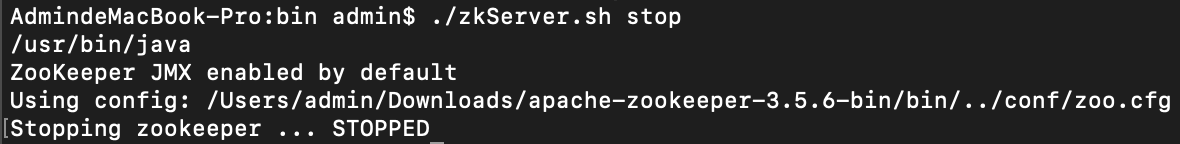
ZooKeeper 可执行脚本
| zkCleanup | 清理 ZooKeeper 历史数据,包括事务日志文件和快照数据文件 |
|---|---|
| zkCli | ZooKeeper 的一个简易客户端 |
| zkEnv | 设置 ZooKeeper 的环境变量 |
| zkServer | ZooKeeper 服务器的启动、停止和重启脚本 |
3. 客户端脚本
客户端连接 ZooKeeper 服务器:sh zkCli.sh -server ip:port。常用操作如下:
使用 create 命令,可以创建一个 ZooKeeper 节点。
create [-s] [-e] path data [acl]
- 其中,-s 或 -e 分别指定节点特性:顺序或临时节点。如不指定默认创建的是持久节点。
- acl 是用来进行权限控制的,缺省情况下,不做任何权限控制。

使用 ls 命令,可以列出 ZooKeeper 指定节点下第一级的所有子节点。
ls path
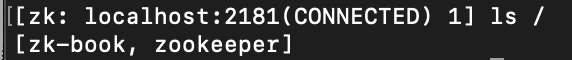
使用 get 命令,可以获取 ZooKeeper 指定节点的数据内容和属性信息。
get path

使用 set 命令可以更新指定节点的数据内容
set [-v version] path data
- data 就是要更新的内容
- ZooKeeper 节点数据是有版本概念的,version 用于指定本次更新操作是基于 ZNode 哪一个数据版本进行的
使用 delete 命令可以删除 ZooKeeper 上的指定节点。
delete [-v version] path
注意,如果要想删除某一个指定节点,该节点必须没有子节点存在。
JAVA 客户端
1. 创建会话
客户端可以通过创建一个 ZooKeeper 实例来连接 ZooKeeper 服务器,ZooKeeper 的四种构造方法如下:
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher);
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, boolean canBeReadOnly);
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, long sessionId, byte[] sessionPasswd);
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, long sessionId, byte[] sessionPasswd, boolean canBeReadOnly);
参数说明如下:
| connectString | ZooKeeper 服务器列表,由逗号分开的 host:port 字符串组成,每一个都代表一台机器。 |
|---|---|
| sessionTimeout | 会话的超时时间,是一个以毫秒为单位的整形值。在一个会话周期内,ZooKeeper 客户端和服务器之间会通过心跳检测机制来维持会话有效性,一旦在 sessionTimeout 时间内没有进行有效的心跳检测,会话就会失效。 |
| watcher | ZooKeeper 允许客户端在构造方法中传入一个 Watcher 接口的实现类来作为默认的 Watcher 事件通知处理器。 |
| canBeReadOnly | 该值用于标识当前会话是否支持 “read-only” 模式。默认在 ZooKeeper 集群中,一个机器如果和集群中过半的机器失去了网络连接,那么这个机器将不再处理客户端请求(包括读请求)。但在某些场景下,当 ZooKeeper 服务器发生此类故障时,我们仍希望 ZooKeeper 服务器能够提供读服务—这就是 ZooKeeper 的 “read-only” 模式。 |
| sessionId 和 sessionPassword | 分别代表会话 ID 和会话密钥。这两个参数能够唯一确定一个会话,同时客户端使用这两个参数可以实现客户端会话复用,从而达到恢复会话的效果。 |
注意:ZooKeeper 客户端和服务端会话的建立是一个异步的过程,构造方法在处理完客户端初始化工作后立即返回,而此时并没有真正建立好一个可用的会话,当该会话真正创建完毕后,ZooKeeper 服务端会向会话对应的客户端发送一个事件通知,以告知客户端,客户端只有在获取这个通知后才算真正建立了会话。
public class ZooKeeperTest implements Watcher {
private static final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ZooKeeper zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper("127.0.0.1:2181", 5000, new ZooKeeperTest());
// 此处为CONNECTING
System.out.println(zooKeeper.getState());
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 此处为CONNECTED
System.out.println(zooKeeper.getState());
}
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
if (Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected == watchedEvent.getState()) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
2. 创建节点
// 同步创建节点
public String create(String path, byte[] data, List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode);
// 异步创建节点
public void create(String path, byte[] data, List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode, StringCallback cb, Object ctx);
参数说明如下:
| path | 需要创建的数据节点的节点路径。 |
|---|---|
| data | 一个字节数组,是节点创建后的初始内容。 |
| acl | 节点的 ACL 策略,如果你的应用场景没有太高的权限要求,那么可以不关注这个参数,只需要传入参数 Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,这就表明之后对这个节点的任 何操作都不受权限控制。 |
| createMode | 节点类型 - 持久(PERSISTENT) - 持久顺序(PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL) - 临时(EPHEMERAL) - 临时顺序(EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL) |
| cb | 注册一个异步回调函数,当服务端节点创建完毕后,ZooKeeper 客户端就会自动调用这个方法。 |
| ctx | 用于传递一个对象,可以在回调方法执行时使用,通常是放一个上下文信息。 |
注意,无论是同步还是异步创建,ZooKeeper 都不支持递归创建节点,即无法在父节点不存在的情况下创建子节点。如果一个节点已经存在了,那么创建同名节点时会抛出 NodeExistsException 异常。ZooKeeper 的节点内容只支持字节数组类型,开发人员需要自己使用序列化工具将节点内容进行序列化和反序列化。
3. 删除节点
// 同步删除节点
public void delete(String path, int version);
// 异步删除节点
public void delete(String path, int version, VoidCallback cb, Object ctx);
在 ZooKeeper 中,只允许删除叶子节点。如果一个节点存在至少一个子节点的话,那么该节点将无法被直接删除,必须先删除掉其所有子节点。
4. 节点操作
查看子节点信息:
// 同步获取
public List<String> getChildren(String path, Watcher watcher);
public List<String> getChildren(String path, boolean watch);
public List<String> getChildren(String path, Watcher watcher, Stat stat);
public List<String> getChildren(String path, boolean watch, Stat stat)
// 异步获取
public void getChildren(String path, Watcher watcher, ChildrenCallback cb, Object ctx);
public void getChildren(String path, boolean watch, ChildrenCallback cb, Object ctx);
public void getChildren(String path, Watcher watcher, Children2Callback cb, Object ctx);
public void getChildren(String path, boolean watch, Children2Callback cb, Object ctx);
参数说明如下:
| watcher | 注册 Watcher,用来订阅子节点列表的变化通知。当子节点列表发生变更时,服务端就会向客户端发送一个 NodeChildrenChanged 类型的事件通知。注意,这个事件通知仅仅只会发出一个通知,而不会把节点的变化情况发送给客户端,客户端必须主动重新获取。另外,Watcher 通知是一次性的,即一旦触发一次通知后,该 Watcher 就失效了,因此客户端需要反复注册 Watcher。 |
|---|---|
| watch | 表明是否需要注册一个 Watcher。如果为 ture,ZooKeeper 客户端会自动使用上下文中的默认 Watcher。 |
| stat | stat 对象中记录了一个节点的基本属性信息,例如节点创建时的事务 ID、节点数据内容的长度等。我们可以将一个旧的 stat 变量传入,该 stat 变量会在方法执行过程中,被来自服务端响应的 stat 对象替换,以此获取这个节点最新的节点状态信息。 |
public class ZooKeeperTest implements Watcher {
private static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
private static ZooKeeper zooKeeper = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper("127.0.0.1:2181", 5000, new ZooKeeperTest());
countDownLatch.await();
// 创建ZNode
zooKeeper.create("/zk-book", "".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
zooKeeper.create("/zk-book/one", "".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
// 获取子列表
List<String> childrenList = zooKeeper.getChildren("/zk-book", true);
System.out.println(childrenList);
// 修改子列表结构
zooKeeper.create("/zk-book/two", "".getBytes(), ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
if (Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected == watchedEvent.getState()) {
if (Event.EventType.None == watchedEvent.getType() && watchedEvent.getPath() == null) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
} else if (Event.EventType.NodeChildrenChanged == watchedEvent.getType()) {
// 子列表结构发生变更,重新获取子列表信息
try {
System.out.println("ReGetChildren :" + zooKeeper.getChildren("/zk-book", true));
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
}
}
获取节点数据内容:
// 同步获取
public byte[] getData(String path, Watcher watcher, Stat stat);
public byte[] getData(String path, boolean watch, Stat stat);
// 异步获取
public void getData(String path, Watcher watcher, DataCallback cb, Object ctx);
public void getData(String path, boolean watch, DataCallback cb, Object ctx);
public class ZooKeeperTest implements Watcher {
private static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
private static ZooKeeper zooKeeper = null;
private static Stat stat = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper("127.0.0.1:2181", 5000, new ZooKeeperTest());
countDownLatch.await();
// 获取ZNode数据内容
byte[] dataInfo = zooKeeper.getData("/zk-book", true, stat);
System.out.println(new String(dataInfo));
System.out.println(stat.getCzxid() + "," + stat.getMzxid() + "," + stat.getVersion());
// 修改ZNode数据内容
zooKeeper.setData("/zk-book", "123".getBytes(), -1);
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
if (Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected == watchedEvent.getState()) {
if (Event.EventType.None == watchedEvent.getType() && watchedEvent.getPath() == null) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
} else if (Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged == watchedEvent.getType()) {
try {
// 数据内容发生变更,重新获取
System.out.println(new String(zooKeeper.getData("/zk-book", true, stat)));
System.out.println(stat.getCzxid() + "," + stat.getMzxid() + "," + stat.getVersion());
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
}
}
更新节点数据内容:
// 同步更新节点
public Stat setData(String path, byte[] data, int version);
// 异步更新节点
public void setData(String path, byte[] data, int version, StatCallback cb, Object ctx);
ZooKeeper 每个节点都有数据版本的概念,在调用更新操作时就可以添加 vsrsion 参数,该参数可以对应于 CAS 原理中的 “预期值”,表明是针对该数据版本进行更新的。如果对 ZooKeeper 数据节点的更新操作没有原子性要求,那么就可以使用 “-1”,表示基于数据的最新版本进行操作。
Curator 客户端
Curator 是 Netflix 公司开源的一套 ZooKeeper 客户端框架,解决了很多 ZooKeeper 客户端非常底层的细节开发工作,包括连接重连、反复注册 Watcher 和 NodeExistsException 异常等。除此之外,Curator 中还提供了 ZooKeeper 各种应用场景(如共享锁服务、Master 选举机制和分布式计数器等)的抽象封装。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
</dependency>
1. 创建会话
首先使用 CuratorFrameworkFactory 这个工厂类的静态方法或 Builder 构造器来创建一个客户端。然后,通过调用 CuratorFramework 中的 start() 方法来启动会话。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExponentialBackoffRetry retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 5, 30 * 1000);
CuratorFramework curator = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
// 会话超时时间
.sessionTimeoutMs(10 * 1000)
// 连接创建超时时间
.connectionTimeoutMs(5 * 1000)
// 重试策略
.retryPolicy(retryPolicy)
// zookeeper服务器列表
.connectString("127.0.0.1:2781")
.build();
// 完成会话创建
curator.start();
}
重试策略(RetryPolicy)的接口定义如下:
boolean allowRetry(int retryCount, long elapsedTimeMs, RetrySleeper sleeper);
2. 节点操作
新增节点
- 通过调用 CuratorFramework 中的 create() 方法来获取一个 CreateBuilder 实例。
- 通过调用 CreateBuilder 中的 creatingParentsIfNeeded() 方法,Curator 能够自动递归创建所有需要的父节点。由于在 ZooKeeper 中规定了所有非叶子节点必须为持久节点,所以该方法自动创建的父节点均为持久节点。
- 通过调用 CreateBuilder 中的 forPath() 方法创建节点。
删除节点
- 通过调用 CuratorFramework 中的 delete() 方法来获取一个 DeleteBuilder 实例。
- 通过调用 DeleteBuilder 中的 forPath() 方法删除一个节点。
- 调用 DeleteBuilder 中的 deletingParentsIfNeeded() 方法,Curator 能自动递归删除其所有子节点。
- 调用 DeleteBuilder 中的 withVersion() 方法,Curator 能强制指定版本进行删除。
- 调用 DeleteBuilder 中的 guaranteed() 方法,Curator 能强制保证删除(反复重试,直至成功)。
读取节点数据
- 通过调用 CuratorFramework 中的 getData() 方法来获取一个 GetDataBuilder 实例。
- 通过调用 GetDataBuilder 中的 forPath() 方法读取一个节点的数据。
- 调用 GetDataBuilder 中的 storingStatIn() 方法获取该节点的 stat。
更新节点数据
- 通过调用 CuratorFramework 中的 setData() 方法来获取一个 SetDataBuilder 实例。
- 通过调用 SetDataBuilder 中的 forPath() 方法更新一个节点的数据。
- 调用 SetDataBuilder 中的 withVersion() 方法强制指定版本更新。
public class CuratorClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExponentialBackoffRetry retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 5, 30 * 1000);
CuratorFramework curator = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()
// 会话超时时间
.sessionTimeoutMs(10 * 1000)
// 连接创建超时时间
.connectionTimeoutMs(5 * 1000)
// 重试策略
.retryPolicy(retryPolicy)
// zookeeper服务器列表
.connectString(ZkConfig.ADDRESS)
.build();
// 完成会话创建
curator.start();
// 创建节点
curator.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/curator", "Hello Curator".getBytes());
// 更新节点数据
curator.setData().forPath("/curator", "new value".getBytes());
// 获取节点数据
Stat stat = new Stat();
byte[] data = curator.getData().storingStatIn(stat).forPath("/curator");
System.out.println(new String(data));
System.out.println(stat);
// 删除节点
curator.delete().deletingChildrenIfNeeded().forPath("/curator");
}
}
3. 事件监听
原生 ZooKeeper 通过注册 Watcher 来进行事件监听,但需要手动反复注册 Watcher。Curator 引入了 Cache 来实现对 ZooKeeper 服务端事件的监听。Cache 是 Curator 中对事件监听的包装,其对事件的监听可以看作是一个本地缓存视图和远程 ZooKeeper 视图的对比过程。同时 Curator 能够自动为开发人员处理反复注册监听,从而大大简化了原生 API 开发的繁琐过程。Cache 分为两类监听类型:节点监听和子节点监听。
注意,使用该功能需要以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.1 NodeCache
NodeCache 用于监听指定 ZooKeeper 数据节点本身的变化。同时,NodeCache 定义了事件处理的回调接口 NodeCacheListener。向 NodeCache 注册 NodeCacheListener 监听器后,当监听节点的数据内容发生变化时会进行回调。
NodeCache 不仅可以用于监听数据节点的内容变更,也能监听指定节点是否存在。如果原本节点不存在,那么 Cache 会在节点被创建后触发回调,但如果该数据节点被删除,则无法触发回调。
public class CuratorTest {
private static String path = "/zk-cache/nodeCache";
private static CuratorFramework curator = CuratorFrameworkFactory
.builder()
.sessionTimeoutMs(10 * 1000)
.connectionTimeoutMs(5 * 1000)
.retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 5, 30 * 1000))
.connectString("127.0.0.1:2781")
.build();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
curator.start();
// 创建节点
curator.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath(path, "init".getBytes());
// 监听节点
final NodeCache cache = new NodeCache(curator, path, false);
// 设置为true时,NodeCache在第一次启动时就会立刻从ZooKeeper对应节点上读取数据内容,并保存在Cache中
cache.start(true);
cache.getListenable().addListener(new NodeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void nodeChanged() throws Exception {
System.out.println("node data update, new data: " + new String(cache.getCurrentData().getData()));
}
});
}
}
3.2 PathChildrenCache
PathChildrenCache 用于监听指定 ZooKeeper 数据节点的子节点变化情况(一级子节点)。向 PathChildrenCache 注册 PathChildrenCacheListener 监听器,当指定节点的子节点发生变化时,就会回调该方法。这里的变化包括:子节点的数量变化和子节点的数据内容变化。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
curator.start();
// 创建节点
curator.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).forPath(path, "init".getBytes());
// 监听节点
PathChildrenCache childrenCache = new PathChildrenCache(curator, path, true);
childrenCache.start(PathChildrenCache.StartMode.POST_INITIALIZED_EVENT);
childrenCache.getListenable().addListener(new PathChildrenCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework client, PathChildrenCacheEvent event) throws Exception {
if (event == null || event.getData() == null || event.getData().getData() == null) {
return;
}
switch (event.getType()) {
case CHILD_ADDED:
System.out.println("CHILD_ADDED," + event.getData().getPath());
break;
case CHILD_UPDATED:
System.out.println("CHILD_UPDATED," + event.getData().getPath());
break;
case CHILD_REMOVED:
System.out.println("CHILD_REMOVED," + event.getData().getPath());
break;
default:
}
}
});
}
4. 工具类
此外,Curator 也提供了很多工具类,其中用的最多的就是 ZKPaths 和 EnsurePath。
ZKPaths:提供了一些简单的 API 来构建 ZNode 路径、递归创建和删除节点等。
EnsurePath:提供了一种能够确保数据节点存在的机制,其内部实现就是试图创建指定数据节点,如果节点已经存在,那么就不进行任何操作,也不对外抛出异常,否则正常创建数据节点。

