通过 crontab 命令,我们可以在固定的间隔时间执行指定的系统指令或 shell script 脚本。时间间隔的单位可以是分钟、小时、日、月、周及以上的任意组合。这个命令非常适合周期性的日志分析或数据备份等工作
crond 服务
Linux 通过 crond 服务来支持 crontab检查 crond 服务
使用 systemctl list-unit-files 命令确认 crond 服务是否已安装。如果为 enabled,表示服务正运行
┌──(jtz㉿JTZ)-[~]└─$ systemctl list-unit-files | grep croncron.service enabled enabled
crond 服务命令
开机自动启动 crond 服务:chkconfig crond on 或者,按以下命令手动启动:
systemctl enable crond.service # 开启服务(开机自动启动服务)systemctl disable crond.service # 关闭服务(开机不会自动启动服务)systemctl start crond.service # 启动服务systemctl stop crond.service # 停止服务systemctl restart crond.service # 重启服务systemctl reload crond.service # 重新载入配置systemctl status crond.service # 查看服务状态
crontab
crontab 命令
crontab 命令格式如下:
crontab [-u user] file crontab [-u user] [ -e | -l | -r ]
参数介绍
- -u user:用来设定某个用户的 crontab 服务;
- file:file 是命令文件的名字,表示将 file 做为 crontab 的任务列表文件并载入 crontab。如果在命令行中没有指定这个文件,crontab 命令将接受标准输入(键盘)上键入的命令,并将它们载入 crontab。
- -e:编辑某个用户的 crontab 文件内容。如果不指定用户,则表示编辑当前用户的 crontab 文件。
- -l:显示某个用户的 crontab 文件内容,如果不指定用户,则表示显示当前用户的 crontab 文件内容。
- -r:从/var/spool/cron 目录中删除某个用户的 crontab 文件,如果不指定用户,则默认删除当前用户的 crontab 文件。
- -i:在删除用户的 crontab 文件时给确认提示。
有两种方法写入定时任务:
- 在命令行输入:crontab -e 然后添加相应的任务,存盘退出。
- 直接编辑 /etc/crontab 文件,即 vi /etc/crontab,添加相应的任务
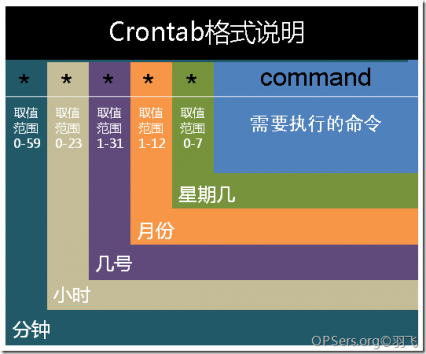
### 标准字段 逗号用于分隔列表。例如,在第 5 个字段(星期几)中使用 MON,WED,FRI 表示周一、周三和周五。 连字符定义范围。例如,2000-2010 表示 2000 年至 2010 年期间的每年,包括 2000 年和 2010 年。 除非用反斜杠()转义,否则命令中的百分号(%)会被替换成换行符,第一个百分号后面的所有数据都会作为标准输入发送给命令。 | 字段 | 是否必填 | 允许值 | 允许特殊字符 | | :—- | :—- | :—- | :—- | | Minutes | 是 | 0–59 | ,- | | Hours | 是 | 0–23 | ,- | | Day of month | 是 | 1–31 | ,- | | Month | 是 | 1–12 or JAN–DEC | ,- | | Day of week | 是 | 0–6 or SUN–SAT | ,- | /etc/crontab 文件示例: ```shell SHELL=/bin/bash PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin MAILTO=root # For details see man 4 crontabs # Example of job definition: # .———————— minute (0 - 59) # | .——————- hour (0 - 23) # | | .————— day of month (1 - 31) # | | | .———- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr … # | | | | .—— day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat # | | | | | # user-name command to be executed # 每两个小时以root身份执行 /home/hello.sh 脚本 0 /2 root /home/hello.sh
# <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">crontab 实例</font>
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 1:每 1 分钟执行一次 myCommand</font>shell
myCommand
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 2:每小时的第 3 和第 15 分钟执行</font>shell
3,15 myCommand
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 3:在上午 8 点到 11 点的第 3 和第 15 分钟执行</font>shell
3,15 8-11 myCommand
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 4:每隔两天的上午 8 点到 11 点的第 3 和第 15 分钟执行</font>shell
3,15 8-11 /2 myCommand
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 5:每周一上午 8 点到 11 点的第 3 和第 15 分钟执行</font>shell
3,15 8-11 1 myCommand
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 6:每晚的 21:30 重启 smb</font>shell
30 21 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 7:每月 1、10、22 日的 4 : 45 重启 smb</font>shell
45 4 1,10,22 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 8:每周六、周日的 1 : 10 重启 smb</font>shell
10 1 6,0 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 9:每天 18 : 00 至 23 : 00 之间每隔 30 分钟重启 smb</font>shell
0,30 18-23 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 10:每星期六的晚上 11 : 00 pm 重启 smb</font>shell
0 23 6 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 11:每一小时重启 smb</font>shell
/1 /etc/init.d/smb restart
## <font style="color:rgb(44, 62, 80);">实例 12:晚上 11 点到早上 7 点之间,每隔一小时重启 smb</font>shell
0 23-7 * /etc/init.d/smb restart
``
# 扩展
## 相关文件
### /etc/crontab全局`
+ 存放的是由系统管理员创建并维护的定时任务
+ 负责调度各种管理和维护任务
### /var/spool/cron/
> 这个目录存放所有用户的定时任务,文件名以用户名称设置,每个用户只能查看自己的定时任务
>
> 我们使用 crontab 命令来编辑的就是这个程序
>
### /etc/cron.d/
> 存放任何要执行的 crontab 文件或脚本
>
## 在线工具
+ crontab执行时间计算
+ 在线Cron表达式生成器
+ Crontab.guru - The cron schedule expression editor
+ Crontab Generator - Generate crontab syntax
# 参考

