Spring框架从2.0版本开始,提供了基于Schema风格的Spring XML格式用来定义bean的扩展机制。引入Schema-based XML是为了对Traditional的XML配置形式进行简化。通过Schema的定义,把一些原本需要通过几个bean的定义或者复杂的bean的组合定义的配置形式,用另外一种简单而可读的配置形式呈现出来。
Schema-based XML由三部分构成,我们由一幅图说明:
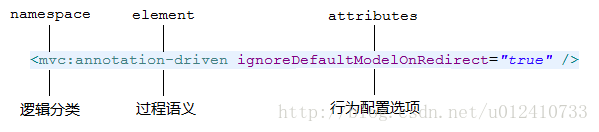
namespace—— 拥有很明确的逻辑分类element—— 拥有很明确的过程语义attributes—— 拥有很简明的配置选项
例如,<mvc:annotation-driven />这段配置想要表达的意思,就是在mvc的空间内实现Annotation驱动的配置方式。其中,mvc表示配置的有效范围,annotation-driven则表达了一个动态的过程,实际的逻辑含义是:整个SpringMVC的实现是基于Annotation模式,请为我注册相关的行为模式。
下面将阐述一下怎么写自定义XML的bean definition解析和集成这个解析到Spring IOC容器中。在后面的内容中我们将会提到一个重要的概念那就是bean definition.其实Spring中有一个重要的概念那就是bean.而BeanDefinition这个对象就是对应的标签解析后的对象。
利用下面几个简答的步骤可以创建新的xml配置扩展:
Authoring一个XML schema用来描述你的自定义element(s)Coding一个自定义的NamespaceHandler实现(这是一个很简单的步骤,don’t worry)Coding一个或者多个BeanDefinitionParse实现(这是最主要的)Registeringr把注册上面的到Spring(这也是一个简单的步骤)
下面将会依次阐述上面的步骤。例如:我们需要创建一个XML扩展(自定义xml element)允许我们可以用一种简单的方式来配置SimpleDateFormat对象(在java.text包中)。最后我们可以定义一个SimpleDateFormat类型的bean definition如下:
<myns:dateformat id="dateFormat"pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"lenient="true"/>123
1、Authoring the schema
创建一个Spring IOC容器的XML配置扩展,我们需要编写一个XML Schema用来描述这个扩展。下面的schema我们可以用来配置SimpleDateFormat对象
<!-- myns.xsd (inside package org/springframework/samples/xml) --><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"targetNamespace="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"elementFormDefault="qualified"attributeFormDefault="unqualified"><xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"/><xsd:element name="dateformat"><xsd:complexType><xsd:complexContent><xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType"><xsd:attribute name="lenient" type="xsd:boolean"/><xsd:attribute name="pattern" type="xsd:string" use="required"/></xsd:extension></xsd:complexContent></xsd:complexType></xsd:element></xsd:schema>
上面的schema将会用来配置SimpleDateFormat对象。直接在一个xml应用context文件使用<myns:dateformat /> element.
<myns:dateformat id="dateFormat"pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"lenient="true"/>123
注意:上面的XML片段本质上和下面的XML片段意义一样。
<bean id="dateFormat" class="java.text.SimpleDateFormat"><constructor-arg value="yyyy-HH-dd HH:mm"/><property name="lenient" value="true"/></bean>1234
2、Coding a NamespaceHandler
针对于上面的的schema,我们需要一个NamespaceHandler用来解析Spring遇到的所有这个特定的namespace配置文件中的所有elements.这个NamespaceHandler将会关心解析myns:dateformat元素。
这个NamespaceHandler接口相对简单,它包括三个重要的方法。
init().会在spring使用handler之前实例化NamespaceHandlerBeanDefinition parse(Element, ParseContext)- 当Spring遇到上面定义的top-level元素(也就是myms)将会被调用,这个方法能够注册bean definitions并且可以返回一个bean definition.BeanDefinitionHolder decorate(Node, BeanDefinitionHolder, ParserContext),当spring遇到一个attribute或者嵌入到namespace中的元素中将会被调用。
在很多情况下在spring xml配置文件中每个top-level的xml元素代表一个single类型的bean definition(在我们的例子中,是一个single的<myns:dateformat>元素代表一个single的SimpleDateFormat bean definition).Spring提供了很多便利的类用来支持这种场景。在这个例子中,我们将使用NamespaceHandlerSupport。
package org.springframework.samples.xml;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {public void init() {registerBeanDefinitionParser("dateformat", new SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser());}}
3、BeanDefinitionParser
BeanDefinitionParser的责任是解析定义schema在top-level的XML元素.在解析过程中,我们必须访问XML元素,因此我们可以解析我们自定义的XML内容,例如下面的例子:
package org.springframework.samples.xml;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;import org.w3c.dom.Element;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;public class SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser { 1protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {return SimpleDateFormat.class; 2}protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {// this will never be null since the schema explicitly requires that a value be suppliedString pattern = element.getAttribute("pattern");bean.addConstructorArg(pattern);// this however is an optional propertyString lenient = element.getAttribute("lenient");if (StringUtils.hasText(lenient)) {bean.addPropertyValue("lenient", Boolean.valueOf(lenient));}}}
注意:
- 我们使用Spring提供的
AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser来处理创建一个single的BeanDefinition的一些基本的工作。 - 我们重写了
AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser父类的doParse方法来实现我们自己创建single类型的BeanDefinition的逻辑。
4、Registering the handler and the schema
编码工作完成了.下面是事情就是在Spring XML解析的逻辑能够织入我们定义的element;我们需要在两个特定的目标properties文件中注册我们自定义的namespaceHandler和自定义的XSD文件。这些properties文件都需要被放置在你项目中的’META-INF’应用下。
1) META-INF/spring.handlers
这个properties文件叫做'spring.handlers',包含XML Schema URIS与namespace处理类的映射。在我们的例子中,我们需要像下面:
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns=org.springframework.samples.xml.MyNamespaceHandler1
键值对的第一个部分(key)是关联你自定义namespace扩展的URI,并且需要匹配你自定义XSD Schema中的'targetNamespace'属性。
2) META-INF/spring.schemas
这个properties文件叫做'spring.schemas',包含XML Schema在classpath中的位置。这个文件主要是防止spring在网络上加载这个schema文件。如果你指定这个properties文件影射,Spring将会在classpath中查找这个schema(在这种情况下会在'org.springframework.samples.xml'包下面的'myns.xsd')
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=org/springframework/samples/xml/myns.xsd1
你最好部署你的XSD文件在你的NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinition类的classpath中。
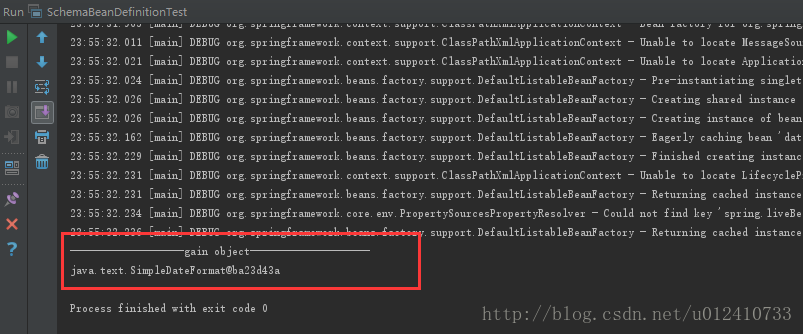
5、最终效果演示
如果你已经完成了以上步骤,那么你就成功的定义了你自己的BeanDefinition在Spring IOC容器中。我们可以Spring IOC容器获取到并使用这个Bean对象。
1)配置文件
schema-beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:myns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd"><myns:dateformat id="dateFormat"pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"lenient="true"/></beans>
2)测试类
SchemaBeanDefinitionTest.java
package org.springframework.samples.xml;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;public class SchemaBeanDefinitionTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("schema-beans.xml");SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = context.getBean("dateFormat", SimpleDateFormat.class);System.out.println("-------------------gain object--------------------");System.out.println(dateFormat);}}
3)项目结构:
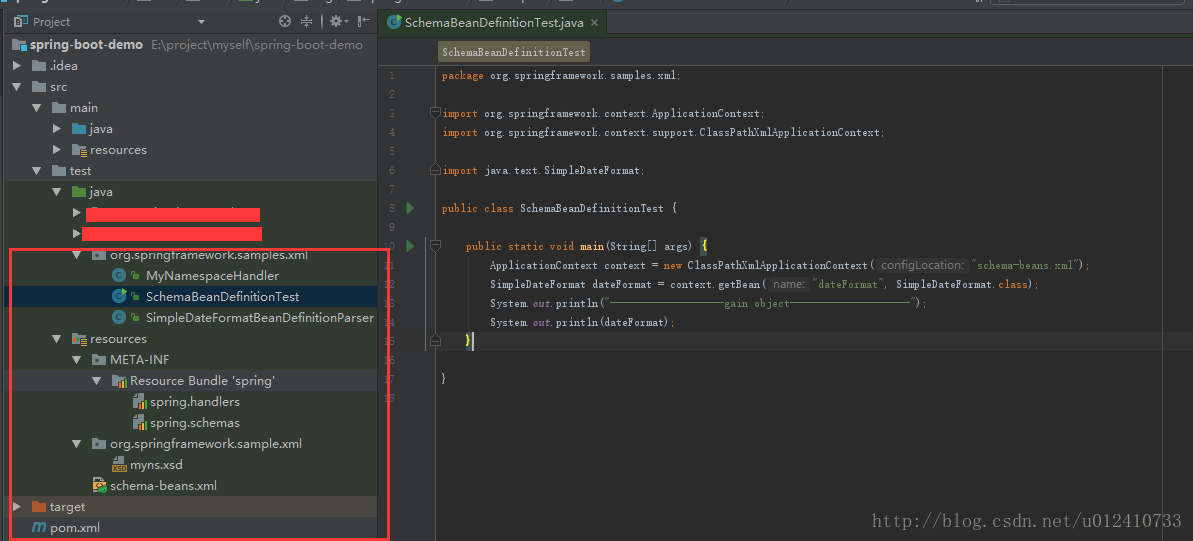
注意:在idea静态资源必须放在resources下面,不然会报错。
4)运行结果: