通过在三维空间中明确指出 x、y 和 z 坐标,可以创建特定的几何体对象。但是,通常在对象本身或其基本 CoordinateSystem 上使用几何变换将几何体移动到其最终位置。
最简单的几何变换是平移,可在 x、y 和 z 方向上将对象移动指定的单位数。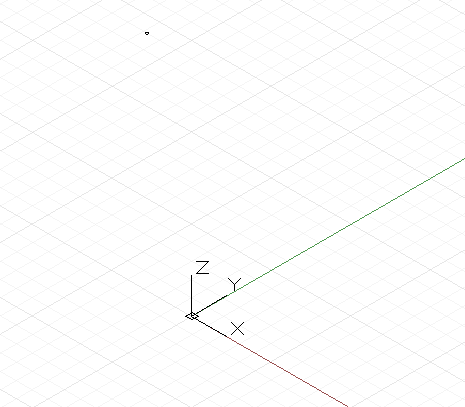
// create a point at x = 1, y = 2, z = 3p = Point.ByCoordinates(1, 2, 3);// translate the point 10 units in the x direction,// -20 in y, and 50 in z// p2’s new position is x = 11, y = -18, z = 53p2 = p.Translate(10, -20, 50);
虽然 Dynamo 中的所有对象均可通过在对象名称末尾附加 .Translate 方法进行转换,但更复杂的变换需要将对象从一个基础坐标系变换到新坐标系。例如,要绕 x 轴将对象旋转 45 度,我们将对象从其现有 CoordinateSystem(不旋转)变换为 CoordinateSystem(已使用 .Transform 方法绕 x 轴旋转 45 度):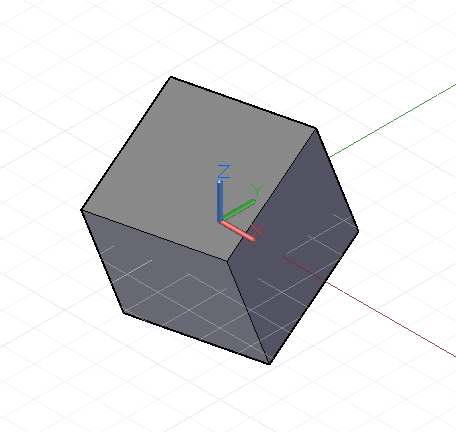
cube = Cuboid.ByLengths(CoordinateSystem.Identity(),10, 10, 10);new_cs = CoordinateSystem.Identity();new_cs2 = new_cs.Rotate(Point.ByCoordinates(0, 0),Vector.ByCoordinates(1,0,0.5), 25);// get the existing coordinate system of the cubeold_cs = CoordinateSystem.Identity();cube2 = cube.Transform(old_cs, new_cs2);
除了平移和旋转外,还可以缩放或剪切 CoordinateSystems。可以使用 .Scale 方法缩放 CoordinateSystem: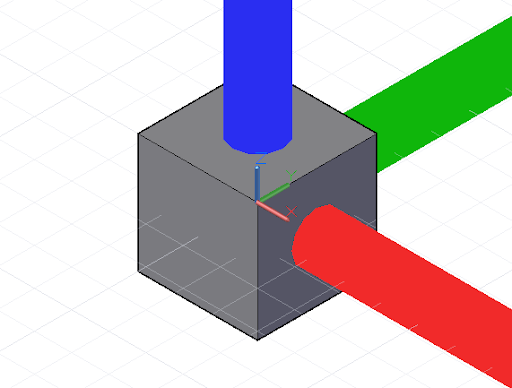
cube = Cuboid.ByLengths(CoordinateSystem.Identity(),10, 10, 10);new_cs = CoordinateSystem.Identity();new_cs2 = new_cs.Scale(20);old_cs = CoordinateSystem.Identity();cube2 = cube.Transform(old_cs, new_cs2);
通过将非正交向量输入 CoordinateSystem 构造函数,可以创建剪切的 CoordinateSystem。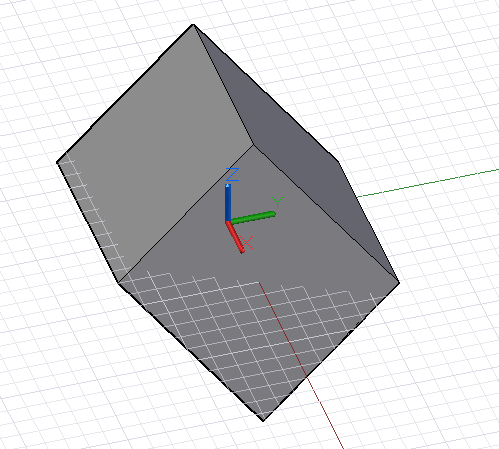
new_cs = CoordinateSystem.ByOriginVectors(Point.ByCoordinates(0, 0, 0),Vector.ByCoordinates(-1, -1, 1),Vector.ByCoordinates(-0.4, 0, 0));old_cs = CoordinateSystem.Identity();cube = Cuboid.ByLengths(CoordinateSystem.Identity(),5, 5, 5);new_curves = cube.Transform(old_cs, new_cs);
缩放和剪切是比旋转和平移更复杂的几何变换,因此并非每个 Dynamo 对象都能进行这些变换。下表概述了 Dynamo 对象可以具有非统一比例缩放的 CoordinateSystems 和剪切的 CoordinateSystems。
| 类 | 非统一比例缩放的 CoordinateSystem | 剪切的 CoordinateSystem |
|---|---|---|
| 弧 | 否 | 否 |
| Nurbs 曲线 | 是 | 是 |
| Nurbs 曲面 | 否 | 否 |
| 圆 | 否 | 否 |
| 直线 | 是 | 是 |
| 平面 | 否 | 否 |
| 点 | 是 | 是 |
| 多边形 | 否 | 否 |
| 实体 | 否 | 否 |
| 曲面 | 否 | 否 |
| 文本 | 否 | 否 |

